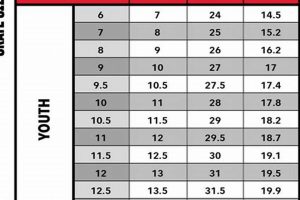
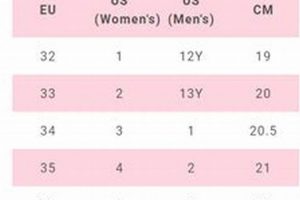
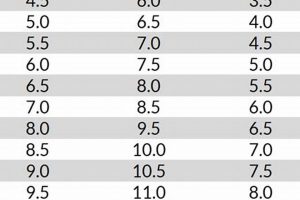
A resource provided by Riedell, this chart correlates foot measurements with suggested skate sizes. It typically outlines foot length and width ranges alongside corresponding skate size recommendations, assisting customers in selecting the appropriate fit for Riedell skates. As an example, a foot measuring 24.5 cm in length and considered “normal” in width may align with a size 6 in a particular Riedell skate model according to the chart.
The importance of accurate skate sizing cannot be overstated. Proper fit impacts performance, comfort, and safety. A chart of this nature aids in minimizing discomfort and preventing injuries often associated with ill-fitting skates. Historically, such sizing guides have evolved alongside advancements in skate design and manufacturing, reflecting a growing emphasis on optimized user experience.
The following sections will delve into the specifics of using these charts effectively, understanding size variations across different Riedell models, and addressing frequently asked questions about obtaining the correct skate fit.
Optimizing Size Selection
The following recommendations aim to improve the accuracy of skate size selection when referencing available resources.
Tip 1: Measure Foot Dimensions Accurately: Employ a calibrated measuring device to determine foot length and width in millimeters or inches. Measurements should be taken while bearing weight to account for foot splay.
Tip 2: Consult Specific Model Charts: Recognize that size designations can vary between Riedell skate models. Always refer to the chart designated for the specific model being considered.
Tip 3: Consider Sock Thickness: Account for the thickness of the socks typically worn while skating. Measurements taken with socks on will provide a more realistic fit estimation.
Tip 4: Compare to Multiple Data Points: Cross-reference foot measurements with both length and width columns. Some individuals may require a wider boot even if length indicates a smaller size.
Tip 5: Allow for Break-in Period: Understand that most skates require a break-in period. Initial tightness may alleviate with use as the boot conforms to the foot.
Tip 6: Seek Expert Advice: Consult with a knowledgeable skate retailer or fitter for personalized recommendations, especially when uncertain about sizing.
Tip 7: Review Customer Feedback: Examine customer reviews and sizing feedback for the specific skate model being considered. This may reveal trends in sizing accuracy or discrepancies.
Adhering to these guidelines promotes a more informed selection process, reducing the likelihood of improper fit and enhancing overall skating experience.
The subsequent section will address the interpretation of specific measurements and the resolution of common sizing dilemmas.
1. Foot Length
Foot length serves as a primary determinant when utilizing resources for Riedell skate sizing. The measurement directly corresponds to the suggested skate size, guiding the initial selection process and influencing subsequent fitting adjustments.
- Direct Correlation to Skate Size
Foot length establishes the baseline for skate size selection according to the chart. A longer foot typically necessitates a larger skate size, and vice versa. For example, a foot measuring 26 cm may correlate with a size 8 in a given model, while a foot measuring 25 cm may align with a size 7. This direct relationship emphasizes the importance of accurate measurement.
- Influence on Boot Selection
Foot length, when considered alongside other factors like foot width, dictates the overall boot selection. Insufficient length can cause toe crowding, leading to discomfort and potential injury. Conversely, excessive length can result in instability and reduced control. Therefore, precise foot length measurement is crucial for identifying an appropriate boot.
- Impact on Performance
Appropriate foot length within the skate boot directly impacts performance. A well-fitted skate enables proper energy transfer and efficient movement. A skate that is too long or too short compromises these factors, hindering the skater’s ability to execute maneuvers effectively. Accurate foot length measurement helps ensure optimal performance.
