Wheels designed for skating on asphalt, concrete, and other outdoor surfaces are typically manufactured with softer durometers compared to those intended for indoor rink use. This characteristic provides enhanced grip and shock absorption, crucial for navigating the irregularities often encountered on external skating environments. For example, a skater traversing a paved trail requires wheels capable of maintaining contact and control despite small rocks or uneven pavement.
The significance of appropriate wheel selection for outside skating lies in optimized performance, user safety, and prolonged equipment lifespan. Softer compositions help mitigate the impact of rough surfaces, reducing fatigue and minimizing the risk of falls. Furthermore, these materials offer increased resistance to wear and tear from abrasive environments, extending the period before replacements become necessary. Their development reflects an ongoing pursuit of improved rolling efficiency and durability in response to the challenges posed by varied outdoor terrain.
The subsequent discussion will delve into the specific factors influencing the selection of such wheels, including durometer, size, profile, and core construction, to provide a comprehensive understanding of their features and application across different skating disciplines.
Guidance on Selecting Outdoor Skating Wheels
Selecting the appropriate wheels for skating on outdoor surfaces is paramount for performance, safety, and equipment longevity. The following guidance will aid in making informed decisions.
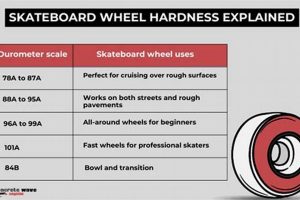
Tip 1: Consider Durometer Ratings. Softer wheels, generally with a durometer rating of 78A to 85A, offer superior grip and shock absorption on rough outdoor surfaces. Higher durometer wheels (above 85A) are harder and faster, but less suitable for uneven terrain.
Tip 2: Evaluate Wheel Size. Larger diameter wheels roll over obstacles more easily and maintain momentum more effectively. Wheel sizes between 70mm and 80mm are often preferred for recreational outdoor skating.
Tip 3: Choose the Appropriate Wheel Profile. A rounded wheel profile provides enhanced maneuverability and is ideal for carving and recreational skating. A flatter profile offers increased stability and speed on straight paths.
Tip 4: Inspect Wheel Core Construction. The core material significantly impacts a wheel’s performance. A robust core made from high-quality materials ensures efficient energy transfer and prevents premature deformation under stress.
Tip 5: Match Wheel Characteristics to Skating Style. Aggressive skaters may favor smaller, harder wheels for tricks and jumps, while distance skaters benefit from larger, softer wheels for efficient rolling.
Tip 6: Prioritize Wheel Material. Polyurethane is the standard material for skate wheels due to its durability, rebound, and versatility. Premium polyurethane blends offer enhanced performance characteristics.
Tip 7: Regular Wheel Maintenance is Essential. Routine cleaning and rotation of wheels contribute to even wear and prolong their lifespan. Prompt replacement of damaged or severely worn wheels is imperative for maintaining safety and optimal performance.
Careful consideration of these factors will enable informed selection of suitable rolling components, maximizing performance and mitigating potential risks associated with external skating environments.
The subsequent sections will further elaborate on specific wheel technologies and their application across different skating modalities.
1. Durometer (Softness)
Durometer, a measure of a material’s resistance to indentation, is a critical property influencing the performance of wheels designed for skating on outdoor surfaces. The durometer rating, typically expressed on the A scale (e.g., 78A, 85A), directly correlates with the wheel’s softness. In the context of outdoor skating, softer wheels (lower durometer ratings) provide enhanced grip on irregular surfaces like asphalt or concrete. This increased friction translates to improved control and maneuverability, particularly when navigating cracks, pebbles, or other obstacles commonly encountered outdoors. For example, a wheel with a durometer of 78A deforms more readily than an 85A wheel, conforming to surface imperfections and maintaining contact, whereas a harder wheel may skip or lose traction.
