The components affixed to a roller skate chassis that facilitate movement across a surface are circular, load-bearing objects. These items are typically manufactured from polyurethane and are available in various diameters, durometers (hardness), and profiles to suit different skating styles and surfaces. Their primary function is to provide a rolling contact point, enabling the skater to glide, turn, and maneuver. An example is a set of 62mm diameter, 85A durometer components designed for rink skating.
These circular components are critical for performance, comfort, and safety in roller skating. The materials, size, and hardness directly impact speed, grip, shock absorption, and overall skating experience. Historically, the evolution of these components has mirrored advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes, resulting in improved durability, performance characteristics, and customization options for skaters of all skill levels. Proper selection and maintenance of these circular items are essential for maximizing the enjoyment and longevity of roller skating.
The subsequent discussion will explore various aspects related to these crucial skate components, including material properties, durometer scales, size considerations, profile types, and maintenance procedures. Furthermore, the different types best suited for specific skating disciplines, such as rink skating, jam skating, derby, or outdoor recreational use, will be addressed.
Essential Considerations for Quad Roller Skate Components
Optimizing performance and ensuring safety when roller skating requires careful attention to the selection and maintenance of the circular components affixed to the skate chassis. Adhering to the following guidelines can significantly enhance the skating experience.
Tip 1: Durometer Selection: The durometer, or hardness, of the rolling elements directly impacts grip and roll. Lower durometers (e.g., 78A) offer greater grip, ideal for slick surfaces or beginner skaters. Higher durometers (e.g., 95A or higher) provide less grip but improved roll speed, suitable for experienced skaters on smooth surfaces.
Tip 2: Size Matters: The diameter of the rolling element affects acceleration and top speed. Smaller diameters (e.g., 57mm) offer quicker acceleration and maneuverability, beneficial for rink skating and jam skating. Larger diameters (e.g., 62mm or larger) provide greater top speed and roll-over ability, suitable for outdoor skating and derby.
Tip 3: Material Composition: Polyurethane is the most common material, but variations exist. Higher-quality polyurethane formulations offer better rebound, durability, and wear resistance. Consider the material’s performance characteristics in relation to the intended skating environment.
Tip 4: Bearing Compatibility: Ensure the rolling elements are compatible with the skate’s bearings. Standard 608 bearings are generally universal, but verify compatibility to avoid performance issues or damage. Proper bearing maintenance, including cleaning and lubrication, is crucial for optimal roll.
Tip 5: Regular Rotation: To ensure even wear and extend the lifespan of the rolling elements, rotate their position on the skate regularly. This practice helps distribute stress and prevent uneven wear patterns.
Tip 6: Surface Considerations: Different surfaces necessitate different rolling element characteristics. Rough surfaces benefit from softer durometers and larger diameters to absorb vibrations. Smooth surfaces allow for harder durometers and smaller diameters for enhanced speed and agility.
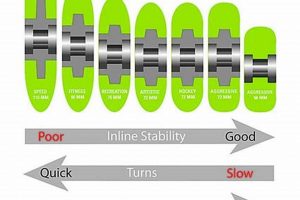
Tip 7: Profile Evaluation: The profile, or shape, of the rolling element influences its contact patch with the skating surface. Rounder profiles offer greater maneuverability, while flatter profiles provide increased stability and speed.
Careful attention to durometer, size, material, bearing compatibility, rotation, surface conditions, and profile will result in enhanced skating performance, improved comfort, and extended equipment longevity.
With these considerations addressed, the following sections will delve into specific types and applications of the skate components, providing a comprehensive guide for skaters of all levels.