- Consideration for Growth (Youth Skates)
For young skaters, accounting for growth is a vital consideration. When using the sizing chart, a slight allowance for growth may be factored into the foot length measurement to ensure the skate remains usable for a reasonable period. However, excessive allowance can compromise fit and safety. A balance is necessary.
The correlation between foot length and skate size, as indicated by the size chart, underscores the critical role of precise measurement in achieving optimal skate fit. Ignoring this relationship can lead to discomfort, performance limitations, and potential injuries. Careful consideration of foot length is therefore paramount when selecting Riedell skates.
2. Foot Width
Foot width is a critical dimension when interpreting size charts, directly influencing the comfort and performance of skates. The charts typically present size options based on length, but neglecting foot width can result in improper fit, leading to discomfort, reduced control, and potential injury. Foot width categories, such as narrow, standard, or wide, often correspond to different last shapes used in skate construction. Example: a skater with a foot length aligning with a size 8 on the chart, but possessing a significantly wider foot, may require a size 8 “wide” or even a size 8.5 in the standard width to accommodate the broader forefoot without undue pressure.
An incorrect width selection impacts skating mechanics. A skate too narrow restricts natural foot movement, causing numbness and pain. A skate too wide fails to provide adequate support, reducing stability and increasing the risk of ankle strain. Therefore, proper measurement and consideration of foot width, cross-referenced with model-specific sizing information, are essential steps in ensuring an appropriate fit. Skaters with atypical foot shapes should seek professional fitting advice to identify models that best accommodate their individual needs. The correct width, combined with appropriate length, ensures optimal energy transfer, comfort, and control on the ice or rink.
In conclusion, the effective application of the sizing resource requires careful attention to both foot length and width. While length provides the initial size estimate, width refines the selection, optimizing comfort and preventing performance-limiting issues. The challenges associated with inaccurate width assessment highlight the importance of professional fitting and the limitations of relying solely on length-based size guides. Recognizing the interplay between foot dimensions and skate design is vital for achieving the best possible fit and maximizing the skating experience.
3. Model Specificity
The utility of sizing information is intrinsically linked to model specificity. Skate sizing is not universal across all Riedell products. Each model incorporates distinct design features, including variations in last shape, internal padding, and boot construction, which directly influence the fit. A size 6 in one Riedell model, therefore, is not necessarily equivalent to a size 6 in another. Failure to acknowledge model-specific sizing can lead to significant discrepancies and an ill-fitting skate. For example, a skater accustomed to a size 8 in a recreational Riedell skate may find that a size 8 in a more performance-oriented figure skate model feels noticeably different, requiring either a size adjustment or a period of break-in to achieve a comfortable fit. The importance of consulting the resource tailored to the specific skate model being considered cannot be overstated.
The implications of disregarding model specificity extend beyond mere comfort. An improperly sized skate can negatively impact performance, stability, and overall control. A boot that is too large can result in excessive foot movement within the skate, hindering responsiveness and increasing the risk of injury. Conversely, a boot that is too small can cause discomfort, pressure points, and restricted circulation. Real-world applications of sizing charts highlight this; figure skaters requiring precise control for jumps and spins rely heavily on sizing tailored to specific models optimized for those movements. Similarly, roller derby skaters selecting skates for agility and speed benefit from model-specific guides for a snug, responsive fit.
In summary, the connection between sizing and model variations is fundamental to effective skate selection. Users must recognize that sizing information is not interchangeable across different Riedell skate models. Consulting the correct sizing resource, coupled with accurate foot measurements and, when possible, professional fitting advice, is essential to ensure optimal fit, performance, and safety. Ignoring the model-specific nature of sizing renders the resource largely ineffective and increases the likelihood of an unsatisfactory outcome.
4. Measurement Accuracy
Accuracy in foot measurement is foundational to the effective use of sizing charts. The charts correlate foot dimensions with suggested skate sizes; therefore, any imprecision in measurement directly translates to potential sizing errors. A measurement error as small as a few millimeters can lead to the selection of an incorrectly sized skate, resulting in discomfort, impaired performance, and an increased risk of injury. For example, if foot length is underestimated due to improper measurement technique, the chart may suggest a skate size that is too small, causing toe crowding and discomfort.
