A visual or tabular reference that provides recommended dimensions for circular components utilized in wheeled footwear. These charts typically correlate the diameter and durometer (hardness) of these components with skating styles, skill levels, and terrain. For example, a chart might suggest smaller, harder components for rink skating and larger, softer components for outdoor or recreational usage.
Accurate selection of these components improves performance, safety, and comfort. Utilizing the appropriate dimensions enhances maneuverability, speed, grip, and vibration absorption, resulting in a more enjoyable and controlled skating experience. Historically, these components were manufactured with limited variations; however, advancements in materials and skating disciplines have necessitated more detailed guidance for optimal selection.
The following sections will elaborate on factors influencing component dimensions, including diameter, durometer, and profile, providing a practical understanding of how these characteristics affect overall skate performance and suitability for specific applications.
Guidance on Selecting Component Dimensions
The selection of appropriate dimensions for circular components utilized in wheeled footwear is crucial. Considerations beyond simply matching existing sizes are warranted to optimize performance and safety. Here are several guiding principles:
Tip 1: Assess Intended Usage: Prioritize the intended skating environment. Indoor surfaces often benefit from smaller diameter, harder components that offer increased maneuverability and control. Outdoor or rough surfaces may require larger diameter, softer components for improved roll and vibration absorption.
Tip 2: Evaluate Skill Level: Beginner skaters may find stability enhanced with wider, lower diameter components. Experienced skaters might prefer narrower, larger diameter components for greater speed and agility.
Tip 3: Consider Durometer Rating: The durometer rating (hardness) significantly affects grip and roll. Lower durometer ratings (softer) provide enhanced grip, particularly on slick surfaces. Higher durometer ratings (harder) offer faster roll and increased durability.
Tip 4: Examine Component Profile: The profile, or shape, of the component influences turning capabilities. A rounded profile promotes smooth turning, while a flatter profile provides increased stability and straight-line speed.
Tip 5: Match All Components on a Skate: Consistency across all components is essential for predictable handling. Mixing components with different durometers or diameters can result in uneven wear and compromised performance.
Tip 6: Regularly Inspect for Wear: Routine inspection is vital. Replace components exhibiting signs of significant wear, such as flat spots or cracks, to maintain safety and performance.
Optimal component dimensions enhance the skating experience, promoting both enjoyment and safety. Careful consideration of these guidelines enables informed decisions regarding component selection and replacement.
The following section will provide a brief overview of different skating disciplines and how dimension selections can be tailored to these specific applications.
1. Diameter (mm)
The dimension, measured in millimeters, represents a primary characteristic detailed within a reference table for wheeled footwear components. This measurement directly influences a component’s rolling efficiency, acceleration, and responsiveness. A larger diameter generally provides greater top-end speed and improved roll-over capability on uneven surfaces. Conversely, a smaller diameter often results in quicker acceleration and enhanced maneuverability. As such, “Diameter (mm)” serves as a critical parameter for determining appropriate components, dependent on the intended skating discipline and user preferences.
The selection of an optimal diameter directly impacts the skater’s performance and experience. For example, aggressive skaters frequently select smaller diameter components (55-60mm) to facilitate tricks and grinds in skate parks. Speed skaters, conversely, often opt for larger diameter components (100-110mm) to maximize speed and maintain momentum over longer distances. Recreational skaters typically choose intermediate diameters (70-80mm) that offer a balance between speed and maneuverability, based on the skating environments and experience level.
The appropriate determination of diameter is crucial when consulting the selection guide. Ignoring the relationship between diameter, intended usage, and skating style can lead to suboptimal performance, reduced safety, and an unsatisfying skating experience. Therefore, a careful examination of the reference table for wheeled footwear, specifically focusing on diameter, enables informed decision-making and promotes both performance and safety.
2. Durometer (A scale)
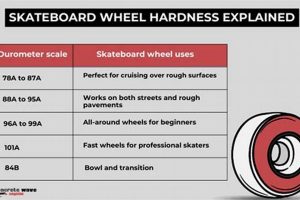
The durometer rating, measured on the A scale, is an integral component of a reference guide for wheeled footwear components. It quantifies the hardness of the material, influencing grip, roll, and wear resistance. A lower durometer rating indicates a softer compound, offering enhanced grip, particularly on slick surfaces. A higher durometer rating signifies a harder compound, promoting faster roll and increased durability. The reference guide incorporates durometer values to provide comprehensive recommendations tailored to various skating styles and environmental conditions. For instance, indoor rink skating often benefits from harder components (88A-101A) to maximize speed, while outdoor recreational skating frequently utilizes softer components (78A-85A) for improved shock absorption and grip on rough terrain. The selection guide would explicitly correlate these durometer ranges with component size and skating discipline to ensure optimal performance and safety.
