Components facilitating movement on roller skates consist of the circular urethane or rubber elements that make contact with the skating surface, coupled with the precision-engineered rotational devices housed within their cores. These parts, working in concert, enable smooth and efficient rolling motion.
The performance of these elements significantly impacts the skater’s speed, maneuverability, and overall experience. Historically, materials have evolved from metal and clay to advanced polymers, providing enhanced grip, durability, and rolling efficiency. Selecting appropriate components is crucial for optimizing performance in various skating disciplines, from recreational use to competitive sports.
The subsequent sections will explore the specific characteristics of these components, including durometer, size, and bearing types, as well as maintenance considerations for maximizing their lifespan and ensuring optimal performance.
Optimizing Roller Skate Performance
Ensuring optimal performance and longevity of roller skates requires attention to the condition and selection of its fundamental rolling components. The following tips provide guidance on how to maintain and choose these parts for diverse skating needs.
Tip 1: Bearing Maintenance: Regular cleaning and lubrication are essential. Remove bearings from the wheel, clean with a solvent, and re-lubricate with a suitable bearing oil or grease. This reduces friction and extends bearing life.
Tip 2: Wheel Durometer Selection: Choose the appropriate wheel hardness based on the skating surface. Softer wheels (lower durometer) provide better grip on smooth surfaces, while harder wheels (higher durometer) offer greater speed and durability on rough surfaces.
Tip 3: Wheel Size Considerations: Larger diameter wheels generally roll faster and maintain momentum better, while smaller diameter wheels offer increased maneuverability. Select based on skating style and intended use.
Tip 4: Regular Inspection: Routinely inspect wheels for signs of wear, such as flat spots or cracking. Damaged wheels should be replaced to maintain stability and control.
Tip 5: Bearing Alignment: Ensure that bearings are properly seated and aligned within the wheel hub. Misalignment can cause premature wear and reduced rolling efficiency.
Tip 6: Wheel Rotation: Periodically rotate the wheels to distribute wear evenly, especially if skating primarily in one direction. This extends the lifespan of the wheel set.
Tip 7: Upgrade Strategically: Consider upgrading to higher-quality components, such as precision bearings or advanced urethane wheels, to improve performance and durability, especially for frequent or competitive skating.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures consistent performance, enhanced safety, and prolonged lifespan for the skating equipment. Proper maintenance and informed selection are pivotal for an enjoyable and efficient skating experience.
The subsequent discussion will delve into specific product recommendations and advanced techniques for optimizing these essential elements.
1. Durometer (Wheel Hardness)
Durometer, in the context of roller skate wheels and bearings, is a critical specification defining the wheel’s hardness. Measured using the “A” scale, durometer dictates the wheel’s resistance to indentation and subsequently, its performance characteristics on various skating surfaces. The selection of an appropriate durometer is paramount to optimizing the skating experience.
- Grip and Rolling Resistance
Lower durometer wheels (e.g., 78A – 85A) offer increased grip due to their softer composition, conforming more readily to uneven surfaces. However, this increased grip comes at the cost of higher rolling resistance, potentially reducing speed and increasing exertion. These wheels are suitable for outdoor skating and slick surfaces.
- Speed and Durability
Higher durometer wheels (e.g., 95A – 101A) exhibit lower rolling resistance, facilitating greater speed. Their increased hardness also provides enhanced durability, resisting wear on smooth surfaces. These wheels are commonly used in indoor skating rinks and for speed skating.
- Surface Type Considerations
The optimal durometer is contingent upon the skating surface. Rough outdoor surfaces necessitate softer wheels to absorb vibrations and maintain contact. Smooth indoor surfaces benefit from harder wheels that maximize speed and efficiency. Incorrect durometer selection can lead to reduced performance, discomfort, or premature wheel wear.
- Impact on Bearing Load
While durometer primarily affects wheel performance, it indirectly influences the load on the bearings. Softer wheels absorb more impact, reducing stress on the bearings. Conversely, harder wheels transmit more impact directly to the bearings, potentially accelerating wear. Proper bearing maintenance is essential, regardless of wheel durometer.