1. Durometer (Hardness)
The durometer of a quad roller skate wheel quantifies its resistance to indentation and, by extension, its hardness. This characteristic significantly impacts the wheel’s performance and suitability for various skating environments. A higher durometer rating indicates a harder wheel, exhibiting less deformation under load and offering reduced rolling resistance on smooth, hard surfaces. Conversely, a lower durometer rating signifies a softer wheel, which deforms more readily, providing increased grip and shock absorption on rough or uneven surfaces. For example, wheels with a durometer rating of 95A or higher are commonly used in indoor rink skating due to their speed and efficiency on the smooth rink floor. In contrast, wheels rated at 78A to 85A are often preferred for outdoor skating or recreational use where rougher surfaces demand enhanced grip and vibration dampening.
The practical significance of understanding durometer lies in its influence on skating style and terrain compatibility. Selecting an inappropriate durometer can lead to decreased performance, reduced comfort, and even safety hazards. For instance, attempting to use overly hard wheels on a rough asphalt surface results in a jarring ride with minimal grip, increasing the risk of falls. Conversely, using excessively soft wheels on a smooth rink may cause the skater to experience sluggishness and reduced speed due to the increased rolling resistance. Competitive skaters carefully consider durometer when optimizing their setup for specific track conditions. The choice is usually balanced by the skaters weight and the expected surface conditions.
In summary, durometer is a crucial factor in determining the performance and suitability of quad roller skate wheels. Its selection should be carefully considered based on the intended skating environment and the skater’s individual needs. While harder wheels offer speed and efficiency on smooth surfaces, softer wheels provide enhanced grip and shock absorption on rough terrain. Accurate selection and consistent monitoring of the wheel’s durometer contribute significantly to a skater’s overall experience and safety. Further research into surface properties and materials science could lead to wheels with dynamically adjustable durometers, allowing for optimal performance in a wider range of conditions, this remains a technological challenge.
2. Diameter (Size)
The diameter, or size, of a quad roller skate wheel is a critical dimension influencing both the maneuverability and the achievable velocity of the skate. Measured in millimeters (mm), the diameter directly affects the wheel’s rolling circumference and, consequently, the distance covered per revolution. Larger diameters generally translate to higher top speeds due to the increased ground covered with each rotation. However, this advantage in speed often comes at the expense of acceleration and agility. A larger wheel requires more initial force to overcome inertia, resulting in slower acceleration compared to smaller wheels. In practical terms, skaters utilizing 65mm wheels will typically achieve greater top-end speed than those using 55mm wheels, assuming equivalent effort and surface conditions. The larger wheel provides a longer stride per revolution but demands more energy to initiate movement.
Smaller diameter wheels, conversely, offer enhanced maneuverability and quicker acceleration. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in environments demanding rapid changes in direction, such as indoor rink skating or jam skating. The reduced rotational inertia of smaller wheels allows for faster starts, stops, and turns. For example, a jam skater might prefer 58mm wheels for their agility and responsiveness when executing complex footwork. Likewise, roller derby skaters often choose smaller diameter wheels to maintain precise control and facilitate rapid lateral movements within the track. The practical implication of this selection is evident in the enhanced ability to navigate tight corners and react quickly to opponents’ maneuvers. The tradeoff, however, lies in a reduced maximum speed compared to skates equipped with larger wheels.
In summary, the diameter of quad roller skate wheels is a significant determinant of both speed and maneuverability. Larger diameters prioritize top speed but compromise acceleration, while smaller diameters enhance agility at the cost of maximum velocity. The optimal wheel diameter depends largely on the intended skating discipline and the skater’s specific requirements. The selection process involves a balance between the desire for speed and the need for agility, tailored to the unique demands of the skating environment and the individual skater’s style. Ongoing advancements in wheel materials and design aim to mitigate the inherent tradeoffs between size and performance, potentially leading to wheels that offer both high speed and exceptional maneuverability.
