These are a type of rollerblade characterized by a wheel size of 90 millimeters in diameter. This specification directly impacts the skate’s speed, roll efficiency, and ability to handle varied terrain. For example, a skate equipped with these wheels will typically achieve higher speeds compared to skates with smaller wheel sizes, assuming similar bearing quality and skater effort.
The utilization of this wheel size offers a balance between maneuverability and speed, making it a popular choice for fitness skating, recreational use on paved surfaces, and some forms of urban skating. Historically, larger wheel sizes have been associated with speed skating, while smaller sizes catered to aggressive skating. This intermediate size represents a convergence of these design philosophies, offering versatility for a wider range of skating styles. The larger diameter also contributes to improved shock absorption and the ability to roll over small obstacles more easily.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific aspects of these skates, including the optimal contexts for their use, the impact of wheel durometer (hardness), frame construction considerations, and maintenance guidelines to ensure longevity and performance. Understanding these factors enables informed decision-making when selecting appropriate equipment for individual skating needs and goals.
Guidance for Optimal Utilization
The following insights are intended to optimize the experience and longevity of inline skates featuring 90mm wheels. These recommendations cover selection, maintenance, and technique considerations.
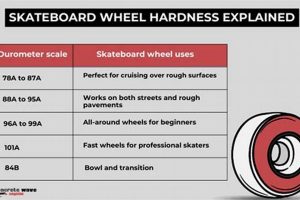
Tip 1: Prioritize Wheel Durometer Based on Skating Surface: Softer wheels (e.g., 82A-85A) provide enhanced grip and shock absorption on rougher surfaces, while harder wheels (e.g., 85A-88A) offer increased speed and durability on smoother surfaces. Evaluate the primary skating environment to determine the appropriate durometer for optimal performance.
Tip 2: Regularly Rotate Wheels to Promote Even Wear: Wheel rotation distributes wear across all eight wheels, extending their lifespan and maintaining consistent rolling performance. Implement a rotation pattern (e.g., crisscross or straight rotation) based on the skate’s frame configuration after every 10-15 hours of use.
Tip 3: Inspect Bearings Periodically and Lubricate as Needed: Clean and lubricate the bearings every 20-30 hours of use, or more frequently if skating in wet or dusty conditions. Use a bearing cleaner and appropriate lubricant designed for inline skate bearings to maintain smooth and efficient rolling.
Tip 4: Ensure Proper Frame Alignment for Optimal Performance: Verify that the frame is securely mounted to the boot and aligned correctly. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear, reduced speed, and increased effort. Consult the skate manufacturer’s guidelines for frame adjustment procedures.
Tip 5: Choose a Frame Material that Aligns with Intended Usage: Aluminum frames offer enhanced stiffness and power transfer for experienced skaters, while composite frames provide increased comfort and vibration absorption for recreational use. Consider the level of skating experience and intended application when selecting a frame material.
Tip 6: Gradually Increase Skating Distance and Intensity: Avoid overexertion and potential injuries by gradually increasing skating distance and intensity. This allows the body to adapt to the demands of skating and minimizes the risk of muscle strain or joint pain.
Tip 7: Utilize Proper Skating Technique for Efficiency and Safety: Employ efficient skating techniques, such as maintaining a low center of gravity and using a smooth, controlled stride. Proper technique reduces fatigue and enhances stability, minimizing the risk of falls.
Adhering to these guidelines will contribute to a more enjoyable and productive skating experience while maximizing the lifespan and performance of inline skates equipped with 90mm wheels.
The following section will address common issues and troubleshooting strategies related to these types of skates.
1. Speed and Efficiency
The relationship between speed and efficiency is a primary consideration in the design and selection of inline skates featuring 90mm wheels. Wheel size, in this context, directly impacts the amount of energy required to achieve and maintain a specific velocity, as well as the attainable maximum speed. Maximizing both requires careful consideration of several interacting factors.
- Wheel Diameter and Rolling Resistance
Larger wheel diameters, such as 90mm, inherently possess a lower rolling resistance compared to smaller wheels. This reduction arises from a smaller deformation area in contact with the skating surface. Consequently, less energy is dissipated as heat due to friction, resulting in greater efficiency and the potential for higher speeds. However, this advantage can be offset by other factors.
- Wheel Durometer and Energy Return
Wheel durometer, measured on the A scale, influences the energy return during each wheel rotation. Harder wheels (e.g., 85A and above) deform less and rebound more efficiently, converting a greater percentage of input energy into forward motion. Softer wheels, while providing better grip on rough surfaces, absorb more energy, reducing overall efficiency and speed. Selecting the appropriate durometer for the intended skating surface is crucial.
