Specialized components affixed to roller skates provide mobility across surfaces. These circular objects, often fabricated from polyurethane or similar materials, directly influence the skating experience. Factors such as diameter, durometer (hardness), and profile determine the suitability for various skating styles and terrains. For instance, smaller, harder versions are typically favored for skate park maneuvers, while larger, softer options are often preferred for outdoor cruising.
The selection of these components significantly impacts performance, comfort, and safety. Different formulations and designs enhance grip, speed, and shock absorption. Historically, materials have evolved from metal and clay to advanced polymers, reflecting advancements in materials science and engineering. These improvements enable a wider range of activities and contribute to the overall enjoyment of roller skating.
The remainder of this discourse will elaborate on selecting suitable types based on intended use, analyzing the material properties that determine performance, and discussing the impact of maintenance on their longevity and reliability. These elements are critical for informed decision-making and optimizing the skating experience.
Guidance on Optimal Roller Skate Wheel Selection
Selecting the appropriate components for roller skates requires careful consideration of several factors. The following guidelines provide a framework for informed decision-making, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
Tip 1: Assess Intended Use: Determine the primary skating environment. Indoor surfaces benefit from harder materials for speed and control, while outdoor surfaces necessitate softer materials for enhanced shock absorption and grip.
Tip 2: Consider Durometer Rating: The durometer, measured on the A scale, indicates hardness. Lower numbers (e.g., 78A) signify softer materials suitable for rough surfaces. Higher numbers (e.g., 101A) denote harder materials ideal for smooth surfaces and aggressive skating.
Tip 3: Evaluate Wheel Diameter: Larger diameters generally provide increased speed and momentum, beneficial for distance skating. Smaller diameters offer improved maneuverability and responsiveness, advantageous for park skating and agility-focused disciplines.
Tip 4: Examine Wheel Profile: A rounded profile promotes smoother transitions and greater stability, suitable for recreational skating. A flatter profile provides increased grip and power transfer, beneficial for speed skating and aggressive maneuvers.
Tip 5: Match Bearing Compatibility: Ensure that the chosen types are compatible with the bearings of the roller skate. Standard bearings typically adhere to the 608 size designation, but variations may exist.
Tip 6: Regularly Inspect and Maintain: Periodically examine them for wear and tear, including cracks, chips, and uneven wear patterns. Rotate regularly to promote even wear and extend their lifespan.
By carefully evaluating these factors, individuals can optimize their skating experience, enhancing performance, comfort, and safety. The selection process should align with individual skating goals and environmental considerations.
The subsequent sections will explore the specific material properties that govern performance and the maintenance practices that ensure longevity. This comprehensive approach enables informed decision-making and maximizes the utility of these vital components.
1. Durometer
Durometer, as a measure of a material’s hardness, is a critical factor in determining the performance characteristics of a roller skate’s wheels. The durometer rating, typically indicated on the wheel using the “A” scale, directly correlates to the wheel’s grip, speed, and shock-absorption capabilities. A lower durometer rating signifies a softer material, resulting in enhanced grip and improved shock absorption. Conversely, a higher rating indicates a harder material, prioritizing speed and durability over grip and shock absorption.
The selection of an appropriate durometer rating directly affects the user experience. For instance, skaters primarily using outdoor surfaces or navigating rough terrain frequently opt for softer wheels (e.g., 78A-85A). These softer compounds provide greater adhesion to uneven surfaces, minimizing vibrations and improving comfort. Conversely, skaters favoring smooth, indoor surfaces, such as skate parks, often select harder wheels (e.g., 95A-101A). The reduced rolling resistance of these harder wheels facilitates increased speed and responsiveness. The choice must consider the skater’s experience level and skating style. Inadequate hardness causes a slow, sluggish feel, whereas excessive hardness reduces control and stability.
Understanding the relationship between durometer and skating performance is paramount for selecting optimal wheel characteristics. Failure to consider this factor can result in compromised performance, reduced comfort, and potentially increased risk of injury. Therefore, durometer remains a foundational element in the design and selection process, aligning wheel properties with specific skating applications.
