The act of replacing the rotating components attached to the frame of a roller skate is a maintenance procedure essential for optimal performance. These circular parts, typically made of polyurethane, experience wear and tear over time, affecting the skater’s speed, grip, and overall skating experience. The process involves removing the old, worn components and installing new ones.
Performing this task is vital for safety and extending the life of roller skates. Fresh components provide better traction, reducing the risk of slips and falls. Additionally, skaters can customize their equipment by selecting components with specific durometers (hardness) and sizes to suit different skating styles and surfaces. Regular replacement also prevents damage to other skate parts, such as bearings and axles.
A comprehensive guide to executing this maintenance task follows, detailing the necessary tools, step-by-step instructions, and important considerations for ensuring a successful outcome.
Tips for Replacement of Roller Skate Wheels
Successful replacement of roller skate wheels hinges on careful preparation and execution. Consider the following tips to ensure a smooth and efficient process.
Tip 1: Secure the Correct Tools: A skate tool or appropriately sized wrenches are indispensable. Attempting the procedure with improper tools can damage axles or bearings.
Tip 2: Work on a Clean Surface: A clean workspace minimizes the risk of contamination affecting bearings and other components. Debris can impede performance and reduce longevity.
Tip 3: Inspect Bearings: Upon removal, thoroughly examine bearings for wear, damage, or debris. Clean or replace bearings as needed to maximize performance.
Tip 4: Consider Wheel Durometer: Choose a wheel durometer appropriate for the skating surface and intended style. Softer wheels offer more grip, while harder wheels provide faster speeds.
Tip 5: Maintain Axle Cleanliness: Before installing new wheels, ensure that the axles are clean and free of any rust or debris. A clean axle promotes smoother rotation.
Tip 6: Tighten Axle Nuts Appropriately: Axle nuts should be tightened sufficiently to prevent wheel wobble but not so tightly that they restrict wheel rotation. Over-tightening can damage bearings.
Tip 7: Rotate Wheels Regularly: To extend the lifespan of the new wheels, rotate them periodically. This distributes wear evenly across all eight wheels.
By adhering to these recommendations, skaters can optimize performance, extend the life of the wheels and bearings, and ensure a safer skating experience.
The following sections will address common issues encountered during the replacement procedure and offer solutions for overcoming these challenges.
1. Tools required
The successful execution of roller skate wheel replacement is directly contingent upon possessing the appropriate tools. The fundamental tool is either a specialized skate tool or a set of appropriately sized wrenches. These instruments are necessary for loosening and tightening the axle nuts that secure the wheels to the skate frame. Without the correct tools, the procedure is likely to result in damaged axles, stripped nuts, or an inability to complete the replacement. For example, attempting to use pliers on an axle nut designed for a wrench may lead to rounding off the nut’s edges, rendering it impossible to tighten or loosen effectively. The precise dimensions of the required wrench or skate tool vary depending on the skate model.
Furthermore, the selection of high-quality tools is as critical as having the correct sizes. Inferior tools are prone to bending, breaking, or otherwise failing under pressure, which can not only halt the replacement process but also potentially cause injury to the user. A durable skate tool, designed specifically for this purpose, often includes additional features such as bearing presses or removal tools, further streamlining the maintenance process. Conversely, an inadequate tool may strip the axle nut, necessitating professional repair and incurring additional costs. Lubricating the axle nuts with a penetrating oil prior to attempting removal, when facing resistance, is a recommended measure to prevent damage and ensure a smooth process.
In summary, acquiring and utilizing the correct tools constitutes the foundational step in roller skate wheel maintenance. Investing in a high-quality skate tool or set of wrenches prevents damage to the skates, ensures user safety, and ultimately facilitates a swift and efficient wheel replacement. Neglecting this initial requirement can lead to complications and potential equipment failure, underscoring the critical interdependence between having the right tools and the capacity to successfully replace roller skate wheels.
2. Bearing Maintenance
Bearing maintenance represents an integral component of the roller skate wheel replacement process. While the primary focus often centers on exchanging worn wheels, neglecting bearing condition compromises the overall efficacy of the procedure and the potential longevity of the new wheels.
- Inspection and Cleaning
Upon removal of old wheels, meticulous inspection of the bearings is imperative. Accumulation of dirt, debris, or degraded lubricant impedes bearing performance. Cleaning bearings involves removing shields, soaking components in a solvent, and re-lubricating them with appropriate bearing oil or grease. Failure to address contamination can result in diminished speed and increased friction, negating benefits derived from new wheels.
- Bearing Replacement
If inspection reveals significant wear, damage (e.g., pitting or deformation), or persistent noise despite cleaning, bearing replacement becomes necessary. Continuing to use compromised bearings can damage axles and compromise skating safety. New bearings should meet or exceed the ABEC rating of the original bearings to maintain comparable performance characteristics.
- Lubrication Practices
Proper lubrication is critical for extending bearing lifespan and ensuring optimal performance. The type of lubricant used should be compatible with the bearing material and the intended skating environment. Over-lubrication can attract dirt and debris, while insufficient lubrication leads to increased friction and premature wear. A few drops of appropriate bearing oil after cleaning is typically sufficient.