- Bearing Quality and Friction Reduction
Bearing quality significantly impacts the rolling efficiency of inline skates. Precision bearings with low friction characteristics minimize energy loss within the wheel assembly. High-quality bearings maintain their performance over time, contributing to sustained speed and efficiency. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and lubrication, is essential to preserve bearing performance.
- Frame Stiffness and Power Transfer
The stiffness of the skate frame plays a critical role in power transfer. A rigid frame efficiently transmits the skater’s energy to the wheels, minimizing energy loss due to frame flex. Frames constructed from materials like aluminum generally offer greater stiffness compared to composite frames. This enhanced power transfer translates into increased speed and efficiency, particularly during acceleration and sustained high-speed skating.
In conclusion, achieving optimal speed and efficiency with inline skates equipped with 90mm wheels necessitates a holistic approach. Factors such as wheel diameter, durometer, bearing quality, and frame stiffness must be carefully considered and balanced to maximize performance and minimize energy expenditure. Understanding these interdependencies allows skaters to make informed equipment choices tailored to their specific needs and skating environments.
2. Maneuverability Balance
The term “maneuverability balance,” when applied to inline skates featuring 90mm wheels, refers to the equilibrium between the skate’s responsiveness to directional changes and its stability at varying speeds. This balance is not inherent solely to the wheel size but is a product of the interplay between wheel diameter, frame length, boot stiffness, and skater skill. The 90mm wheel size presents a particular set of considerations in achieving this optimal balance. A larger wheel, such as 90mm, typically increases the skate’s rolling speed and efficiency on smooth surfaces but can, if not appropriately managed through other design elements, reduce maneuverability compared to skates with smaller wheels. Conversely, an overly short frame paired with 90mm wheels might create excessive agility, sacrificing stability at higher speeds. The importance of achieving this balance is evident in various skating disciplines. Fitness skaters require a degree of maneuverability to navigate pedestrian traffic and changing terrain, while maintaining stability for efficient long-distance skating. Urban skaters need both agility for quick turns and obstacle avoidance, and stability for controlled descents and variable surfaces.
Achieving the desired maneuverability balance frequently involves trade-offs. For example, a shorter frame enhances agility but might compromise stability at higher speeds, requiring greater skater skill to maintain control. Boot stiffness also plays a crucial role; a stiffer boot offers greater responsiveness to skater input but can reduce comfort over longer distances. The skater’s experience level and skating style are also significant factors. A novice skater might prioritize stability and ease of use, while an experienced skater might favor greater responsiveness for executing advanced maneuvers. Frame design also affects maneuverability, with some frames offering adjustable wheel positions to fine-tune the balance between agility and stability. Rockering, where the front and rear wheels are slightly elevated, can significantly enhance maneuverability at the expense of some rolling efficiency.
In summary, maneuverability balance in inline skates equipped with 90mm wheels is a critical performance attribute that requires careful consideration of multiple interacting factors. Wheel size, frame length and design, boot stiffness, and skater skill all contribute to achieving the optimal balance for a given skating application. Understanding these factors allows skaters to select equipment that aligns with their skill level, skating style, and intended use, maximizing both enjoyment and performance. The challenge lies in finding the right combination of components to suit individual needs and preferences, acknowledging that a single “perfect” setup is unlikely to exist. This knowledge is practically significant for both manufacturers in designing balanced skates and for skaters in selecting equipment that matches their specific goals and skill level.
3. Surface Adaptability
The capacity to maintain consistent performance across varying terrains defines surface adaptability in the context of inline skates. Inline skates incorporating 90mm wheels exhibit a particular profile of surface adaptability, attributable to the wheel diameter’s influence on rolling resistance and obstacle negotiation. A larger wheel, such as 90mm, experiences reduced rolling resistance compared to smaller diameters on moderately uneven surfaces. This reduced resistance stems from a shallower angle of attack when encountering surface imperfections, leading to smoother rolling and less energy expenditure. However, the advantages of 90mm wheels regarding surface adaptability are not uniformly beneficial across all conditions. Extremely rough or debris-laden surfaces can negate the benefits of the larger diameter, as the increased wheel size does not inherently improve grip or stability on significantly compromised terrains. For example, skating on a smooth, paved bike path will be notably more efficient with 90mm wheels compared to a heavily cracked or gravel-strewn surface.
