Components attached to the trucks of a skateboard, typically constructed from polyurethane, facilitate movement and directional control. These circular elements enable the rider to glide across surfaces, executing various maneuvers. The quality and characteristics of these elements significantly affect a skateboard’s performance.
High-performance versions offer enhanced grip, speed, and durability, contributing to a superior riding experience. Their development has significantly impacted skateboarding, allowing for faster speeds, smoother rides, and more complex tricks. Throughout skateboarding’s evolution, advancements in material science have led to constant refinements and performance improvements.
The following sections will delve into specific aspects, including material composition, durometer ratings, profile types, and their impact on different skateboarding styles. Understanding these factors is crucial for selecting the appropriate set to optimize performance and enjoyment.
Guidance for Optimal Performance
Selecting the appropriate rolling components is crucial for skateboard performance and riding style. These guidelines offer insight into optimizing selection and maintenance.
Tip 1: Consider Durometer. Harder options provide higher speed and slide capability, ideal for street and park skating. Softer ones offer better grip, suitable for cruising or rough surfaces. Selecting the appropriate hardness rating should align with the intended use case.
Tip 2: Evaluate Diameter. Larger diameters generally result in faster speeds and smoother transitions over obstacles. Smaller diameters offer quicker acceleration and lower board height. Diameter selection should be based on preferred riding style and terrain.
Tip 3: Assess Profile Shape. Wider options offer increased stability and grip, advantageous for vert and transition skating. Narrower options provide more maneuverability and responsiveness, suitable for technical street skating. Profile selection should align with stability and maneuverability requirements.
Tip 4: Match to Riding Style. Street skaters should favor durable, smaller diameter options. Park skaters often benefit from medium diameter and hardness. Cruisers require softer, larger diameter options for comfort and rolling efficiency. Matching to the specific skateboarding discipline is paramount.
Tip 5: Regular Maintenance. Consistent cleaning removes dirt and debris, maintaining optimal rolling speed. Bearing maintenance, including lubrication, is also essential for longevity and performance. Proactive maintenance extends the lifespan and maintains performance.
Tip 6: Inspect for Wear. Regularly examine for flat spots, chips, and other damage. Worn components compromise performance and safety. Prompt replacement of worn components is crucial.
Adhering to these guidelines enables skaters to select suitable components, contributing to enhanced performance, safety, and enjoyment.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific models and comparisons, providing a more granular understanding of available options.
1. Durometer
Durometer, a measurement of hardness, plays a crucial role in the performance characteristics of skateboard wheels. The durometer rating directly impacts grip, speed, and durability, thereby influencing the rider’s experience and suitability for specific skating styles when considering any brand.
- Durometer Scale & Measurement
The standard scale employed for skateboard elements is the A scale. A lower number indicates a softer composition, whereas a higher number signifies a harder one. A durometer of 78A indicates a very soft material, and 100A represents an exceptionally hard material. Some manufacturers use the B scale for harder wheels, offering finer resolution for measurements above 100A. This is determined by the material of the wheels which can affect skating performance.
- Impact on Grip
Softer options, such as those around 78A-85A, provide enhanced grip. This is advantageous for cruising, filming, or navigating rough surfaces where traction is paramount. The increased grip facilitates control and stability, particularly for novice skaters. Conversely, harder options offer reduced grip, enabling easier sliding and drifting, which is preferred for street and park skating.
- Influence on Speed
Harder variations, typically 99A and above, generally exhibit higher rolling speed on smooth surfaces. This is because they deform less under pressure, minimizing energy loss. Softer options, while offering greater grip, tend to roll slower due to increased deformation and energy absorption. Speed management is paramount for experienced riders.
- Durability Considerations
Harder versions resist wear and tear more effectively on smooth surfaces. However, they can be more prone to chipping or cracking on rough or uneven terrain. Softer versions wear down more quickly but offer better impact absorption and resilience on challenging surfaces. Thus, planned use cases need to be considered.
Understanding the interplay between durometer and other wheel characteristics allows skateboarders to select components that best suit their individual needs and preferences. A balanced approach ensures a harmonious blend of grip, speed, and durability, leading to an enhanced and more enjoyable skateboarding experience. Each Bones wheel is designed with particular durometer for particular purposes.