2. Material
The selection of materials constitutes a primary determinant in the performance, durability, and overall aesthetic appeal of roller skate wheels. The material composition influences factors such as grip, rebound, wear resistance, and vibration absorption, impacting the skating experience significantly. Various polymers and composite materials are utilized, each exhibiting distinct properties suitable for specific skating applications.
- Polyurethane Formulation
Polyurethane (PU) is the most prevalent material in roller skate wheel manufacturing. Variations in PU formulation allow for precise control over durometer, rebound, and wear characteristics. Higher-grade PU formulations exhibit superior abrasion resistance, extending the lifespan of the wheels. Custom PU blends often incorporate additives to enhance grip or reduce heat buildup during extended use. The specific formulation directly impacts the wheel’s ability to maintain consistent performance under varying conditions.
- Core Material and Design
Many high-performance wheels feature a rigid core, typically constructed from nylon, polycarbonate, or aluminum. The core provides structural support and enhances power transfer, reducing energy loss during acceleration and turns. Core design influences the wheel’s weight and stiffness. Some cores incorporate ribs or spokes to optimize strength-to-weight ratio. The core material and design collectively contribute to the wheel’s responsiveness and stability.
- Additives and Fillers
Manufacturers incorporate various additives and fillers into the PU matrix to modify its properties. Examples include pigments for coloration, reinforcing agents for increased strength, and lubricants for reduced friction. Certain fillers can enhance grip or improve the wheel’s ability to dissipate heat. The judicious use of additives allows for fine-tuning of the wheel’s performance characteristics to meet specific requirements.
- Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing process significantly affects the uniformity and consistency of the wheel’s material properties. Precision casting and molding techniques ensure even distribution of materials and minimize internal stresses. Post-processing steps, such as heat treatment, can further enhance the material’s strength and durability. Advanced manufacturing processes are essential for producing high-quality wheels that deliver consistent performance.
The interplay of these material-related factors dictates the overall quality and suitability of roller skate wheels for various skating disciplines. A comprehensive understanding of material properties and manufacturing techniques is essential for selecting wheels that provide optimal performance, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
3. Diameter
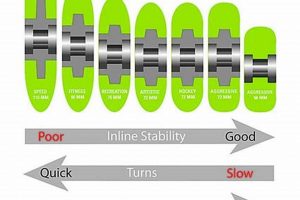
The diameter of a roller skate wheel exerts a direct influence on speed, maneuverability, and the overall skating experience. Larger diameters generally equate to higher top speeds due to increased ground coverage per revolution. This effect is particularly noticeable on smooth, flat surfaces where sustained momentum is advantageous. Smaller diameters, conversely, enhance agility and responsiveness, facilitating quicker turns and more intricate maneuvers. Therefore, the selection of wheel diameter must align with the skater’s intended use and skating environment.
Consider, for example, the differences between speed skating and artistic skating. Speed skaters typically favor larger diameters (e.g., 100mm to 110mm) to maximize velocity during races. The increased rolling circumference allows them to maintain higher speeds with less effort. Artistic skaters, on the other hand, often opt for smaller diameters (e.g., 70mm to 80mm) to achieve greater control and precision during complex routines. The reduced size enables faster acceleration and tighter turns, crucial for executing intricate footwork and jumps. Similarly, skaters using roller skates for urban commuting may choose an intermediate diameter (e.g., 80mm to 90mm) to balance speed and maneuverability in a varied environment.
In summary, diameter is a critical parameter influencing a roller skate wheel’s performance characteristics. Its impact on speed and maneuverability necessitates careful consideration based on skating discipline, surface conditions, and individual preferences. Selecting an inappropriate diameter can hinder performance and compromise the overall skating experience. A practical understanding of this relationship is essential for informed wheel selection and achieving optimal skating performance.
4. Profile
The profile of a roller skate wheel significantly influences its handling characteristics, including grip, stability, and maneuverability. Variations in profile design cater to different skating styles and performance requirements, impacting the contact patch between the wheel and the skating surface.
- Round Profile
A round profile, characterized by its curved shape from edge to edge, facilitates smooth transitions and enhanced maneuverability. This profile allows for gradual engagement and disengagement of the wheel’s edge during turns, promoting fluid motion and improved control. Round profiles are commonly favored by skaters engaged in recreational skating, artistic disciplines, and situations where agility is paramount. The reduced contact patch provides less grip at extreme angles but allows for effortless pivoting and directional changes.