The durometer (hardness) of the wheel, in conjunction with its diameter, plays a critical role in determining surface adaptability. Softer wheels (82A-84A) provide enhanced grip and vibration absorption on rougher surfaces, mitigating some of the challenges posed by uneven terrain. However, softer wheels also exhibit increased rolling resistance on smooth surfaces, reducing speed and efficiency. Conversely, harder wheels (85A+) maximize speed on smooth surfaces but offer diminished grip and shock absorption on uneven terrain, potentially leading to instability and reduced control. Frame design also contributes to surface adaptability. Frames with lower profiles enhance stability, particularly when navigating uneven surfaces, while longer frames can provide improved rolling efficiency on smooth terrain. The choice of frame material also influences vibration dampening, with composite frames generally offering better shock absorption compared to aluminum frames. A practical example of the interplay between these factors can be seen in urban skating, where skaters frequently encounter a mix of smooth and rough surfaces. Skaters often opt for wheels with moderate durometer (83A-86A) and frames designed for both stability and maneuverability to effectively manage the varied terrain.
In summary, the surface adaptability of inline skates featuring 90mm wheels is a multifaceted characteristic influenced by wheel diameter, durometer, frame design, and skating technique. While 90mm wheels offer advantages in rolling efficiency on moderately uneven surfaces, these benefits are contingent upon the specific terrain and the integration of complementary design elements. The optimal configuration for surface adaptability involves balancing wheel diameter and durometer to match the predominant skating conditions. Challenges arise when skaters encounter highly variable surfaces, necessitating compromises in wheel hardness and frame design. Understanding these interdependencies is essential for selecting equipment that provides both efficient rolling and stable control across a range of skating environments.
4. Wheel Hardness (Durometer)
Wheel hardness, quantified using the durometer scale (typically the A scale for inline skate wheels), exerts a significant influence on the performance characteristics of inline skates equipped with 90mm wheels. The durometer rating dictates the wheel’s resistance to deformation under load, directly affecting its grip, rolling resistance, and wear rate. For instance, a wheel with a lower durometer rating (e.g., 82A) will deform more readily, resulting in enhanced grip on rough or uneven surfaces, but also increased rolling resistance and a faster rate of wear. Conversely, a wheel with a higher durometer rating (e.g., 88A) will deform less, leading to reduced rolling resistance and prolonged lifespan, but at the expense of grip, particularly on slick surfaces. This trade-off between grip and rolling resistance underscores the importance of selecting a durometer rating that aligns with the intended skating environment and skating style. A skater prioritizing speed and efficiency on smooth, paved surfaces would typically opt for harder wheels, while a skater navigating varied terrain in an urban setting might prefer softer wheels for improved control and comfort.
The interaction between wheel hardness and wheel diameter is particularly relevant for inline skates featuring 90mm wheels. The larger diameter, compared to smaller wheels, inherently reduces rolling resistance and enhances roll-over capability. However, this advantage can be negated if the wheel hardness is not appropriately matched to the surface conditions. A 90mm wheel with a high durometer rating on a rough surface may result in a jarring ride and diminished control, negating the benefits of the larger diameter. In contrast, a 90mm wheel with a lower durometer rating on a smooth surface may feel sluggish and unresponsive, limiting the potential for speed and efficiency. Furthermore, the skater’s weight and skating technique also influence the optimal durometer selection. Heavier skaters or those employing aggressive skating techniques may benefit from harder wheels to prevent excessive deformation and maintain rolling efficiency, while lighter skaters or those with a more relaxed skating style may prefer softer wheels for improved comfort and grip. A practical example involves fitness skaters training for long-distance events on smooth asphalt; they commonly choose 90mm wheels with a durometer rating in the range of 85A-88A to maximize speed and minimize fatigue.
In conclusion, wheel hardness, as measured by durometer, is a critical parameter influencing the performance of inline skates equipped with 90mm wheels. The selection of an appropriate durometer rating requires careful consideration of the skating environment, skating style, skater weight, and the desired balance between grip, rolling resistance, and wheel lifespan. The challenges associated with selecting the optimal durometer stem from the inherent trade-offs between these competing factors, necessitating a compromise that best suits the skater’s individual needs and preferences. A thorough understanding of the relationship between wheel hardness and wheel diameter enables skaters to make informed equipment choices, enhancing their skating experience and maximizing their performance potential.
5. Frame Material Impact
The selection of frame material significantly influences the performance characteristics of inline skates equipped with 90mm wheels. The frame, serving as the structural link between the boot and the wheels, directly affects power transfer, stability, vibration dampening, and overall durability. Disparate materials, such as aluminum alloys and composite polymers, offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, impacting the skating experience in varied ways. For example, an aluminum frame, typically characterized by high stiffness, facilitates efficient power transfer from the skater’s foot to the wheels, resulting in enhanced acceleration and speed. However, aluminum frames tend to transmit more road vibrations, potentially leading to increased fatigue during extended skating sessions. Conversely, a composite frame, generally exhibiting greater flexibility, provides improved vibration dampening and enhanced comfort, but may compromise power transfer, resulting in reduced acceleration and top speed. A skater prioritizing speed and responsiveness might favor an aluminum frame, while one seeking comfort and shock absorption might opt for a composite frame.