The interplay between wheel durometer and skating surface is fundamental. Selecting an appropriate durometer optimizes the balance between grip, speed, and durability, contributing significantly to the overall performance and enjoyment of roller skating. Understanding this relationship empowers skaters to make informed decisions regarding their equipment.
2. Bearing ABEC Rating
The Annular Bearing Engineering Committee (ABEC) rating is a common, albeit sometimes misunderstood, standard in the context of roller skate wheels and bearings. It defines the manufacturing tolerances of bearings, influencing their precision and potential performance. While often associated with speed and smoothness, ABEC rating is not the sole determinant of bearing quality or suitability for skating.
- ABEC Scale Defined
The ABEC scale ranges from 1 to 9, with odd numbers (1, 3, 5, 7, 9) representing increasing levels of precision. A higher ABEC rating indicates tighter tolerances in the bearing’s dimensions, theoretically leading to smoother and faster rolling. However, this measurement focuses primarily on dimensional accuracy and does not encompass factors like materials, lubrication, or assembly quality, which are equally important.
- Performance Implications in Skating
While higher ABEC-rated bearings may offer marginally improved performance in controlled laboratory settings, the practical benefits in real-world skating scenarios are often negligible for most skaters. Factors like road debris, impact forces, and improper maintenance can quickly negate the advantages of high-precision bearings. Lower-rated bearings, if well-maintained and properly lubricated, can often provide comparable performance for recreational and even some competitive skating.
- Alternative Performance Metrics
Beyond ABEC rating, other factors significantly impact bearing performance. Material quality, such as the type of steel used in the races and balls, affects durability and resistance to deformation. Seal design influences the bearing’s ability to keep out contaminants. Lubricant type and viscosity impact rolling efficiency. These parameters are often more crucial than ABEC rating in determining a bearing’s real-world performance and longevity.
- Marketing vs. Reality
The ABEC rating is frequently used as a marketing tool, leading consumers to believe that higher is always better. However, the incremental performance gains of higher ABEC ratings may not justify the increased cost for many skaters. Focusing on reputable brands known for quality materials, robust construction, and effective lubrication often provides a better return on investment than solely prioritizing ABEC rating.
In conclusion, while the ABEC rating provides a standardized measure of bearing manufacturing tolerances, it is only one piece of the puzzle when assessing the suitability of bearings for roller skate wheels and bearings. Factors like material quality, construction, lubrication, and maintenance play equally, if not more, significant roles in determining bearing performance and longevity. Skaters should consider these holistic aspects rather than solely relying on ABEC ratings when selecting bearings.
3. Wheel Diameter (Size)
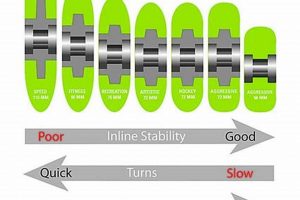
Wheel diameter, measured in millimeters, is a fundamental parameter affecting the performance characteristics of roller skate wheels and bearings. The diameter directly influences the skater’s speed, maneuverability, and overall skating experience. Larger wheels generally provide increased speed due to greater circumference and reduced rolling resistance over uneven surfaces. However, larger wheels can compromise maneuverability, making quick turns and intricate movements more challenging. Conversely, smaller wheels offer enhanced agility and responsiveness but may sacrifice top-end speed. The selection of appropriate wheel diameter is thus a critical consideration, dependent on the intended skating discipline and the skater’s preferences. For example, speed skaters often utilize wheels with larger diameters (e.g., 100mm-110mm) to maximize velocity on smooth, dedicated tracks. In contrast, artistic skaters or roller derby participants might favor smaller diameter wheels (e.g., 70mm-80mm) for improved control and agility within confined spaces.
The relationship between wheel diameter and bearing performance is also noteworthy. Larger diameter wheels, while potentially faster, place greater leverage on the bearings due to the increased distance from the axle. This leverage can result in higher stress on the bearings, potentially leading to accelerated wear and reduced lifespan, particularly if the bearings are of inferior quality or improperly maintained. Smaller diameter wheels, conversely, exert less leverage on the bearings, potentially prolonging their lifespan under similar skating conditions. This interaction highlights the importance of selecting both wheels and bearings that are appropriately matched in terms of size and performance capabilities. Using high-quality bearings with robust construction becomes increasingly critical as wheel diameter increases to mitigate the elevated stress levels. Maintenance practices, such as regular cleaning and lubrication, are also essential for preserving bearing integrity and maximizing performance, irrespective of wheel diameter.