2. Diameter
Diameter, measured in millimeters (mm), significantly impacts the performance characteristics of skateboard wheels. Its influence extends to acceleration, top speed, obstacle clearance, and overall stability. Selection is crucial, aligning with the intended skateboarding discipline. The diameter of these items directly affects ride dynamics.
Larger diameters, typically ranging from 55mm to 60mm, offer increased top speed and smoother navigation over cracks and debris. This is due to their greater rotational inertia and reduced angle of attack when encountering obstacles. Examples include vert skaters utilizing larger diameters for sustained speed on ramps, and longboarders prioritizing roll-over capability for distance cruising. Conversely, smaller diameters, generally 50mm to 54mm, provide quicker acceleration and a lower center of gravity, enhancing responsiveness for technical street skating. Street skaters often select smaller diameters for rapid maneuvers and flip tricks.
Understanding the effect of diameter allows skaters to optimize their setup for specific terrains and styles. While larger diameters provide advantages in speed and obstacle clearance, smaller diameters offer improved acceleration and maneuverability. The appropriate diameter selection depends on balancing these factors. A well-informed diameter choice results in enhanced performance, improved control, and an optimized skateboarding experience.
3. Profile Shape
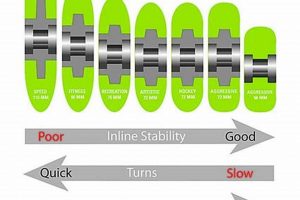
Profile shape, referring to the cross-sectional form of a skateboard wheel, significantly impacts grip, slide characteristics, and overall stability. This attribute, while often overlooked, plays a crucial role in the performance of skateboard wheels, including offerings from established manufacturers. The shape influences how the wheel interacts with the riding surface, directly affecting handling and control. For instance, a wider profile provides increased contact area, enhancing grip and stability, while a narrower profile facilitates easier sliding and maneuverability. The specific application dictates the optimal profile shape; vert skaters often prefer wider profiles for enhanced stability during high-speed transitions, whereas street skaters may opt for narrower profiles to facilitate quicker turns and slides.
Manufacturers tailor profile shapes to cater to diverse skateboarding styles and preferences. Offerings include conical shapes, which are conducive to sliding and freestyle tricks, radial shapes that prioritize grip and stability, and hybrid designs that seek to balance both characteristics. Selecting the appropriate profile shape depends on understanding the intended use case and desired performance attributes. A profile that is too wide may hinder slide initiation, while one that is too narrow might compromise stability at higher speeds. Consequently, skateboarders should carefully consider profile shape alongside other factors, such as durometer and diameter, to optimize their setup.
In conclusion, profile shape is a fundamental aspect of skateboard design, influencing grip, slide, and stability. Its importance lies in its direct impact on the riding experience. Matching the profile shape to the intended skateboarding style allows for enhanced control and optimized performance. Therefore, when selecting skateboard wheels, profile shape warrants careful consideration alongside other technical specifications.
4. Rebound
Rebound, referring to the capacity of a material to return energy after deformation, is a critical performance characteristic. Within the context of these rolling components, rebound directly influences rolling speed and efficiency. A higher rebound coefficient indicates greater energy return, resulting in faster speeds and reduced energy loss during each rotation. Conversely, lower rebound diminishes speed and increases the effort required for propulsion. The polyurethane formulation utilized in these components directly dictates the extent of rebound achieved. Precise manufacturing processes are essential for optimizing this characteristic.
The practical significance of rebound manifests in various skateboarding disciplines. Street skaters benefit from enhanced rolling speed for maintaining momentum between tricks. Park skaters rely on rebound for generating speed on transitions and ramps. Cruisers and longboarders experience increased efficiency and reduced fatigue during extended rides. Empirical evidence demonstrates that variations in rebound correlate directly with observed speed differences and rider effort levels. For example, two otherwise identical setups tested on the same surface exhibit speed discrepancies directly proportional to the rebound coefficient of the components.