The relationship between frame material and wheel size is particularly relevant when considering 90mm wheels. The larger diameter of these wheels generates greater rolling momentum and increased centrifugal forces, placing higher demands on the frame’s structural integrity. A frame constructed from a material with insufficient stiffness may exhibit undesirable flex, compromising stability and control, particularly at higher speeds. The frame’s length and mounting configuration further influence its impact on skating performance. A longer frame provides increased stability, while a shorter frame enhances maneuverability. The mounting system, whether direct-mount or raised, also affects power transfer and vibration dampening. For instance, a raised frame may offer greater shock absorption but might reduce the skater’s feel for the road. Many manufacturers also implement hybrid designs, combining aluminum with composite materials to achieve a balance between stiffness and comfort. A practical example can be found in speed skating, where aluminum frames are nearly ubiquitous due to the emphasis on maximizing power transfer and minimizing energy loss.
In conclusion, frame material selection is a critical determinant of inline skate performance, particularly when combined with 90mm wheels. The trade-offs between stiffness, comfort, and durability necessitate a careful evaluation of the intended skating application and the skater’s individual preferences. Hybrid frame designs represent an attempt to mitigate these trade-offs, offering a compromise between the performance characteristics of aluminum and composite materials. The challenges associated with frame material selection lie in accurately assessing the relative importance of various performance attributes and selecting a material that optimizes the skating experience for the specific intended use.
6. Bearing Maintenance
The operational efficiency of inline skates with 90mm wheels hinges significantly on diligent bearing maintenance. Bearings facilitate the wheel’s rotation around the axle; their condition directly impacts rolling speed, energy expenditure, and overall skating experience. Contamination from dirt, moisture, and debris introduces friction, impeding rotation and necessitating increased effort from the skater to maintain a given speed. Neglecting maintenance results in diminished performance and accelerated wear, shortening the bearings’ lifespan and potentially damaging the wheels themselves. For instance, a skater consistently exposed to wet conditions without proper bearing cleaning and lubrication will likely experience rust formation, leading to stiffness and eventual bearing failure. Such failures necessitate replacement, incurring additional costs and downtime.
Proper bearing maintenance involves several key steps. Regular cleaning removes contaminants, restoring optimal rolling efficiency. This process typically involves disassembling the wheels, extracting the bearings, and using a solvent-based cleaner to dissolve accumulated grime. Following cleaning, thorough drying is essential to prevent rust formation. Lubrication then minimizes friction between the bearing’s internal components, ensuring smooth rotation. A light oil or grease specifically formulated for inline skate bearings is typically used. The frequency of maintenance depends on skating conditions. Skating in dry, clean environments necessitates less frequent maintenance compared to skating in wet or dusty conditions. Furthermore, the quality of the bearings themselves influences maintenance requirements. High-precision bearings often incorporate seals that offer greater protection against contamination, extending maintenance intervals. Routine inspection is also crucial, allowing for early detection of damage or wear, preventing catastrophic failures during use.
In summary, bearing maintenance is an indispensable component of ensuring the longevity and performance of inline skates featuring 90mm wheels. The failure to maintain bearings leads to diminished speed, increased effort, and premature component wear. Adhering to a regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection schedule optimizes rolling efficiency, extends bearing lifespan, and contributes to a more enjoyable and cost-effective skating experience. This practice is particularly critical for skaters who routinely use their skates in adverse environmental conditions or those who demand peak performance from their equipment.
7. Skating Technique
Effective skating technique is paramount when utilizing inline skates equipped with 90mm wheels. The larger wheel size offers advantages in speed and efficiency, but these benefits are fully realized only with proper form and execution. Suboptimal technique can negate the advantages of the equipment and increase the risk of injury.
- Stride Length and Frequency
A longer, more deliberate stride is generally more efficient with 90mm wheels compared to shorter, quicker strides. The larger wheel diameter allows for greater roll per stride, maximizing energy transfer. However, excessively long strides can lead to instability, particularly for novice skaters. Maintaining an appropriate stride frequency, coordinated with the desired speed, is essential.
- Body Positioning and Balance
Maintaining a low center of gravity, with a slight forward lean, enhances stability and control, especially at higher speeds attainable with 90mm wheels. Proper weight distribution over the wheels ensures even wear and optimal grip. Avoiding excessive leaning or twisting of the torso minimizes energy expenditure and promotes efficient skating.