The relationship between component diameter and durometer rating is significant. Larger diameter components, when combined with softer durometers, are commonly employed for long-distance skating or uneven surfaces, where vibration dampening and consistent roll are paramount. Conversely, smaller diameter components, paired with harder durometers, are favored in aggressive skating disciplines for enhanced responsiveness and durability when performing tricks and grinds. Failure to consider the durometer rating in conjunction with the component size can lead to compromised performance, such as reduced grip on indoor surfaces or excessive vibration and wear on outdoor surfaces. Understanding this interplay is critical for proper component selection.
In summary, the durometer rating, as presented within the reference guide, serves as a key determinant in component selection for wheeled footwear. It dictates grip, roll, and wear characteristics, significantly impacting performance and safety. Careful consideration of the durometer rating, in conjunction with component size and intended usage, enables skaters to make informed decisions, optimizing their skating experience across various disciplines and environments. The absence of this parameter from the reference guide would render it incomplete and potentially misleading, emphasizing the critical importance of the “Durometer (A scale)” within the selection process.
3. Bearing Size (608/627)
Bearing size, designated as either 608 or 627, dictates the compatibility of the bearing with both the axle of the skate and the inner diameter of the circular component. The 608 bearing, with an 8mm inner diameter, represents the industry standard for most inline and roller skate applications. The 627 bearing, featuring a 7mm inner diameter, is less common but may be found in older or specialized skate designs. The component selection reference typically assumes the use of 608 bearings unless otherwise specified. Incompatibility between bearing size and component inner diameter will prevent proper assembly and function, rendering the skate unusable. For example, attempting to install a circular component designed for 608 bearings onto an axle intended for 627 bearings, or vice versa, will result in either a loose fit or an inability to mount the circular component.
Understanding bearing size is critical when replacing circular components. Mismatched bearing and component sizes can lead to unsafe skating conditions, including component wobble, bearing failure, or complete detachment of the circular component from the skate. It is therefore crucial to verify that the intended replacement circular component is compatible with the existing axle and bearing configuration. Certain components are designed to accommodate both 608 and 627 bearings through the use of adapters or spacers; however, this information is typically noted within the component specifications included on the “roller skate wheel size chart”. The correct specification of bearing size is often located on the same reference document as the diameter, durometer, and profile of the circular component.
In conclusion, the correct bearing size is a non-negotiable factor in component selection, as defined by a reference guide. Mismatched bearing sizes lead to immediate functional issues and potential safety hazards. While the 608 bearing represents the prevailing standard, skaters must diligently verify compatibility before purchasing or installing replacement circular components, cross-referencing the reference document to ensure proper fit and function.
4. Profile (Round/Flat)
Component profile, delineated as round or flat, is a critical parameter within the context of a wheeled footwear component reference guide. This geometric characteristic directly influences the component’s contact patch with the skating surface, subsequently affecting maneuverability, stability, and rolling efficiency.
- Round Profile: Enhanced Maneuverability
A round profile exhibits a curved contact surface, enabling smoother transitions and tighter turns. This design facilitates quicker directional changes and is favored in disciplines such as roller derby or artistic skating, where agility is paramount. A “roller skate wheel size chart” will often recommend round profiles for these applications. This configuration sacrifices some straight-line stability for increased responsiveness.
- Flat Profile: Increased Stability
A flat profile presents a wider, more consistent contact surface, providing enhanced stability at higher speeds and improved grip during straight-line skating. This design is commonly preferred for speed skating or recreational skating on varied terrain. Reference materials for wheeled footwear components will typically suggest flat profiles when stability and sustained momentum are prioritized.
- Hybrid Profiles: Balancing Attributes
Hybrid profiles represent a compromise between round and flat designs, seeking to balance maneuverability and stability. These profiles offer a moderate contact patch, providing a blend of responsiveness and grip. A “roller skate wheel size chart” might list hybrid profiles as suitable for general recreational skating or entry-level speed skating, offering versatility across different skating styles.