- Bearing Seating
When installing bearings into new wheels, ensuring proper seating is vital. A bearing press tool evenly distributes force, preventing damage to the bearing races or the wheel core. Incorrectly seated bearings can cause vibrations, uneven wear, and premature failure of both the bearings and the wheels.
The interconnectedness of bearing maintenance and wheel replacement is evident in their mutual impact on skate performance and lifespan. Neglecting bearings during wheel replacement effectively limits the potential benefits of new wheels, while proper bearing maintenance maximizes the skater’s investment and enhances safety. Therefore, bearing evaluation and maintenance should be considered an indispensable step in the wheel replacement workflow.
3. Wheel durometer
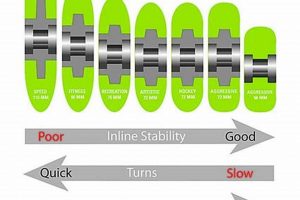
The selection of wheel durometer is a critical consideration during the process of roller skate wheel replacement. The durometer value, measured on the Shore A scale, quantifies the hardness of the wheel’s polyurethane material. This hardness directly influences the skating experience, affecting grip, speed, and wear characteristics.
- Grip and Control
Softer wheels, characterized by lower durometer values (e.g., 78A-85A), provide enhanced grip on various surfaces. This increased grip facilitates better control and maneuverability, particularly beneficial for recreational skating, dance skating, and skating on slick indoor surfaces. During replacement, selecting a softer durometer will necessitate more frequent changes due to faster wear.
- Speed and Roll
Harder wheels, denoted by higher durometer values (e.g., 95A-101A), offer greater rolling speed and reduced rolling resistance. This translates to faster acceleration and sustained velocity, advantageous for speed skating, roller derby, and skating on smooth outdoor surfaces. However, harder wheels generally provide less grip, increasing the risk of slippage, especially on uneven or wet surfaces. Replacement considerations involve assessing the skater’s preference for speed versus control.
- Surface Compatibility
The optimal wheel durometer is heavily dependent on the skating surface. Rougher surfaces demand softer wheels to absorb vibrations and maintain grip. Smoother surfaces permit the use of harder wheels to maximize speed. Replacement choices must account for the predominant skating environment. For instance, skaters transitioning from outdoor to indoor rinks may require wheels with drastically different durometer ratings.
- Wear Rate
Wheel durometer also impacts wear rate. Softer wheels wear down more rapidly than harder wheels, especially when subjected to abrasive surfaces or aggressive skating styles. During replacement, skaters should consider their skating frequency and intensity when selecting wheel hardness. Frequent skaters may opt for harder wheels to reduce the frequency of replacements, while less frequent skaters may prioritize grip and comfort over longevity.
Understanding the relationship between wheel durometer and skating conditions is paramount when performing wheel replacement. The selection process should be informed by the skater’s skill level, skating style, and the characteristics of the intended skating environment. Choosing an inappropriate durometer can negatively impact performance, safety, and the overall skating experience. This is a primary component to this process.
4. Axle Security
Axle security is a critical element within the process of roller skate wheel replacement. The proper securing of axles directly influences the operational safety and performance of the skates. Incorrect axle tightening, stemming from improper wheel installation or worn hardware, can lead to wheel detachment during use, resulting in potential injury to the skater and damage to the equipment.
The relationship between the replacement process and axle security is causal. When new wheels are installed, the skater must ensure the axle nuts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specified torque. Under-tightening the nuts allows wheels to wobble, damaging bearings and potentially causing the nut to loosen completely. Over-tightening, conversely, can compress the bearings, restricting wheel rotation and leading to premature bearing failure. A real-world scenario involves a skater who, after changing wheels, experiences a wheel detachment mid-session due to inadequate tightening. This incident highlights the necessity of meticulously following torque specifications and employing proper tightening techniques.
In conclusion, the consideration of axle security during roller skate wheel replacement transcends a mere step in the procedure; it is a fundamental safety requirement. The consequences of neglecting axle security can range from compromised performance to hazardous equipment failure. Consistent verification of axle nut tightness, the use of appropriate tightening tools, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines are essential for maintaining the integrity and safety of the skates. The process demands attention to detail, as proper axle security ensures a stable and safe skating experience.
5. Rotation patterns
Rotation patterns constitute a critical aspect of roller skate wheel maintenance, influencing both the longevity and performance characteristics of these components. Integrating wheel rotation into the replacement process represents a proactive measure to ensure even wear and maximize the lifespan of the wheel set.
- Extending Wheel Lifespan
Roller skate wheels experience uneven wear due to variations in skating style, surface conditions, and individual skating habits. Rotating the wheels periodically redistributes this wear, preventing premature degradation of specific wheels. By strategically repositioning wheels, skaters can equalize the wear across the entire set, substantially extending the time between replacements.
- Maintaining Consistent Performance
Unevenly worn wheels can negatively affect skating performance, impacting grip, speed, and stability. Rotating the wheels helps maintain a more uniform wheel profile, preserving consistent handling characteristics. This is particularly noticeable when wheels on one side of the skate exhibit significantly greater wear than those on the other, leading to a skewed skating experience.