Ultimately, the optimal wheel diameter is a compromise between speed, maneuverability, and bearing longevity, tailored to the specific needs and preferences of the skater. There are many real-life cases of skating styles and types. Recreational skaters often opt for mid-range diameters (e.g., 80mm-90mm) as a versatile compromise suitable for various skating environments. Competitors need very specific wheels that make them win. Understanding the implications of wheel diameter on both skating performance and bearing stress is paramount for making informed equipment choices and ensuring a safe and enjoyable skating experience. The complexity in optimizing these parameters remains a key consideration for both manufacturers and skaters seeking to maximize the potential of their equipment.
4. Bearing Lubrication
Bearing lubrication is a critical factor influencing the performance and longevity of roller skate wheels and bearings. The presence of a suitable lubricant minimizes friction between the bearing’s internal components the balls, races, and retainers enabling smooth rotation and efficient energy transfer. Without adequate lubrication, increased friction generates heat, leading to accelerated wear, reduced speed, and ultimately, bearing failure. Proper lubrication safeguards the bearing’s integrity and ensures consistent rolling performance. For example, competitive speed skaters meticulously maintain bearing lubrication to minimize energy loss and maximize velocity during races.
The selection of an appropriate lubricant is paramount. Grease-based lubricants offer greater protection against contaminants and are suitable for applications where high impact or exposure to harsh environments is expected. Oil-based lubricants, with their lower viscosity, reduce rolling resistance, leading to increased speed. However, oil-based lubricants may require more frequent application to maintain optimal performance. Synthetic lubricants often provide a compromise, offering both good protection and relatively low friction. Proper application is also key; over-lubrication can attract dirt and debris, while under-lubrication fails to provide adequate protection. The consequences of improper lubrication are evident in recreational skates, where neglected bearings often exhibit reduced speed, noisy operation, and premature failure.
Understanding the principles of bearing lubrication is essential for maximizing the investment in roller skate wheels and bearings. Regular maintenance, involving cleaning and re-lubrication with a suitable product, extends the bearing’s lifespan and ensures consistent performance. Failure to adhere to proper lubrication practices compromises performance, increases the risk of bearing failure, and reduces the overall skating experience. The cost of proper lubricant and maintenance is minimal compared to the expense of replacing damaged bearings and wheels, making lubrication a cost-effective strategy for preserving skating equipment.
5. Wheel Material (Urethane)
The selection of urethane as the primary material for roller skate wheels exerts a significant influence on the overall performance characteristics of roller skate wheels and bearings. Urethane’s properties, including its hardness, rebound, and resistance to abrasion, directly dictate the grip, speed, and durability of the wheel, and consequently, the stress placed upon the bearings. Inferior urethane formulations may exhibit rapid wear, necessitating frequent wheel replacements and potentially introducing debris into the bearing assembly, accelerating bearing degradation. High-quality urethanes, conversely, maintain their shape and integrity for extended periods, providing consistent performance and minimizing the risk of bearing contamination. For instance, a recreational skater using low-grade urethane wheels on asphalt may experience rapid wheel wear and reduced rolling efficiency, ultimately affecting bearing performance.
The durometer, a measure of urethane hardness, is a critical consideration. Softer urethanes (lower durometer values) offer increased grip, conforming more readily to uneven surfaces, while harder urethanes (higher durometer values) provide greater speed and durability on smooth surfaces. The selection of an appropriate durometer is thus contingent upon the skating environment. Incorrect durometer selection not only compromises performance but can also impact bearing stress. Softer wheels, while providing better grip, may generate more friction, increasing the load on the bearings. Harder wheels, while faster, may transmit more impact forces directly to the bearings, potentially leading to premature failure. Speed skaters typically favor harder urethane wheels on smooth tracks to maximize velocity, while roller derby athletes often opt for softer wheels to enhance grip and maneuverability in the rink.