- Impact on Contact Patch
The profile influences the contact patch; round profiles concentrate force onto a smaller area, enhancing grip at extreme angles, while flat profiles distribute force across a broader area, increasing stability and minimizing wear. This variability requires careful consideration in a reference document, as users rely on the “roller skate wheel size chart” to match the profile to the intended skating style.
The selection of an appropriate component profile is crucial for optimizing skating performance and safety. A comprehensive reference guide for wheeled footwear components will accurately depict the round or flat characteristic and correlate it with specific skating applications, enabling informed decision-making based on individual needs and preferences.
5. Hub Material
Hub material represents a critical, though often overlooked, specification within a reference guide for wheeled footwear components. The composition of the central core significantly influences component performance, durability, and overall skating experience. The material impacts load distribution, energy transfer, and resistance to deformation under stress. Understanding the properties of different hub materials is therefore essential for informed component selection, ensuring compatibility with intended usage and skating style.
- Aluminum Hubs: Rigidity and Power Transfer
Aluminum hubs are characterized by high rigidity and efficient power transfer. This construction minimizes energy loss during acceleration and provides a responsive feel. Aluminum hubs are frequently utilized in high-performance applications, such as speed skating or aggressive skating, where immediate response and precise control are paramount. These hubs typically command a higher price point due to the cost of materials and manufacturing complexity. A “roller skate wheel size chart” may denote aluminum hubs as suitable for advanced skaters seeking maximum performance.
- Nylon/Plastic Hubs: Vibration Dampening and Cost-Effectiveness
Nylon or plastic hubs offer enhanced vibration dampening and a more compliant ride. These materials absorb road imperfections, improving comfort during recreational skating or long-distance cruising. Nylon/plastic hubs are also more cost-effective than aluminum alternatives, making them a common choice for entry-level or recreational components. However, the lower rigidity of nylon/plastic hubs may result in reduced power transfer and a less responsive feel. A reference chart might recommend nylon/plastic hubs for beginner skaters or those prioritizing comfort over performance.
- Composite Hubs: Balancing Rigidity and Compliance
Composite hubs combine different materials, such as reinforced nylon or fiberglass-infused polymers, to achieve a balance between rigidity and compliance. These hubs aim to provide both efficient power transfer and vibration dampening, catering to a wide range of skating styles. Composite hubs often represent a mid-range option in terms of cost and performance, offering a compromise between the extremes of aluminum and basic nylon/plastic hubs. A selection guide may indicate composite hubs as versatile options suitable for various recreational and fitness skating applications.
- Impact Resistance and Durability
The choice of hub material directly affects impact resistance and overall component durability. Aluminum hubs are generally more resistant to deformation under high loads, making them suitable for aggressive skating maneuvers. Nylon/plastic hubs may be more susceptible to cracking or deformation upon impact. The “roller skate wheel size chart” should ideally include information on the material’s impact resistance, allowing skaters to select components that can withstand the demands of their chosen skating discipline.
In summary, hub material is an important specification when referencing a components data sheet. Selecting the proper hub enhances the skating experience, safety, and performance. Different hub types provide a unique feel. All of this must be considered to find a balance in desired skate attributes.
6. Core Design
Core design, within the context of wheeled footwear components, refers to the internal structure of the component, impacting load distribution, rebound characteristics, and overall structural integrity. Its specification within a “roller skate wheel size chart” is crucial, as it directly influences performance attributes, such as grip, speed, and stability. Variation in core design affects the interaction between the bearing, hub material, and outer urethane layer, dictating how forces are transmitted and dissipated during skating. A well-designed core optimizes energy transfer, enhancing the skater’s efficiency and control. For example, a spoked core design can reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity, beneficial in speed skating where minimizing mass is paramount. Conversely, a solid core design may provide increased durability and stability for aggressive skating.
The selection of an appropriate core design, guided by the “roller skate wheel size chart,” requires consideration of skating discipline, skill level, and environmental conditions. A rigid core enhances responsiveness, preferred by experienced skaters seeking precise control. A more flexible core absorbs vibrations, improving comfort for recreational skating on uneven surfaces. The specific core design correlates with component size and durometer, creating distinct performance profiles. Small diameter components with rigid cores are often utilized in aggressive skating for grinds and tricks, while larger diameter components with flexible cores excel in long-distance skating, mitigating road vibrations. This interdependence necessitates a detailed specification on the “roller skate wheel size chart,” enabling skaters to make informed decisions regarding component selection.