The softness of the wheel also contributes significantly to shock absorption. Outdoor surfaces are typically less smooth than indoor skating rinks, subjecting the skater to vibrations and impacts. Softer wheels dampen these forces, reducing fatigue and improving ride comfort. This is particularly important for longer distance skating or recreational use, where sustained exposure to rough terrain can lead to discomfort and decreased performance. Conversely, wheels with higher durometer ratings, while potentially offering higher speeds on smooth surfaces, transmit more of the surface’s irregularities to the skater, compromising control and comfort on outdoor terrain.
In summary, durometer directly influences the grip, control, and comfort experienced while skating outdoors. Choosing wheels with an appropriate durometer rating, generally in the 78A to 85A range, is essential for mitigating the challenges posed by uneven surfaces, ensuring a safer and more enjoyable skating experience. Selection should consider individual skater weight, skating style, and the typical surface conditions encountered. Prioritizing appropriate durometer enhances both performance and user well-being when skating externally.
2. Wheel Size (Diameter)
Wheel diameter, a fundamental characteristic of rolling components, significantly influences skating dynamics, particularly on outdoor surfaces. The size of the rolling element directly affects speed, maneuverability, and the ability to navigate terrain irregularities. Wheel diameter is typically measured in millimeters (mm) and ranges from smaller wheels utilized in aggressive skating styles to larger wheels employed for distance and recreational skating.
- Roll-Over Capability
Larger diameter wheels possess an improved roll-over capability, enabling skaters to more easily traverse cracks, pebbles, and other minor obstructions common on outdoor surfaces. A larger wheel encounters these obstacles at a shallower angle, requiring less energy to overcome them and maintaining momentum more effectively. For example, a wheel of 80mm will navigate a small crack in the pavement with greater ease than a 72mm wheel.
- Speed and Momentum
Larger diameter wheels, due to their greater circumference, cover more ground per revolution than smaller wheels. This characteristic translates to increased speed and enhanced momentum. Once accelerated, larger wheels maintain their velocity with less effort, making them advantageous for sustained skating on outdoor paths and trails. The effect becomes noticeable in longer skating distances.
- Maneuverability and Agility
Smaller diameter wheels generally offer greater maneuverability and agility. Their compact size allows for quicker turns and more responsive handling, which can be beneficial for skating in crowded areas or performing intricate maneuvers. However, this increased agility comes at the expense of speed and roll-over capability. A smaller wheel turns faster and handles the weight on the wheels well.
- Surface Contact Area
Wheel size affects the contact area between the wheel and the skating surface. While diameter is the primary factor, wheel profile also influences this. Larger wheels can have a larger contact area when used for outdoor skating. Increased contact area increases the friction on the road.
The selection of wheel diameter represents a trade-off between speed, roll-over capability, and maneuverability. Outdoor skaters must carefully consider their skating style, the typical terrain encountered, and their individual preferences to determine the optimal wheel size. A balance of factors is required for selection.
3. Polyurethane Composition
The formulation of polyurethane used in skate wheels significantly influences performance characteristics, particularly when utilized on outdoor surfaces. The polymer blend determines factors such as grip, rebound, durability, and resistance to abrasion.
- Hardness and Durometer Rating
Polyurethane composition dictates the final durometer rating of the wheel, expressed as a numerical value on the A scale. Outdoor skating necessitates softer formulations, typically in the 78A-85A range, to provide adequate grip on uneven asphalt. The specific blend of polymers, additives, and curing agents directly controls the hardness and compliance of the wheel.
- Rebound and Energy Return
Polyurethane possesses inherent elastic properties, enabling it to deform under load and subsequently return to its original shape. The degree of rebound, often referred to as “energy return,” affects rolling efficiency and responsiveness. Formulations designed for outdoor wheels often prioritize a balance between grip and rebound to maintain speed without sacrificing control.