- Rotation Schemes
Several established rotation schemes exist, each designed to address specific wear patterns. Common schemes involve cross-rotation (switching wheels diagonally), lateral rotation (switching wheels from one side of the skate to the other), or a combination thereof. The choice of rotation scheme depends on individual skating style and observed wear patterns. For instance, skaters who frequently execute turns may opt for a scheme that prioritizes the even wear of the wheels on their turning foot.
- Practical Implementation During Replacement
The act of wheel replacement presents an ideal opportunity to implement a wheel rotation scheme. Upon removing the old wheels, the skater should assess the wear pattern and determine the appropriate rotation before installing the new set. This seamless integration of rotation into the replacement procedure ensures that wheels are strategically positioned from the outset, maximizing their lifespan and maintaining consistent skating performance.
The synergy between replacement and rotation patterns underscores a holistic approach to roller skate wheel maintenance. By integrating rotation into the replacement process, skaters not only extend the lifespan of their wheels but also maintain a more consistent and predictable skating experience.
6. Skating surface
The type of skating surface significantly influences the frequency and requirements of roller skate wheel replacement. Different surfaces impart varying degrees of wear and necessitate specific wheel characteristics for optimal performance.
- Indoor Surfaces (Rinks, Gymnasiums)
Indoor skating surfaces, typically composed of polished wood or coated concrete, are generally smooth and offer low rolling resistance. Wheels used on these surfaces tend to wear less rapidly compared to outdoor applications. However, specific durometer ratings are essential for achieving optimal grip and maneuverability. During replacement, wheel selection should prioritize appropriate hardness to prevent slippage and ensure controlled movement.
- Outdoor Surfaces (Asphalt, Concrete Sidewalks)
Outdoor surfaces, characterized by roughness, debris, and uneven textures, induce accelerated wear on roller skate wheels. Asphalt and concrete sidewalks abrade the wheel material, leading to decreased diameter and compromised performance. Replacement frequency is typically higher for skates used primarily outdoors. Wheel selection should consider durability and abrasion resistance to prolong lifespan.
- Specialized Surfaces (Skate Parks, Ramps)
Skate parks and ramps, designed for aggressive skating styles, present unique challenges to wheel integrity. The impact forces and abrasive textures associated with tricks and maneuvers lead to rapid wear and potential damage. Replacement decisions must account for the specific demands of the skating style, often requiring specialized wheels with high durability and impact resistance. Furthermore, wheel profiles and bearing quality become critical factors.
- Surface Cleanliness
The cleanliness of a skating surface impacts the operational life of roller skate wheels and bearings. Outdoor surfaces often accumulate debris such as dirt, sand, and small stones. These contaminants can embed in the wheel material, increasing wear and reducing grip. Similarly, debris can infiltrate bearings, compromising their performance and leading to premature failure. During wheel replacement, bearings should be thoroughly cleaned and inspected, and wheel selection should consider debris resistance to mitigate these effects.
The interplay between skating surface characteristics and wheel selection emphasizes the need for informed decision-making during the replacement process. Considering the specific demands of the skating environment enables skaters to optimize performance, extend wheel lifespan, and maintain a safe and enjoyable skating experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding roller skate wheel replacement, offering concise and informative responses.
Question 1: How often should roller skate wheels be replaced?
The frequency of wheel replacement depends on factors such as skating style, surface conditions, and wheel durometer. Visual inspection for wear and performance degradation is the most reliable indicator.
Question 2: What tools are essential for completing this task?
A skate tool or appropriately sized wrenches are necessary to loosen and tighten axle nuts. Specific dimensions vary depending on the skate model.
Question 3: Is bearing maintenance necessary during wheel replacement?
Bearing inspection and cleaning are highly recommended. Damaged or contaminated bearings compromise the performance of new wheels.
Question 4: How does wheel durometer affect skating performance?
Lower durometer wheels offer greater grip, while higher durometer wheels provide increased speed. The optimal choice depends on the skating surface and desired skating style.
Question 5: Is wheel rotation a beneficial practice?
Wheel rotation promotes even wear, extending the lifespan of the wheel set and maintaining consistent performance characteristics.
Question 6: What are the risks associated with improper axle tightening?
Under-tightening can lead to wheel detachment, while over-tightening can damage bearings. Adherence to specified torque values is essential.
Accurate answers to these questions will improve the process, promoting safety and performance.
The next section discusses troubleshooting common issues encountered during the act of replacing worn components.
Conclusion
The preceding discussion has comprehensively explored the essential elements of how to change roller skate wheels. From selecting appropriate tools and maintaining bearings to understanding the influence of wheel durometer and skating surfaces, each aspect contributes to a successful and safe maintenance procedure. Understanding axle security and implementing rotation patterns further optimizes performance and extends equipment longevity.
Mastery of this process empowers skaters to maintain their equipment effectively, ensuring both safety and optimal performance. Regular maintenance and thoughtful component selection are crucial for a prolonged and enjoyable skating experience. Prioritize these procedures to maximize the lifespan of the equipment and minimize the risk of skating-related incidents.