Optimization of rebound involves a complex interplay of material science and manufacturing precision. Achieving a desirable rebound profile requires careful consideration of polyurethane composition, curing processes, and quality control measures. While theoretically beneficial, maximizing rebound at the expense of other characteristics, such as durability or grip, can compromise overall performance. Therefore, skateboard component design necessitates a balanced approach, carefully weighing the trade-offs between rebound and other essential attributes. The interplay between the elements that compose the structure, like rebound, can make or break skating performance.
5. Material Composition
The performance characteristics of “bones skate wheels” are intrinsically linked to their material composition, primarily the type and formulation of polyurethane utilized. The specific blend determines the wheel’s durometer (hardness), rebound, abrasion resistance, and overall durability. A proprietary polyurethane formula allows for a tailored balance of these attributes, enabling the creation of wheels optimized for various skateboarding styles. Variations in polymer chain length, cross-linking density, and the inclusion of additives affect the resulting mechanical properties.
For instance, a higher percentage of diisocyanate monomers yields a harder, more abrasion-resistant wheel suitable for street skating, where durability is paramount. Conversely, a formulation incorporating a higher proportion of polyol monomers results in a softer wheel offering enhanced grip and shock absorption, advantageous for cruising or filming. The addition of specific additives, such as colorants or fillers, also influences performance characteristics. Improper material selection or processing can lead to premature wear, reduced performance, or even catastrophic failure.
Consequently, a thorough understanding of the material science underlying “bones skate wheels” is essential for both manufacturers and consumers. This knowledge enables the selection of appropriate wheels for a given skateboarding application, maximizing performance and extending the lifespan of the product. The interplay between polymer chemistry and skateboarding performance underscores the practical significance of material composition.
6. Bearing Seat
The bearing seat, an integral design element, directly influences the performance of “bones skate wheels.” This precisely machined recess within the wheel’s core accommodates the bearing, ensuring concentricity and minimizing play. A properly designed bearing seat maintains alignment, reducing friction and maximizing rolling speed. Conversely, a poorly designed or manufactured bearing seat can lead to bearing misalignment, increased friction, and premature bearing failure. This manifests as reduced speed, increased vibration, and a shortened lifespan for both the wheel and the bearing.
The importance of a precisely toleranced bearing seat is amplified in high-performance skateboarding. For example, professional skateboarders executing demanding tricks require consistent and predictable wheel performance. A slight misalignment in the bearing seat can introduce unwanted wobble or instability, affecting the skater’s ability to land tricks cleanly. Furthermore, consistent pressure on the bearing’s internal components creates unnecessary wear. Some skaters have noticed this especially when the wheel itself is manufactured with a cheaper bearing seat. Precision machining techniques and rigorous quality control are therefore essential to ensure proper bearing seat dimensions and surface finish, directly impacting the skater’s skill and the wheel’s longevity.
In conclusion, the bearing seat represents a critical interface between the wheel and the bearing, profoundly affecting performance and durability. While seemingly a minor detail, its precision directly translates to enhanced rolling speed, reduced vibration, and extended lifespan. Understanding the practical significance of bearing seat design enables informed decisions regarding wheel selection and maintenance, ultimately contributing to a more satisfying and reliable skateboarding experience.
7. Core Design
Core design, referring to the internal structure of “bones skate wheels”, plays a crucial role in influencing performance characteristics such as weight, rigidity, and heat dissipation. The presence or absence of a core, its material composition, and its geometric configuration directly impact the wheel’s overall feel and suitability for various skateboarding styles. Different designs offer varying levels of support and responsiveness, affecting speed, grip, and slide control.
- Cored vs. Uncored Construction
Cored wheels incorporate a rigid inner structure, typically made of a high-strength polymer. This core provides enhanced support, preventing deformation under load and improving rolling efficiency. Uncored wheels, conversely, consist solely of polyurethane, offering a more forgiving ride and increased grip. The choice between cored and uncored depends on the skater’s preference for responsiveness versus comfort. Cored models, commonly found in park and street wheels, are favored for their speed and precision. Uncored models are generally preferred for cruising or filming due to their smoother ride.