- Abrasion Resistance and Durability
Outdoor surfaces present a harsh environment for skate wheels, exposing them to constant abrasion from asphalt, concrete, and debris. The selection of high-quality polyurethane polymers and the incorporation of additives that enhance wear resistance are critical for prolonging wheel lifespan and maintaining performance characteristics over time. Specific additives will increase the lifespan and performance of wheels.
- Hysteresis and Energy Loss
Hysteresis refers to the energy lost during the deformation and recovery cycle of the polyurethane material. A lower hysteresis value indicates greater energy efficiency and reduced heat buildup. Controlling hysteresis through precise polymer formulation is crucial for minimizing rolling resistance and maximizing performance, particularly during prolonged skating sessions.
The optimized polyurethane composition for rolling components represents a carefully engineered balance of properties. The specific requirements of external skating, including the need for grip, durability, and efficient rolling, necessitate meticulous attention to the formulation process. Achieving this balance results in a product capable of withstanding the rigors of outdoor use while delivering the desired performance characteristics for the skater.
4. Core Design (Material)
The core of a skate wheel, often overlooked, is a critical component that significantly influences performance, particularly in the context of wheels designed for outdoor skating. The core’s design and the materials employed directly affect the wheel’s ability to transmit power, absorb impact, and maintain structural integrity under the stresses of varied outdoor terrains.
- Stiffness and Energy Transfer
A stiffer core material, such as high-grade nylon or reinforced polymers, enhances energy transfer from the skater’s push to the wheel’s rotation. This minimizes energy loss through core deformation, resulting in improved speed and efficiency. However, excessive stiffness can reduce shock absorption, potentially leading to a harsher ride on rough surfaces. The balance between stiffness and compliance is crucial for optimal outdoor performance.
- Impact Resistance and Durability
Outdoor skating environments subject wheels to impacts from cracks, pebbles, and other debris. The core material must possess sufficient impact resistance to prevent cracking or deformation, which can compromise wheel performance and safety. Durable materials like fiberglass-reinforced polymers offer enhanced impact resistance, extending the lifespan of outdoor skating wheels.
- Core Geometry and Support
The internal geometry of the wheel core, including spoke design and ribbing, contributes to its overall strength and support for the polyurethane tire. A well-designed core distributes stress evenly across the wheel, preventing premature wear and tear. Certain core designs incorporate features to enhance grip or improve heat dissipation during prolonged use.
- Bonding with Polyurethane
The material and surface treatment of the wheel core must promote a strong bond with the surrounding polyurethane tire. Poor bonding can lead to delamination, where the tire separates from the core, rendering the wheel unusable. Surface treatments such as etching or chemical priming enhance adhesion, ensuring a durable and reliable bond between the core and the tire.
Effective wheel construction for outdoor skating necessitates careful consideration of core design and materials. The selection of appropriate materials and geometries, combined with robust bonding techniques, is critical for achieving the desired balance of performance, durability, and safety. Neglecting core design can significantly diminish the overall quality and lifespan of wheels intended for external skating applications.
5. Grip (Surface Adhesion)
Surface adhesion, commonly referred to as grip, is a paramount characteristic dictating the performance and safety of wheels intended for skating on outdoor surfaces. It directly impacts the skater’s ability to maintain control, execute maneuvers, and effectively transfer power, particularly on the varied and often unpredictable terrains encountered externally.
- Durometer and Contact Area
Softer compounds, typically characterized by lower durometer ratings (e.g., 78A-85A), exhibit greater surface adhesion than harder materials. This is due to their ability to conform more readily to irregularities in the skating surface, increasing the contact area and, consequently, the frictional force. A wheel exhibiting a lower durometer rating will achieve greater surface adhesion to asphalt as opposed to wheels with higher ratings.
- Polyurethane Formulation and Additives
The specific polyurethane formulation and the incorporation of specialized additives significantly influence surface adhesion. Certain additives are designed to increase the coefficient of friction between the wheel and the skating surface, enhancing grip in both dry and wet conditions. Manipulation of the polyurethane will increase how the wheel will grip the road.