In summary, the urethane composition of roller skate wheels is inextricably linked to both wheel performance and bearing longevity. High-quality urethane formulations, combined with appropriate durometer selection and diligent maintenance practices, optimize the performance and durability of both wheels and bearings, contributing to an enhanced skating experience. The interplay between wheel material and bearing function underscores the importance of considering these components as an integrated system, rather than as isolated elements, when selecting and maintaining roller skate equipment. Challenges exist in finding urethane with high grip, high durability and the price for the same, making it difficult for skaters with restricted fund to find wheels.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions and answers address common concerns and misconceptions regarding roller skate wheels and bearings. This information is intended to provide a clear understanding of these critical components.
Question 1: What is the expected lifespan of roller skate wheels?
The lifespan of roller skate wheels is dependent on several factors, including the urethane formulation, durometer, skating surface, and frequency of use. High-quality wheels, used primarily on smooth surfaces and regularly rotated, can last for several years. Conversely, lower-quality wheels subjected to rough surfaces and infrequent maintenance may require replacement within a few months.
Question 2: How frequently should roller skate bearings be cleaned and lubricated?
Bearing maintenance frequency is determined by usage and environmental conditions. Bearings used in clean, dry environments may require cleaning and lubrication every few months. Bearings exposed to dirt, moisture, or frequent impacts should be serviced more frequently, perhaps every few weeks. The presence of noise or reduced rolling efficiency indicates a need for immediate maintenance.
Question 3: Is a higher ABEC rating always indicative of a superior roller skate bearing?
While ABEC rating signifies the manufacturing tolerances of a bearing, it is not the sole determinant of performance. Factors such as material quality, seal design, and lubricant type also play crucial roles. A lower ABEC-rated bearing constructed with high-quality materials and properly maintained can often outperform a higher ABEC-rated bearing of inferior construction.
Question 4: What is the significance of wheel durometer in roller skate performance?
Wheel durometer, measured on the “A” scale, indicates the wheel’s hardness. Softer wheels (lower durometer) offer increased grip, suitable for slippery surfaces. Harder wheels (higher durometer) provide reduced rolling resistance and increased speed, ideal for smooth surfaces. The optimal durometer is contingent upon the skating environment and desired performance characteristics.
Question 5: Can roller skate wheels and bearings be mixed and matched across different brands?
While mixing and matching is generally possible, compatibility should be verified. Ensure that the bearing seat within the wheel hub is compatible with the bearing dimensions. Furthermore, consider the performance characteristics of the components; pairing high-performance bearings with low-quality wheels may not yield optimal results.
Question 6: What are the warning signs that roller skate wheels or bearings require replacement?
Warning signs include excessive wheel wear (e.g., flat spots, cracking), reduced rolling efficiency, noisy bearing operation, and excessive play or wobble in the wheel. Ignoring these signs can compromise safety and negatively impact the skating experience.
In summary, understanding the nuances of roller skate wheels and bearings is essential for optimizing performance, ensuring safety, and prolonging the lifespan of skating equipment. Regular maintenance and informed component selection are critical.
The following section will provide information and instructions about maintenance of roller skate wheels and bearings.
Roller Skate Wheels and Bearings
This discourse has comprehensively examined the critical components of roller skate wheels and bearings, emphasizing their impact on performance, safety, and longevity. Key considerations include durometer selection for optimal grip and speed, ABEC ratings as a limited measure of bearing precision, the significance of wheel diameter for maneuverability, and the necessity of proper lubrication for bearing maintenance. The material composition of the wheels, particularly the urethane formulation, was also highlighted as a determinant of durability and performance.
The efficient operation of roller skates relies on the careful selection and maintenance of these components. The longevity of the equipment requires the user to ensure ongoing care and maintenance to maximize performance and safety of its users. Continuing research and development in material science promise advancements in wheel and bearing technology, further enhancing the skating experience.






![Get Rolling! Best Roller Skates With Wheels [Guide] How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks Get Rolling! Best Roller Skates With Wheels [Guide] | How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks](https://cruzskateshop.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-414-300x200.jpg)