These components, characterized by their small diameter and hard durometer, are integral to the specialized form of skating focused on performing tricks on various obstacles. Constructed to withstand substantial impact and friction, these items enable skaters to execute grinds, slides, and aerial maneuvers in skate parks and urban environments.
The use of these robust elements contributes significantly to the longevity of the skating experience and the ability to perform challenging tricks. Historically, the development of these wheels marked a significant shift in skating, enabling a more technical and acrobatic style of skating. Their design directly impacts performance, allowing for controlled slides and reliable landings.
Further discussion will explore the specific characteristics of these items, including durometer ratings, core types, and optimal applications for different skating styles and environments. Examining these elements will provide a deeper understanding of their role in enhancing skating performance and overall rider experience.
Guidance on Component Selection
The following recommendations aim to inform skaters in making appropriate selections for their specific needs and skill levels.
Tip 1: Durometer Considerations: Higher durometer ratings (88A-90A) provide enhanced speed and durability, ideal for park skating and smooth surfaces. Lower durometer ratings (86A or lower) offer improved grip and shock absorption, suitable for street skating and rougher terrains.
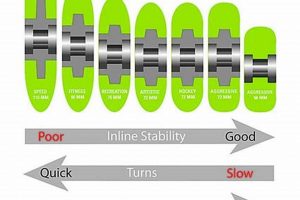
Tip 2: Size Selection: Smaller diameters (55mm-60mm) facilitate faster acceleration and maneuverability, advantageous for technical tricks. Larger diameters (60mm+) offer increased speed and roll-over ability, beneficial for transitions and cruising.
Tip 3: Core Material: High-quality urethane cores enhance energy transfer and responsiveness. Aluminum cores offer superior strength and durability for skaters executing high-impact maneuvers.
Tip 4: Profile Shape: A rounded profile enhances speed and reduces friction during grinds. A flat profile provides a more stable platform for landings and maintaining balance on rails.
Tip 5: Bearing Compatibility: Ensure chosen components are compatible with the bearing size and type used in the skater’s setup. Proper bearing fit is crucial for smooth roll and optimal performance.
Tip 6: Regular Inspection: Routine examination for wear and tear is essential. Replace components exhibiting significant wear to maintain performance and prevent potential injury.
Proper selection of these components can significantly impact skating performance, longevity of equipment, and skater safety. Adhering to these recommendations contributes to an improved and safer skating experience.
The following section will delve into the maintenance practices essential for extending the lifespan of these components.
1. Durometer Ratings
Durometer ratings represent a critical specification of these wheels, directly influencing performance characteristics. The durometer scale, most commonly using the “A” scale in this context, quantifies the hardness of the urethane material. A higher durometer rating indicates a harder wheel, while a lower rating signifies a softer wheel. This measurement significantly affects the grip, speed, and shock absorption capabilities of these components. The choice of durometer rating is a strategic decision dependent on the skater’s style, the terrain being skated, and the desired balance between speed and control.
A harder, higher-durometer wheel, such as an 88A or 90A, will roll faster on smooth surfaces like skate park ramps and polished concrete. This increased speed is beneficial for maintaining momentum during trick execution and allows for quicker transitions between obstacles. However, these harder wheels offer less grip, potentially making them less suitable for rougher street surfaces where maintaining control is paramount. Conversely, softer, lower-durometer wheels, such as an 86A or lower, provide increased grip and shock absorption. This makes them ideal for street skating, where skaters encounter uneven surfaces and need to absorb impacts from landings and transitions. The increased grip enhances stability and control, allowing for more precise movements and a greater margin for error. As an example, consider a skater performing a grind on a rough concrete ledge. A wheel with a lower durometer will grip the ledge better, providing more stability and control during the grind, reducing the likelihood of slipping off.
In summary, durometer ratings are a foundational element in selecting these wheels. The optimal rating depends heavily on the intended use. Skaters should carefully consider their skating environment and personal preferences when choosing a durometer rating. A well-informed choice directly translates to enhanced performance, improved control, and a more enjoyable skating experience. The interplay between durometer rating and skating surface characteristics is paramount in achieving optimal performance and safety.
2. Diameter Size
The diameter of aggressive skate wheels is a critical parameter influencing various aspects of performance, from acceleration and maneuverability to speed and obstacle clearance. It represents the dimension across the wheel, typically measured in millimeters (mm), and is a key factor in determining the suitability of the wheel for different skating styles and environments.
- Acceleration and Maneuverability
Smaller diameter wheels (typically 55mm to 60mm) offer faster acceleration and enhanced maneuverability. This is particularly advantageous for technical skating, where quick starts, stops, and changes of direction are essential for executing intricate tricks. The reduced rotational inertia of smaller wheels allows skaters to react more rapidly to obstacles and maintain control during complex maneuvers.