The charts are predicated on the assumption of accurate input data. When foot length and width are measured precisely, the chart serves as a reliable guide. However, when measurements are inaccurate, the tool loses its predictive value. Consider a skater whose foot width is overestimated due to measurement error; this may lead to selecting a skate with excessive width, compromising stability and control. Moreover, inconsistencies in measurement units (e.g., using inches when the chart specifies millimeters) can introduce significant sizing discrepancies. The process should also consider the socks that will be worn as they can alter the reading.
In conclusion, the utility of the sizing resource hinges on the fidelity of the input measurements. Inaccurate measurements introduce error into the size selection process, negating the benefits of using the tool. The link between accurate measurement and appropriate skate fit is therefore direct and undeniable. Efforts to improve the precision of foot measurement, through the use of calibrated devices and standardized techniques, are essential for maximizing the effectiveness of sizing charts and ensuring a comfortable and safe skating experience. A lack of meticulous measurements has consequences.
5. Sizing Conversion
Sizing conversion forms an integral component of utilizing skate size charts. It represents the bridge between raw foot measurements and the corresponding skate size designation. The accuracy and proper application of this conversion process are essential for effective skate selection, directly impacting comfort and performance.
- Foot Measurement to Numerical Size
This facet involves translating foot length and width, typically expressed in inches or millimeters, into a numerical skate size. Size charts provide a mapping between measurement ranges and size values, which can vary depending on the model. In the absence of a standardized system across all manufacturers, this conversion is critical for determining the appropriate skate size for a given foot dimension. For instance, a foot measuring 260 mm in length may correspond to a size 8 in one Riedell model, but the same measurement could translate to a different size in another. The need for precise conversion is evident.
- Consideration of Width Designation
Sizing conversion extends beyond length to include width considerations. Feet come in various widths, and skates are often available in narrow, standard, and wide designations. The size charts frequently incorporate width measurements to guide the selection of the appropriate width designation alongside the length-based size. Ignoring width during conversion can lead to an ill-fitting skate, resulting in discomfort or impaired performance. An individual with a foot length indicating a size 7 but possessing a wider foot may require a size 7W (wide) for optimal fit. Width should always be checked.
- Account for Sock Thickness and Type
The sizing conversion process must also account for the thickness and type of socks that will be worn while skating. Thicker socks will increase the effective foot size, potentially necessitating a larger skate size. Conversely, thinner socks will have a minimal impact on the overall fit. The conversion must therefore be adjusted to reflect the anticipated sock thickness to ensure a snug yet comfortable fit. Failing to account for sock thickness can result in a skate that is either too tight or too loose, affecting performance and comfort.
- Model Specificity in Conversion Tables
The conversion from foot measurement to skate size is not universally applicable across all skate models. Variations in last shape and internal padding can influence the fit. Consequently, sizing charts are model-specific, and the conversion must be performed using the chart corresponding to the particular skate model being considered. Using the wrong conversion table can lead to inaccurate sizing and an unsuitable skate. This is an important thing to consider.
The facets of sizing conversion, from numerical size determination to width and sock consideration, directly impact the accurate and effective utilization of size charts. Model-specific conversion tables are essential to ensure that foot measurements translate to the appropriate skate size, maximizing comfort, performance, and safety.
6. Break-in Allowance
Break-in allowance recognizes that newly manufactured skates typically require a period of use for the boot material to conform to the wearer’s foot. This factor interacts with size charts by influencing the perceived fit of the skate immediately after purchase versus after a period of use. Understanding break-in is crucial for interpreting size chart recommendations accurately.
- Initial Fit vs. Long-Term Fit
Initial fit refers to the feel of the skate when first tried on. Size charts often guide selection based on this initial assessment. However, the long-term fit accounts for changes in the skate’s internal dimensions as the boot compresses and molds to the foot during break-in. A skate that feels slightly snug initially may become ideally fitted after break-in, while a skate chosen for immediate comfort may become too loose over time. Figure skaters, for instance, generally accept a tighter initial fit, knowing that the leather boot will eventually mold precisely to their foot, providing crucial support.