- Core Material and Rigidity
The material used for the core directly influences its rigidity. Stiffer materials, such as high-density nylon or fiberglass-reinforced polymers, provide maximum support and energy transfer. This results in increased rolling speed and responsiveness. Softer core materials offer greater vibration damping and a more compliant feel. The degree of core rigidity should align with the intended application. A core that is too stiff may transmit excessive vibrations, while a core that is too flexible may compromise speed and control.
- Core Geometry and Lip Support
Core geometry affects the distribution of stress within the wheel. Some designs feature ribs or spokes that provide additional support to the wheel’s lips (the edges of the wheel’s contact patch). This lip support prevents deformation during hard turns and slides, maintaining a consistent contact patch and improving grip. Different core geometries cater to specific skateboarding styles. For example, a conical core with minimal lip support facilitates easier sliding, while a cylindrical core with substantial lip support maximizes grip for carving.
- Heat Dissipation
Friction generates heat within the wheel during use. Cored designs, particularly those with open geometries or heat-conductive materials, can facilitate heat dissipation. This prevents the polyurethane from softening and losing grip during prolonged periods of intense skating. Overheating can lead to a significant reduction in performance, so effective heat dissipation is crucial for maintaining consistent wheel behavior. Heat dissipation is generally not a major consideration for casual skaters but becomes increasingly important for those engaged in demanding disciplines such as downhill or aggressive street skating.
In summary, core design profoundly influences the performance of “bones skate wheels”. Factors such as cored versus uncored construction, core material, core geometry, and heat dissipation contribute to a wheel’s overall characteristics. Skaters should consider these aspects carefully to select wheels that best match their individual needs and skateboarding style. The optimal core design balances support, responsiveness, and durability for a consistent and reliable riding experience. Core designs are not all equal.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Bones Skate Wheels
The following section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions concerning these components, providing detailed explanations to assist in informed decision-making.
Question 1: What factors differentiate Bones Skate Wheels from other brands?
Bones Skate Wheels are known for their high-quality urethane formula, designed for durability and performance. Key differentiators include rigorous testing protocols and consistent manufacturing standards, resulting in predictable slide and wear characteristics.
Question 2: How does durometer affect Bones Skate Wheel performance?
Durometer, a measure of hardness, significantly influences grip and speed. Softer compounds (lower durometer ratings) provide increased grip, while harder compounds (higher durometer ratings) offer greater speed and slide capability. Selection should align with the intended skating style and terrain.
Question 3: Are Bones Skate Wheels suitable for all skateboarding disciplines?
Bones Skate Wheels manufactures a range of wheels designed for specific skateboarding styles. Street, park, and transition skating each benefit from distinct wheel characteristics. Selecting the appropriate model is crucial for optimal performance.
Question 4: What is the expected lifespan of Bones Skate Wheels?
Lifespan varies depending on several factors, including riding style, terrain, and frequency of use. Proper maintenance, such as regular cleaning, can extend the lifespan. Consistent abrasion and impact will eventually necessitate replacement.
Question 5: How should Bones Skate Wheels be maintained?
Maintenance primarily involves cleaning to remove dirt and debris, which can impede rolling speed. Periodic inspection for wear or damage is also recommended. Avoid prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures, as this can affect urethane integrity.
Question 6: What is the significance of the Bones Skate Wheels bearing seat?
The bearing seat ensures proper alignment and secure fitment of the bearings. Precise machining is essential for minimizing friction and maximizing rolling efficiency. A poorly designed bearing seat can lead to premature bearing wear and reduced performance.
The information presented herein should provide a clearer understanding of Bones Skate Wheels and their impact on skateboarding performance.
The next section will focus on specific model comparisons and performance reviews.
Bones Skate Wheels
The preceding discussion elucidates the multifaceted attributes and considerations relevant to optimal utilization of Bones Skate Wheels. Key parameters, including durometer, diameter, profile shape, rebound, material composition, bearing seat design, and core construction, significantly influence performance characteristics. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is essential for informed selection and maintenance practices.
Ultimately, the performance capabilities depend upon a holistic integration of design features and diligent user practices. Further exploration and refinement of materials and manufacturing processes will undoubtedly yield continued advancements in skateboard wheel technology, enhancing the skateboarding experience for both amateur and professional practitioners. Consistent assessment and adjustment are paramount.