- Grind Clearance and Obstacle Navigation
The diameter directly impacts the clearance between the skater’s boot and the grinding surface. A smaller diameter allows for a lower center of gravity and reduces the risk of boot contact during grinds, providing a more stable and controlled grind experience. Conversely, larger diameter wheels can improve the ability to roll over minor obstacles, such as cracks or small debris on the skating surface.
- Speed and Roll-Over Ability
Larger diameter wheels (exceeding 60mm) generally offer increased speed and improved roll-over ability on uneven surfaces. The larger circumference allows for greater distance covered per revolution, resulting in a higher top speed. This is particularly beneficial for skaters who incorporate elements of transition skating or who require sustained speed for specific tricks.
- U-turn control & Momentum Keep
The use of big aggressive wheels enables skater to control their movement in U-turn, and they can maintain momentum for longer duration.
The selection of an appropriate diameter involves a trade-off between acceleration, maneuverability, grind clearance, and speed. Skaters should carefully consider their skating style, preferred terrain, and the types of tricks they intend to perform when choosing a wheel diameter. The diameter selection is a pivotal decision in customizing the skating experience and optimizing performance.
3. Core Material
The core material within aggressive skate wheels significantly impacts performance and durability. This central component provides structural integrity and influences energy transfer. Two prevalent materials are urethane and aluminum, each imparting distinct characteristics. Urethane cores, typically found in less expensive wheels, offer a degree of flexibility that can dampen vibrations and improve grip, but they are generally less durable than aluminum. This decreased durability leads to a shorter lifespan, particularly under the high-impact conditions characteristic of aggressive skating.
Aluminum cores, on the other hand, provide superior strength and stiffness. This enhances energy transfer, allowing for more responsive and efficient skating. The rigidity of aluminum cores also contributes to improved durability, enabling wheels to withstand the stresses of grinds, jumps, and landings. A skater executing a demanding trick, such as a gap to grind, benefits from the increased stability and responsiveness provided by aluminum-cored wheels. The trade-off is a potentially harsher ride, as aluminum does not absorb vibrations as effectively as urethane. Despite this, the enhanced performance and longevity often make aluminum cores the preferred choice for serious aggressive skaters.
Understanding the properties of core materials is crucial for informed wheel selection. While urethane cores offer a cost-effective option for beginners or skaters prioritizing comfort, aluminum cores deliver the performance and durability demanded by experienced aggressive skaters. The core material serves as a foundational element that dictates the wheel’s overall responsiveness, resilience, and ultimately, its suitability for the rigors of aggressive skating.
4. Profile Shape
The profile shape of aggressive skate wheels defines the cross-sectional contour of the wheel, significantly affecting grinding performance and stability. Two primary profile shapes are prevalent: rounded and flat. Rounded profiles reduce friction during grinds, enabling smoother transitions and sustained sliding. This design minimizes the contact area between the wheel and the grinding surface, allowing for quicker movements and reduced resistance. Flat profiles, conversely, offer enhanced stability, particularly when landing tricks or maintaining balance on rails. A larger contact patch between the wheel and surface creates a more secure platform, mitigating the risk of slippage during landings or intricate maneuvers. The profile shape, therefore, directly influences the skater’s ability to execute specific types of tricks.
The choice of profile shape depends largely on the skater’s preferred style and the types of obstacles encountered. Skaters who frequently perform grinds on ledges or rails often benefit from a rounded profile, allowing for faster and more fluid movements. For example, a skater executing a backslide on a round rail would find a rounded profile advantageous, as it would reduce friction and allow the skater to maintain momentum. Conversely, skaters who prioritize stability and control, particularly when landing jumps or navigating technical street obstacles, might opt for a flat profile. A skater attempting a gap to rail landing requires a stable platform, and a flat profile will provide increased grip and reduce the likelihood of a washout upon impact.The understanding of profile shape selection enables better decision-making for improved skating performance and safety. For instance, a skater who is beginner may find a flat profile better since it is more stable than rounded profile.
In summary, the profile shape of these wheels represents a critical design element that directly affects grinding performance and stability. Rounded profiles prioritize reduced friction, while flat profiles emphasize enhanced contact and control. The optimal choice depends on individual skating style and the specific demands of the terrain, reflecting a fundamental aspect of wheel customization in aggressive skating.
5. Bearing Compatibility
Bearing compatibility represents a fundamental consideration in the selection and maintenance of aggressive skate wheels. The successful integration of bearings and wheels directly impacts roll speed, smoothness, and overall performance. Mismatched components can lead to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and potential safety hazards. Understanding the nuances of bearing compatibility is crucial for optimizing the skating experience.
- Standard Bearing Size
Aggressive skate wheels predominantly utilize the 608 bearing size, characterized by an 8mm inner diameter, 22mm outer diameter, and 7mm width. This standardized dimension ensures interchangeability across various wheel and bearing brands. Deviation from this standard necessitates specialized adaptations or alternative equipment, complicating the setup process.