- Material Properties and Break-in Time
The composition of the skate boot directly affects the duration and extent of break-in. Leather boots, commonly found in figure and some hockey skates, tend to exhibit a more significant break-in period than synthetic materials. Size charts do not explicitly account for material differences, so users must consider this factor independently. A skate constructed of stiff leather may require several weeks of use to achieve optimal fit, while a synthetic boot may break in much faster. This affects the initial decision.
- Impact on Size Selection
Awareness of break-in allowance influences size selection strategies. Skaters anticipating significant boot molding may opt for a slightly smaller size than initially recommended by the chart to compensate for the eventual expansion of the boot. Conversely, those preferring immediate comfort may choose a size that aligns more closely with their foot measurements, accepting the potential for a slightly looser fit after break-in. Size charts provide a starting point, not an absolute mandate.
- Professional Fitting and Adjustments
Professional skate fitters are trained to assess break-in potential and provide informed recommendations. They can evaluate foot characteristics, boot materials, and the skater’s intended use to guide size selection and predict the extent of break-in. Fitters may also employ techniques like heat molding to accelerate the break-in process and customize the fit. While size charts offer a general guideline, expert assessment refines the selection process.
The interplay between break-in allowance and Riedell skate size charts necessitates a nuanced approach to skate selection. While size charts provide a valuable starting point, users must account for material properties, anticipated break-in, and individual preferences to achieve optimal fit. Professional fitting offers the most personalized and accurate sizing assessment, mitigating the uncertainties associated with break-in allowance.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common queries concerning the interpretation and application of sizing information.
Question 1: How often are the sizing dimensions updated to reflect revisions to the product line?
Product sizing is subject to change as models evolve. It is crucial to consult the resource available on the official Riedell website or from authorized retailers to ensure current dimensions are referenced.
Question 2: What is the procedure for handling discrepancies between foot measurements and size recommendations?
Inconsistencies between measurements and recommendations necessitate careful evaluation. Factors such as sock thickness, foot shape, and individual preferences must be considered. Consulting a qualified skate fitter is advisable.
Question 3: Are the dimensions standardized across all skate types, including figure, roller, and speed skates?
Sizing is not uniform across different skate types. Variations in boot construction and intended use necessitate distinct sizing considerations. Specific resources should be consulted based on the selected skate type.
Question 4: What level of precision is required when measuring foot length and width?
Precision in measurement is paramount. Measurements should be taken in millimeters or fractions of an inch, utilizing a calibrated measuring device. Rounding errors can lead to improper size selection.
Question 5: How does foot swelling influence proper sizing selection?
Foot swelling, which may occur during periods of activity or warmer temperatures, can impact fit. Measurements should be taken under conditions that approximate typical skating scenarios to account for potential swelling.
Question 6: What are the implications of selecting a size based solely on the chart, without professional fitting?
Relying solely on sizing without professional fitting carries inherent risks. Individual foot characteristics and skating style are not accounted for, potentially leading to discomfort, impaired performance, or injury.
It is vital to consider this section of the article carefully, and to consider professional assistance if needed.
The subsequent section provides concluding remarks.
Conclusion
This exploration has underscored the multifaceted nature of the “riedell skate size chart.” Its effective application requires meticulous foot measurement, awareness of model-specific sizing nuances, and consideration of break-in allowance. Sizing resources serve as a valuable guide, yet cannot fully replace the expertise of a professional skate fitter, who can account for individual foot characteristics and skating style. The inherent limitations of relying solely on the resource highlight the need for a balanced approach to size selection.
Optimal skate fit directly influences performance, comfort, and safety. Therefore, users should prioritize accuracy and seek professional assistance when uncertainties arise. Future advancements in skate design and manufacturing may lead to more refined sizing methodologies, but the fundamental principles of careful measurement and individual assessment will remain paramount.