3. Material Composition
The performance characteristics of quad roller skate wheels are directly and profoundly influenced by their material composition. Polyurethane (PU) is the predominant material used in their manufacturing, but the specific formulation, additives, and manufacturing processes dictate the final properties of the wheel. The primary influence of material composition is on durometer (hardness), rebound, wear resistance, and grip. For instance, a wheel constructed from a high-rebound polyurethane compound will exhibit a greater return of energy, resulting in a faster, more efficient roll. Conversely, a lower-grade polyurethane may offer less rebound, reducing speed and increasing the effort required for propulsion. The presence of fillers or additives within the polyurethane matrix can further modify these properties, either enhancing or detracting from overall performance. As an example, some manufacturers incorporate specialized additives to improve abrasion resistance, extending the lifespan of wheels used in harsh outdoor environments.
The practical significance of understanding material composition lies in its direct impact on skating performance and safety. Skaters choose wheels with specific material properties to suit their skating style and the surfaces they encounter. For example, a competitive speed skater will prioritize wheels with high rebound and low rolling resistance, selecting a formulation designed for maximum speed on smooth, prepared surfaces. In contrast, a recreational skater using their skates on sidewalks and paved trails will require wheels with greater durability and shock absorption, achieved through a different polyurethane formulation. In the context of roller derby, wheels must withstand significant lateral forces and impacts, necessitating a robust material composition capable of withstanding these stresses without delamination or rapid wear. The choice of material therefore dictates a wheel’s suitability for a given discipline, impacting factors such as speed, grip, control, and longevity.
In conclusion, the material composition of quad roller skate wheels is a fundamental determinant of their performance characteristics and suitability for different skating applications. While polyurethane is the primary component, variations in its formulation, additives, and manufacturing processes create a spectrum of wheel properties that skaters must carefully consider. The careful selection of wheels, based on their material composition, is essential for optimizing performance, ensuring safety, and maximizing the enjoyment of roller skating. Future research into advanced materials and manufacturing techniques holds the potential to further refine wheel properties, addressing existing limitations and enabling new possibilities in roller skating performance. The challenge lies in balancing the various desired properties to create a wheel that excels in a specific application or offers a more versatile performance profile.
4. Bearing Seat
The bearing seat, an integral component of quad roller skate wheels, serves as the receptacle for bearings. Its precise dimensions and structural integrity are crucial for ensuring proper bearing alignment and smooth wheel rotation. A properly manufactured bearing seat allows for a snug fit, preventing excessive play or wobble during use. This alignment is paramount, because misalignment could generate friction, reducing skating performance and potentially damaging the bearings and wheels.
Bearing seats are not standardized, hence bearings seat varies. Some wheels have bearing seats designed for press-fit bearings, requiring specialized tools for installation and removal. Other seats accommodate bearings that are manually inserted and extracted. The diameter of the bearing seat must precisely match the outer diameter of the bearing to ensure a secure and functional interface. A loose fit can cause vibrations, while a tight fit may damage the bearing during installation or removal. Common bearing size is 608, 688, and 627 where 608 is almost universally used.
Therefore, the design and manufacturing precision of the bearing seat are fundamental to the overall performance and durability of the wheels. A well-executed bearing seat contributes to efficient energy transfer, smooth rolling, and extended bearing life. Ensuring compatibility between the bearing and the seat is essential for optimal skating performance.
5. Profile (Shape)
The profile, or shape, of a quad roller skate wheel refers to the cross-sectional contour of the wheel’s rolling surface. This geometric characteristic significantly influences a wheel’s grip, maneuverability, and speed. A rounder profile, characterized by a more curved contact surface, facilitates smoother transitions and greater agility, particularly in turns. Conversely, a flatter profile, with a wider, more rectangular contact area, provides increased stability and enhanced straight-line speed. The selection of a wheel profile, therefore, directly affects the skater’s ability to execute specific maneuvers and maintain control under various conditions. The profile is not a standardized element; the profile shape is highly variable.