- Bearing Seat Precision
The bearing seat, the recess within the wheel core designed to house the bearing, must be precisely manufactured to ensure a secure and concentric fit. Deviations in the bearing seat’s dimensions can cause bearing misalignment, leading to uneven wear, reduced roll speed, and increased friction. In extreme cases, a poorly formed bearing seat can compromise the wheel’s structural integrity.
- Bearing Shields and Seals
Bearing shields and seals protect internal components from contaminants, such as dirt and moisture, which can degrade performance and shorten lifespan. Open bearings offer minimal protection and are unsuitable for aggressive skating. Sealed bearings provide enhanced protection, while shielded bearings offer a balance between protection and ease of maintenance. Selection depends on skating environment and maintenance practices.
- Bearing Installation and Removal
Proper installation and removal techniques are essential for preserving both bearing and wheel integrity. Forceful or improper methods can damage the bearing seat or distort the bearing itself, leading to performance degradation. Specialized tools, such as bearing presses and pullers, facilitate safe and efficient installation and removal, minimizing the risk of damage.
The interplay between these facets underscores the significance of meticulous attention to bearing compatibility. Selecting components adhering to established standards, ensuring precise fitment, and implementing proper maintenance protocols collectively contribute to optimized performance, extended equipment lifespan, and a safer skating experience. Disregard for these considerations can compromise the functionality and longevity of aggressive skate wheels, ultimately diminishing the skater’s capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following provides concise answers to common inquiries regarding these components. These responses aim to clarify misconceptions and offer practical guidance.
Question 1: What distinguishes aggressive skate wheels from those used in other skating disciplines?
These specialized components are designed for high-impact trick skating, featuring smaller diameters and harder durometers to withstand rigorous use on abrasive surfaces. Standard skating wheels are typically larger and softer, prioritizing speed and comfort over durability for trick performance.
Question 2: How does wheel durometer affect performance?
Durometer measures wheel hardness. Higher durometer values (e.g., 88A-90A) denote harder wheels, offering increased speed and durability on smooth surfaces. Lower durometer values (e.g., 86A and below) signify softer wheels, providing enhanced grip and shock absorption on rougher terrains. The appropriate durometer rating is dictated by skating style and environmental conditions.
Question 3: What diameter size is recommended for aggressive skating?
Diameter sizes range from 55mm to 60mm are most prevalent. Smaller diameters facilitate faster acceleration and enhanced maneuverability, while larger diameters provide increased speed and improved roll-over capability on uneven surfaces. Selection should be aligned with the skater’s preference for technical maneuvers versus sustained speed.
Question 4: Why are some aggressive skate wheels constructed with aluminum cores?
Aluminum cores provide superior strength and stiffness compared to urethane cores. This enhances energy transfer and improves durability, enabling wheels to withstand the stresses of grinds, jumps, and landings. Aluminum cores are generally preferred by experienced skaters engaged in high-impact maneuvers.
Question 5: How frequently should aggressive skate wheels be replaced?
Replacement frequency is contingent upon skating intensity, terrain, and wheel quality. Regular inspection for wear, such as flat spots or core damage, is essential. Significant wear compromises performance and safety, necessitating prompt replacement. Rotation of wheels can extend their lifespan.
Question 6: Are aggressive skate wheels compatible with all skate bearings?
The vast majority utilize the 608 bearing size, adhering to a standardized dimension for interchangeability. However, precise bearing seat dimensions are critical. Deviations can result in misalignment, reduced roll speed, and uneven wear. It is important to ensure a secure and concentric fit during installation.
Selecting and maintaining these components requires careful consideration of durometer, diameter, core material, and bearing compatibility. A well-informed approach ensures optimal performance, extended equipment lifespan, and a safer skating experience.
The subsequent section will address maintenance and care strategies.
Conclusion
The preceding discourse has explored the critical attributes of these specialized components, encompassing durometer ratings, diameter sizes, core materials, profile shapes, and bearing compatibility. Each element contributes uniquely to performance, influencing speed, maneuverability, stability, and durability. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is paramount for informed decision-making.
The appropriate selection and diligent maintenance of these wheels are essential for maximizing performance and ensuring skater safety. As aggressive skating continues to evolve, ongoing innovation in wheel technology will undoubtedly further refine the limits of trick execution. Therefore, skaters must remain abreast of advancements in material science and design to optimize their equipment and enhance their capabilities. The future of aggressive skating is inextricably linked to the continued development and refinement of these critical components.





![Get Rolling! Best Roller Skates With Wheels [Guide] How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks Get Rolling! Best Roller Skates With Wheels [Guide] | How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks](https://cruzskateshop.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-414-300x200.jpg)