- Flat Profile
A flat profile presents a wider, more rectangular contact patch with the skating surface. This design maximizes grip and stability, particularly during straight-line skating and high-speed maneuvers. The increased contact area provides enhanced traction, enabling skaters to maintain control and execute powerful pushes. Flat profiles are frequently utilized in speed skating and aggressive skating disciplines where stability and power transfer are critical.
- Elliptical Profile
An elliptical profile represents a hybrid design, combining elements of both round and flat profiles. The slightly rounded shape offers a balance between maneuverability and grip, providing versatility for various skating styles. Elliptical profiles are often favored by skaters seeking a compromise between agility and stability, suitable for mixed-terrain skating or recreational use with an emphasis on performance.
- Conical Profile
A conical profile features a tapered or angled edge, often employed in aggressive skating disciplines. The conical shape enhances edge control and facilitates grinding maneuvers on rails and ledges. This profile enables skaters to lock onto surfaces securely, allowing for precise execution of tricks and slides. Conical profiles sacrifice some stability at high speeds but provide unparalleled control during technical maneuvers.
The choice of profile must align with the skater’s primary objectives and skating environment. Different profiles alter the feel and response of the roller skates, and finding the ideal profile enhances both performance and enjoyment. Skaters often experiment with different profiles to discover the optimal configuration for their specific needs and preferences, influencing skating style and overall control.
5. Bearings
The rotational efficiency of roller skate wheels hinges significantly on the quality and specifications of the bearings integrated within them. Bearings, typically housed within the wheel’s central bore, facilitate smooth and low-friction rotation around the axle. In the context of specialized or high-performance wheels, the selection of appropriate bearings is paramount for achieving optimal speed, glide, and overall performance. A substandard bearing choice can negate the benefits of advanced wheel materials and designs.
Consider, for example, the application of ceramic bearings in performance-oriented wheels. Ceramic bearings, characterized by their reduced friction and heat generation compared to traditional steel bearings, contribute to enhanced speed and extended glide times. These features are particularly advantageous in speed skating and long-distance skating applications. Conversely, in recreational skating, the cost-benefit ratio of ceramic bearings may be less pronounced, and high-quality steel bearings may suffice. Further, bearing tolerances, measured by ABEC or ISO ratings, dictate the precision of bearing components and consequently, the smoothness of rotation. Higher ratings indicate tighter tolerances, resulting in reduced vibration and increased efficiency. Proper lubrication and maintenance are also critical for preserving bearing performance and preventing premature wear. Contamination from dirt, debris, or moisture can significantly impede bearing function, necessitating regular cleaning and re-lubrication.
In summary, the interplay between bearing specifications and wheel design is critical for optimizing roller skate performance. Careful consideration of bearing type, tolerance, and maintenance practices can significantly enhance speed, efficiency, and the overall skating experience. Choosing inadequate bearings compromises the potential of even the most technologically advanced roller skate wheels.
6. Aesthetics
The visual appeal of roller skate wheels is a tangible factor influencing consumer preference and brand identity. While performance metrics such as durometer and diameter remain critical, the aesthetic design contributes to the overall perception of quality and desirability. A deliberate aesthetic design can elevate the perceived value and differentiate a product in a competitive market.
- Coloration and Pigmentation
The selection of colors and pigmentation techniques plays a significant role in the visual impact. Vibrant, saturated colors can convey energy and excitement, while muted or neutral tones project sophistication and elegance. The use of translucent or fluorescent pigments adds a unique visual dimension, enhancing visibility and aesthetic appeal. Color consistency and durability are critical considerations, ensuring that the visual impact remains consistent over time. Certain pigment choices can also impact the material properties, such as UV resistance, requiring careful evaluation of potential trade-offs.
- Graphic Design and Branding
The incorporation of logos, patterns, and other graphic elements enhances brand recognition and provides opportunities for personalization. Precisely applied graphics using techniques such as pad printing or hydro-dipping offer durability and visual clarity. The graphic design should align with the overall aesthetic and target demographic, conveying the intended brand message effectively. The size, placement, and complexity of graphics must be carefully considered to avoid detracting from the wheel’s performance or creating visual clutter.