The practical implications of wheel profile are evident across diverse skating disciplines. For instance, in roller derby, skaters often favor rounder profiles to enable quick lateral movements and agile pivoting within the confined track space. The curved surface allows for a more gradual engagement with the skating surface during turns, reducing the likelihood of sudden grip loss and facilitating smoother transitions. In contrast, speed skaters frequently opt for flatter profiles to maximize contact area and minimize rolling resistance on straightaways, thereby achieving greater velocity. The wider contact patch provides improved stability at high speeds and enhances power transfer from the skater to the ground. Moreover, the profile affects the wheel’s susceptibility to wear and tear. Rounder profiles tend to wear more evenly across the rolling surface, while flatter profiles may exhibit accelerated wear on the edges due to concentrated pressure.
In conclusion, the profile of a quad roller skate wheel is a critical design element that directly impacts a skater’s performance. It determines the wheels handling characteristics, influencing its grip, maneuverability, and speed. Choosing the correct profile to complement a preferred skating style is paramount to successful performance. Further research into optimized wheel profiles, combined with advanced material science, will likely lead to further refined designs that enhance performance and skater experience. The primary challenge continues to be balancing the inherent trade-offs among speed, agility, and stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, maintenance, and performance characteristics of components used for quad roller skates. The information provided is intended to enhance understanding and optimize the skating experience.
Question 1: How does the durometer of a roller skate wheel affect performance?
The durometer, measured on the A scale, indicates the wheel’s hardness. Lower durometer values (e.g., 78A-85A) denote softer wheels, offering enhanced grip and shock absorption, suitable for rough surfaces. Higher durometer values (e.g., 90A and above) represent harder wheels, promoting greater speed and roll efficiency on smooth surfaces. The selection must align with the skating environment.
Question 2: What is the significance of wheel diameter?
Wheel diameter, typically measured in millimeters, impacts speed and maneuverability. Larger diameters generally yield higher top speeds due to increased rolling circumference. Smaller diameters facilitate quicker acceleration and enhanced agility. The ideal diameter depends on the skating discipline and desired performance characteristics.
Question 3: How frequently should roller skate wheels be rotated?
Wheel rotation frequency depends on usage patterns and skating surface conditions. Uneven wear can compromise performance and shorten wheel lifespan. Regular rotation, typically after every 5-10 hours of skating, helps distribute wear and maintain optimal rolling characteristics. Observe wear patterns and adjust rotation frequency accordingly.
Question 4: What are the recommended cleaning practices for roller skate wheels?
Cleaning practices should focus on removing dirt, debris, and contaminants that can impede bearing function and wheel performance. Use a soft brush and mild detergent to clean the wheels. Ensure thorough drying to prevent corrosion of the bearings. Avoid harsh chemicals or solvents that can damage the wheel material.
Question 5: How does wheel profile impact skating performance?
Wheel profile refers to the cross-sectional shape of the wheel. Rounder profiles offer greater maneuverability and smoother transitions, while flatter profiles enhance stability and straight-line speed. The selection of a suitable profile depends on the skater’s style and the intended skating discipline.
Question 6: What factors contribute to the longevity of roller skate wheels?
Longevity is influenced by several factors, including material composition, durometer, skating surface, maintenance practices, and skating style. Higher-quality materials, appropriate durometer selection, regular cleaning and rotation, and careful skating techniques can significantly extend wheel lifespan.
Proper understanding and application of these principles will lead to enhanced performance, improved safety, and extended equipment lifespan. Consultation with a qualified skate technician or experienced skater can provide further guidance.
The following section delves into the diverse applications of these skate components and the various skate types.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration of quad roller skate wheels has elucidated the critical parameters influencing performance, longevity, and skater experience. Durometer, diameter, material composition, bearing seat compatibility, and profile each contribute uniquely to the overall functionality of these essential components. Precise selection and diligent maintenance, aligned with intended skating discipline and environmental factors, are crucial for maximizing performance and ensuring safety.
Recognizing the nuanced interplay of these variables empowers skaters to make informed decisions, optimizing their equipment for specific needs. Continued advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques promise further refinements in wheel design, potentially mitigating existing limitations and enhancing overall skating capabilities. Ongoing research and development efforts remain focused on achieving a more dynamic performance range with maximized component lifespans, driving improvement and innovation within this sector.