- Arm Swing and Momentum
Coordinated arm swing contributes significantly to momentum and balance. The arms should swing naturally, parallel to the body, and in opposition to the legs. Exaggerated or uncoordinated arm movements waste energy and disrupt balance, particularly during acceleration and turns. A controlled arm swing helps maintain a consistent rhythm and propulsion.
- Edge Control and Turning
Effective edge control is crucial for executing smooth and controlled turns. Leaning into the turn, while maintaining balance and applying pressure to the inside edges of the wheels, allows for efficient directional changes. The larger wheel size necessitates greater attention to edge control to prevent loss of grip and maintain stability, especially at higher speeds.
In summary, skating technique profoundly impacts the performance and safety of inline skates with 90mm wheels. Optimizing stride length, body positioning, arm swing, and edge control maximizes the benefits of the larger wheel size, enabling greater speed, efficiency, and control. Conversely, poor technique can negate these advantages and increase the risk of falls or injuries. Mastering these elements is essential for skaters of all skill levels seeking to fully realize the potential of their equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, maintenance, and performance characteristics of inline skates equipped with 90mm wheels, providing clarity and guidance for informed decision-making.
Question 1: What are the primary advantages of utilizing 90mm wheels on inline skates?
The 90mm wheel diameter offers a balance between speed, roll efficiency, and maneuverability. It enables higher top speeds and improved rolling efficiency compared to smaller wheels, while still maintaining a reasonable level of agility for various skating styles. The increased wheel size also facilitates smoother rolling over minor surface imperfections.
Question 2: How does wheel durometer (hardness) impact the performance of inline skates with 90mm wheels?
Wheel durometer, measured on the A scale, determines the wheel’s resistance to deformation. Softer wheels (e.g., 82A-85A) provide enhanced grip and shock absorption on rougher surfaces, while harder wheels (e.g., 85A-88A) offer increased speed and durability on smoother surfaces. The appropriate durometer selection depends on the intended skating environment.
Question 3: What factors should be considered when selecting a frame material for inline skates with 90mm wheels?
Frame material influences power transfer, stability, and vibration dampening. Aluminum frames offer enhanced stiffness and power transfer for experienced skaters, while composite frames provide increased comfort and vibration absorption for recreational use. The frame’s length and mounting configuration also affect skating performance.
Question 4: How frequently should bearings be cleaned and lubricated on inline skates with 90mm wheels?
Bearing maintenance frequency depends on skating conditions. Clean and lubricate the bearings every 20-30 hours of use, or more frequently if skating in wet or dusty environments. Use a bearing cleaner and lubricant specifically designed for inline skate bearings.
Question 5: What skating techniques are most effective when using inline skates with 90mm wheels?
Efficient skating techniques include maintaining a low center of gravity, employing a smooth, controlled stride, and utilizing coordinated arm movements. Proper edge control is crucial for executing controlled turns, particularly at higher speeds.
Question 6: Are inline skates with 90mm wheels suitable for beginners?
Inline skates with 90mm wheels can be suitable for beginners who possess a reasonable level of balance and coordination. However, smaller wheel sizes may be more forgiving for novice skaters. Prioritize stability and control when learning, and gradually increase wheel size as skills improve.
Selecting and maintaining inline skates with 90mm wheels involves careful consideration of various factors, including wheel durometer, frame material, and skating technique. Addressing these key aspects ensures optimal performance and a safe, enjoyable skating experience.
The subsequent section will delve into common troubleshooting strategies related to inline skates equipped with 90mm wheels, addressing potential issues and providing practical solutions.
Concluding Assessment
The preceding analysis has presented a comprehensive overview of inline skates 90mm wheels, encompassing design considerations, performance characteristics, and maintenance protocols. Emphasis has been placed on the interplay between wheel dimensions, material properties, and skating technique in achieving optimal performance. The exploration highlights the critical role of informed decision-making in equipment selection, aligning component attributes with individual skating requirements and environmental conditions.
Effective utilization of inline skates 90mm wheels necessitates a holistic understanding of the factors discussed. Continued adherence to proper maintenance procedures and skillful execution of skating techniques will maximize equipment lifespan and enhance the overall skating experience. Future advancements in materials science and design may further refine the performance capabilities of these skates, warranting ongoing assessment and adaptation to emerging technologies.


![Easy Roller! How to Clean Roller Skate Wheels [Guide] How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks Easy Roller! How to Clean Roller Skate Wheels [Guide] | How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks](https://cruzskateshop.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-43-300x200.jpg)