In summary, core design is an integral factor impacting component performance and should be explicitly detailed in a comprehensive “roller skate wheel size chart.” Variations in core structure influence energy transfer, weight distribution, and durability, necessitating careful consideration based on skating discipline and individual preferences. Failure to account for core design when selecting components can result in suboptimal performance, reduced safety, and a less enjoyable skating experience. Therefore, a complete reference chart includes precise specifications regarding core materials, geometry, and intended applications, empowering skaters to make informed choices.
7. Skating Style
Skating style dictates the optimal combination of component characteristics detailed on a component selection reference. Each discipline places unique demands on the components, influencing the ideal diameter, durometer, profile, and core design. Aggressive skating, for example, necessitates smaller diameter, harder components for durability and maneuverability during grinds and tricks. Speed skating, conversely, favors larger diameter, harder components to maximize rolling efficiency and maintain high speeds. The reference therefore functions as a crucial tool for aligning component specifications with the specific requirements of the intended skating style. Disregarding this connection results in suboptimal performance, increased component wear, and potential safety hazards.
Recreational skating represents a broad category encompassing diverse terrain and skill levels. Components selection for this style should consider the typical skating environment. Smooth, paved surfaces often benefit from medium-diameter components with moderate durometer ratings, providing a balance between speed and comfort. Rough or uneven surfaces may require larger diameter, softer components to absorb vibrations and maintain stability. Artistic skating prioritizes maneuverability and control, often utilizing smaller diameter components with round profiles to facilitate quick turns and intricate footwork. These examples highlight the importance of tailoring component selection to the nuances of each skating discipline, leveraging the reference as a guide.
Ultimately, skating style serves as the primary determinant when consulting a component selection reference. Understanding the specific demands of each discipline ensures the selection of components that optimize performance, enhance safety, and improve the overall skating experience. Failure to consider skating style can lead to compromised performance, increased risk of injury, and reduced component lifespan. Thus, a clear understanding of skating style is fundamental to the effective utilization of a components selection reference.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common queries regarding dimensions and their impact on skating performance and safety.
Question 1: Why is reference to a components selection document necessary?
A components selection document provides comprehensive information regarding appropriate size, hardness, and profile for various skating styles and skill levels. Proper selection enhances performance, safety, and overall skating enjoyment.
Question 2: What are the consequences of selecting improperly sized components?
Improperly sized components can lead to decreased maneuverability, reduced speed, increased vibration, and a higher risk of falls or injuries. Such components can also experience accelerated wear.
Question 3: How frequently should components be replaced?
Replacement frequency depends on usage, skating style, and terrain. Components exhibiting significant wear, such as flat spots, cracks, or excessive deformation, should be replaced immediately to maintain performance and safety.
Question 4: Can components of different durometers be mixed on the same skate?
Mixing components with varying durometers is generally discouraged, as it can lead to uneven wear, inconsistent handling, and compromised performance. Uniformity in component characteristics is recommended for predictable control.
Question 5: Does components diameter affect skating speed?
Yes, diameter directly influences speed. Larger diameter components generally provide higher top-end speeds, while smaller diameter components offer quicker acceleration. Selection should align with the intended skating style and environment.
Question 6: Is professional consultation recommended for component selection?
While not always necessary, consultation with a knowledgeable skate technician or experienced skater can provide valuable insights, especially for individuals with specialized needs or specific performance goals. Guidance from experts supports optimization and safety.
Proper consideration of component dimension and regular maintenance are crucial for safe and enjoyable skating. Consult a reference document to make an informed decision based on experience, skating environment, and overall goals.
The subsequent section will provide instructions for measuring components dimensions to ensure accurate selections and consistent performance.
Conclusion
The preceding discussion elucidates the critical parameters encompassed within a roller skate wheel size chart. Diameter, durometer, profile, hub material, core design, and bearing size collectively influence performance characteristics and safety considerations. A thorough understanding of these factors enables informed component selection, optimizing the skating experience for diverse disciplines and skill levels.
Adherence to dimensional specifications outlined in a roller skate wheel size chart is paramount. Careful attention to these guidelines ensures proper functionality, reduces the risk of injury, and maximizes the longevity of skating equipment. The information provided serves as a foundation for future exploration and refinement of component technology, ultimately contributing to the advancement of the sport and the safety of its participants.