- Wheel Profile and Edge Control
The profile of the wheel, specifically the shape of its contact surface, affects the distribution of pressure and the available edge control. A rounder profile generally provides more consistent grip during turns and maneuvers, while a flatter profile may offer increased stability on straightaways. The edge grip of the wheel will increase or decrease how the wheel can be used to turn.
- Surface Conditions and Environmental Factors
External surface conditions, including the presence of moisture, dirt, and debris, directly affect surface adhesion. Wheels designed for outdoor use often incorporate tread patterns or specialized compounds to maintain grip in adverse conditions. The presence of such outside conditions can greatly affect surface adhesion.
Consequently, the selection of appropriate wheels for external skating necessitates careful consideration of surface adhesion characteristics. Prioritizing materials, formulations, and designs that maximize grip ensures optimal control, safety, and performance across diverse outdoor environments. Understanding and addressing these grip-related facets is crucial for skaters seeking to navigate external terrains effectively and confidently.
6. Rolling Resistance
Rolling resistance, a force opposing the motion of a rolling object on a surface, directly impacts the efficiency and speed of wheels designed for outdoor skating. Minimizing this resistance is crucial for skaters seeking to maximize their energy expenditure and achieve higher velocities. The interplay between wheel material, surface conditions, and skater technique determines the magnitude of the rolling resistance experienced.
- Wheel Durometer and Deformation
Softer wheels, characterized by lower durometer ratings (e.g., 78A-85A), deform more readily under load than harder wheels. While this deformation enhances grip on uneven surfaces, it also increases rolling resistance due to the energy dissipated during the deformation and recovery cycle of the polyurethane material. A balance must be struck between grip and rolling efficiency when selecting a wheel hardness appropriate for outdoor skating. The harder the wheel the easier it to overcome rolling resistance.
- Surface Roughness and Hysteresis
Rough outdoor surfaces, such as asphalt or concrete, increase rolling resistance compared to smooth indoor surfaces. The irregularities of the surface cause greater deformation of the wheel, leading to increased hysteresis, the energy lost during the deformation process. Smoother surfaces typically leads to less rolling resistance.
- Wheel Diameter and Contact Patch
Larger diameter wheels generally exhibit lower rolling resistance than smaller diameter wheels, assuming all other factors remain constant. This is primarily due to the larger radius of curvature, which reduces the angle of deformation and the amount of energy dissipated per revolution. The total area of the patch is an important element to consider for rolling resistance.
- Wheel Material and Rebound
The specific polyurethane compound used in the manufacturing of wheels significantly affects rolling resistance. Materials with higher rebound characteristics return more energy during the deformation cycle, reducing the overall energy lost to rolling resistance. This results in a faster, more efficient roll. The selection of material is an important piece for rolling resistance.
The factors outlined above underscore the complexity of minimizing rolling resistance in wheels utilized for outdoor skating. Skaters should consider the trade-offs between grip, comfort, and rolling efficiency when selecting their equipment. Optimizing wheel characteristics for the specific skating environment is essential for maximizing performance and minimizing energy expenditure.
7. Abrasion Resistance
Abrasion resistance is a crucial material property influencing the lifespan and performance of wheels used for skating on outdoor surfaces. The abrasive nature of asphalt, concrete, and other external terrains subjects wheels to constant wear, necessitating robust materials capable of withstanding frictional forces.
- Polyurethane Formulation
The specific polyurethane compound used in wheel construction significantly affects its abrasion resistance. Higher-quality formulations, often incorporating additives and specialized polymers, exhibit superior resistance to wear compared to cheaper, less durable materials. The choice of polyurethane formulation is a primary determinant of wheel lifespan when used outdoors.