- Material Finish and Texture
The surface finish of roller skate wheels significantly impacts their visual appearance and tactile feel. A glossy finish reflects light, creating a vibrant and eye-catching appearance. A matte finish, conversely, reduces glare and provides a more subdued and sophisticated look. Textured surfaces can enhance grip and provide a tactile element, adding to the overall sensory experience. The choice of finish depends on the desired aesthetic and the intended application, with considerations for durability and ease of cleaning.
- Core Design and Visibility
The design and visibility of the wheel core contributes to the overall aesthetic. A visually striking core, often constructed from contrasting materials or colors, can enhance the wheel’s perceived value. The core design may incorporate intricate patterns or geometric shapes, adding a level of visual complexity. Transparent or translucent cores can reveal the internal mechanisms and bearing placement, showcasing the wheel’s construction and engineering. The core design should integrate seamlessly with the tire material, creating a cohesive and visually appealing product.
The aesthetic design of roller skate wheels is not merely a superficial element; it is an integral component of the overall product experience. A carefully considered aesthetic enhances brand perception, differentiates products in the market, and contributes to the skater’s sense of style and self-expression. The visual appeal serves to complement the performance attributes, creating a holistic product that appeals to both the functional and aesthetic sensibilities of the consumer.
Frequently Asked Questions About Roller Skate Wheels
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, maintenance, and performance characteristics of roller skate wheels.
Question 1: What factors dictate the suitability of a wheel for indoor versus outdoor skating?
The primary determinant is durometer. Indoor surfaces generally necessitate harder wheels (95A or higher) for reduced rolling resistance and increased speed. Outdoor surfaces typically benefit from softer wheels (85A or lower) for enhanced shock absorption and grip on uneven terrain.
Question 2: How does wheel diameter affect skating performance?
Larger diameter wheels generally provide increased speed and momentum due to a greater rolling circumference per revolution. Smaller diameter wheels offer improved maneuverability and acceleration, suitable for agility-focused skating disciplines.
Question 3: What is the significance of the ABEC rating on roller skate bearings?
The Annular Bearing Engineers’ Committee (ABEC) rating quantifies the precision and tolerances of bearings. Higher ABEC ratings (e.g., ABEC 7, ABEC 9) indicate tighter tolerances, resulting in smoother and faster rotation. However, higher ABEC ratings do not necessarily correlate with increased durability.
Question 4: How frequently should roller skate wheels be rotated?
Rotation frequency depends on usage and wear patterns. Irregular wear can result from asymmetrical skating techniques or uneven surfaces. Regular rotation, typically every 10-20 hours of skating, promotes even wear and extends wheel lifespan.
Question 5: What cleaning agents are recommended for roller skate wheels?
Mild soap and water are generally sufficient for cleaning roller skate wheels. Harsh chemicals or solvents can degrade the polyurethane material, compromising performance and durability. Bearings should be shielded from water during cleaning to prevent corrosion.
Question 6: How does wheel profile influence grip and stability?
A flatter wheel profile provides a larger contact patch with the skating surface, resulting in increased grip and stability, particularly during straight-line skating. A rounded profile allows for smoother transitions and enhanced maneuverability, suitable for agility-focused skating.
Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing the skating experience and ensuring the longevity of roller skate components.
The following section will address advanced topics related to wheel materials and manufacturing processes.
Cool Roller Skate Wheels
The preceding analysis has explored the multifaceted nature of roller skate components, encompassing material science, design principles, and performance considerations. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is critical for informed decision-making and optimizing the skating experience. Factors such as durometer, diameter, profile, bearing quality, and aesthetic design contribute significantly to overall performance and user satisfaction.
The continued evolution of materials and manufacturing techniques promises further advancements in roller skate wheel technology. A commitment to informed selection and diligent maintenance ensures both optimal performance and extended product lifespan, thereby maximizing the potential of this essential skating component.





![Get Rolling! Best Roller Skates With Wheels [Guide] How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks Get Rolling! Best Roller Skates With Wheels [Guide] | How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks](https://cruzskateshop.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-414-300x200.jpg)