- Durometer and Wear Rate
While softer wheels (lower durometer) offer enhanced grip, they generally exhibit lower abrasion resistance compared to harder wheels. The softer material deforms more readily under stress, leading to increased surface contact and accelerated wear. Selecting an appropriate durometer involves balancing grip requirements with the need for durability.
- Wheel Profile and Contact Area
The profile of the wheel influences the distribution of pressure across the contact surface. A wider, flatter profile distributes the load over a larger area, potentially reducing localized wear. However, it may also increase overall friction and, consequently, abrasion. The wheel profile should be chosen to mitigate wear while maintaining desired handling characteristics.
- Skating Surface and Debris
The type of skating surface and the presence of debris significantly impact abrasion. Rough asphalt and concrete accelerate wheel wear compared to smoother surfaces. The presence of sand, gravel, and other debris further exacerbates abrasion. Regular wheel maintenance, including cleaning and rotation, can help mitigate these effects.
The multifaceted relationship between abrasion resistance and wheels used for outdoor skating underscores the importance of selecting high-quality components and implementing proper maintenance practices. Optimizing for abrasion resistance ensures prolonged wheel life, consistent performance, and reduced replacement frequency in the demanding conditions of external skating environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common concerns regarding rolling components specifically engineered for external skating environments. Accurate understanding is critical for optimal performance and safety.
Question 1: What durometer rating is appropriate for wheels intended for outdoor use?
For asphalt and concrete surfaces, a durometer rating between 78A and 85A is generally recommended. This range provides a balance between grip and durability, essential for navigating uneven terrain.
Question 2: How does wheel size impact performance on outdoor surfaces?
Larger diameter wheels (70mm-80mm) roll over obstacles more easily and maintain momentum more effectively compared to smaller wheels. However, maneuverability may be slightly reduced.
Question 3: What materials are best suited for manufacturing wheels designed for external skating?
High-quality polyurethane formulations offer the optimal combination of abrasion resistance, rebound, and grip required for the demands of outdoor use. Select premium material.
Question 4: How frequently should wheels used for outdoor skating be rotated?
Rotating wheels regularly, typically every 5-10 skating sessions, promotes even wear and prolongs their lifespan. This practice is particularly important for mitigating the effects of uneven surfaces.
Question 5: Can wheels designed for indoor rinks be used on outdoor surfaces?
While possible, the use of indoor-specific wheels (typically harder durometer) on asphalt or concrete is not recommended. The lack of grip and shock absorption increases the risk of falls and premature wear.
Question 6: What factors contribute to the lifespan of wheels used for outdoor skating?
Lifespan is influenced by several factors, including wheel material, durometer, skating surface, skater weight, and maintenance practices. Regular cleaning and rotation significantly extend wheel longevity.
Appropriate selection and consistent maintenance are paramount for optimizing the performance and lifespan of rolling equipment used on external terrains. This attention mitigates risks and maximizes enjoyment.
The discussion now transitions to a comparative analysis of different rolling stock technologies and their application to specific skating disciplines.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored critical factors influencing the selection and performance of rolling components engineered for skating on external surfaces. Considerations such as durometer, wheel size, polyurethane composition, core design, grip, rolling resistance, and abrasion resistance each contribute to the overall effectiveness and longevity of skate outdoor wheels. The careful evaluation and optimization of these characteristics is paramount for maximizing skater safety, control, and enjoyment in varied outdoor environments.
Ultimately, informed decision-making regarding rolling equipment empowers skaters to confidently navigate the challenges inherent in external terrains. Continued advancements in material science and design will undoubtedly further enhance the capabilities of skate outdoor wheels, pushing the boundaries of performance and expanding the possibilities for external skating disciplines. Prioritizing quality and appropriate selection remains essential for realizing the full potential of this technology.





![Easy Roller! How to Clean Roller Skate Wheels [Guide] How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks Easy Roller! How to Clean Roller Skate Wheels [Guide] | How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks](https://cruzskateshop.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-43-300x200.jpg)
