This specialized equipment facilitates movement across ice surfaces, typically employed in recreational or competitive ice skating. The design often incorporates a supportive boot structure attached to a blade, enabling controlled gliding and maneuverability. For instance, individuals participating in ice hockey or figure skating rely on these to perform specific movements and techniques.
The significance of this equipment lies in its ability to enhance performance and safety. A well-designed model can improve energy transfer, providing skaters with greater speed and agility. Historically, advancements in materials and construction techniques have progressively improved the comfort, durability, and performance characteristics of these items, leading to enhanced user experience and reduced risk of injury.
The ensuing sections will delve into the specific features, technical specifications, and comparative advantages of this type of ice skating apparatus, offering a detailed analysis relevant to both casual users and serious athletes.
Tips for Optimal Usage
The following guidelines aim to maximize the performance and longevity of this ice skating equipment, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience. Adherence to these recommendations is crucial for both novice and experienced users.
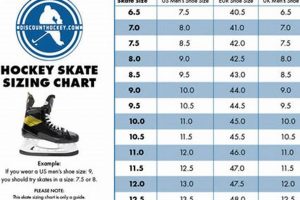
Tip 1: Proper Fit Assessment: Prioritize accurate sizing to prevent discomfort and potential injuries. Foot should be snug but not constricted within the boot. Ensure adequate ankle support.
Tip 2: Blade Maintenance: Regularly inspect the blade for nicks or burrs. Sharpen the blade as needed, typically every 10-20 hours of use, to maintain optimal edge control.
Tip 3: Drying and Storage: After each use, thoroughly dry the boot interior and blade. Store in a well-ventilated area to prevent rust and mildew formation. Use blade guards when not in use.
Tip 4: Lacing Technique: Employ a consistent lacing pattern to provide uniform support. Avoid over-tightening, which can restrict circulation and reduce comfort. Experiment to find the optimal tension for individual skating style.
Tip 5: Ankle Support Adjustment: Some models feature adjustable ankle support. Fine-tune this feature to match individual skating proficiency and desired level of control. Consult a professional if unsure.
Tip 6: Regular Cleaning: Periodically clean the boot exterior with a damp cloth to remove dirt and debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners, which can damage the materials.
Tip 7: Inspect Fasteners: Routinely check all fasteners (e.g., buckles, straps, rivets) for tightness and wear. Replace any damaged or worn components promptly to maintain structural integrity.
Implementing these tips will contribute to enhanced performance, improved comfort, and extended lifespan of the equipment. Consistent maintenance is paramount for safe and effective use.
The subsequent section will explore common issues encountered with this type of skating equipment, along with troubleshooting methods to resolve them effectively.
1. Blade Material
The selection of materials for the blade directly impacts the performance, longevity, and overall suitability of the ice skating equipment. The material properties influence edge retention, resistance to corrosion, and the skater’s control on the ice surface. Understanding these factors is critical for optimal usage.
- Steel Composition and Hardness
Different steel alloys offer varying levels of hardness and resistance to wear. Higher carbon content generally increases hardness but may also affect brittleness. Stainless steel is often preferred for its corrosion resistance, minimizing maintenance requirements and extending the lifespan of the blade. The Rockwell hardness rating provides a quantitative measure of the blade’s resistance to indentation, which is directly related to edge retention. A blade that dulls quickly necessitates more frequent sharpening.
- Edge Retention and Glide Efficiency
The ability of the blade to maintain a sharp edge dictates the skater’s control and responsiveness. Superior edge retention allows for more precise turns, stops, and intricate maneuvers. Glide efficiency, influenced by the blade’s finish and profile, affects the speed and ease of movement across the ice. A polished, well-maintained blade minimizes friction, translating into improved performance. Consider the skill level and skating discipline of the user when evaluating edge retention.
- Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
Exposure to moisture and ice can lead to corrosion, which degrades the blade’s performance and structural integrity. Stainless steel and coated blades offer enhanced protection against rust and pitting. Regular drying and cleaning are essential maintenance practices to prevent corrosion. The selection of a blade material with appropriate corrosion resistance minimizes the effort required for upkeep and extends the equipment’s usable lifespan.
- Impact on Performance Characteristics
The blade material significantly affects the overall feel and performance characteristics. A stiffer blade provides more direct power transfer and enhanced control, while a more flexible blade offers greater responsiveness and maneuverability. The weight of the blade, influenced by the material and design, impacts the skater’s agility and fatigue levels. The interplay between material properties and skating style dictates the optimal choice for individual users.
Therefore, the choice of blade material is a critical decision that balances performance requirements with considerations of durability, maintenance, and cost. Selecting the appropriate material is paramount for maximizing the benefits and ensuring a safe and enjoyable skating experience.
2. Boot Stiffness
Boot stiffness, a critical parameter in ice skating equipment, directly influences performance and control. The rigidity of the boot affects energy transfer, ankle support, and the skater’s ability to execute various maneuvers. An appropriate selection of boot stiffness is paramount for optimizing skating efficiency and minimizing the risk of injury.
- Energy Transfer Efficiency
Stiffer boots facilitate a more direct transfer of energy from the skater’s leg to the blade. This enhances propulsion and acceleration, particularly beneficial for activities requiring bursts of speed, such as hockey. In contrast, a more flexible boot absorbs some energy, potentially reducing power output but increasing comfort. The choice depends on the skater’s priorities: maximizing performance versus prioritizing comfort.
- Ankle Support and Injury Prevention
High boot stiffness provides increased ankle support, reducing the likelihood of ankle sprains and other injuries. This is particularly crucial for beginners or individuals with weaker ankles. However, excessive stiffness can restrict ankle mobility, limiting the skater’s range of motion and potentially hindering certain techniques. A balance between support and flexibility is essential, often achieved through adjustable support systems.
- Control and Responsiveness
Stiffer boots offer enhanced control and responsiveness, allowing for more precise movements and sharper turns. This is advantageous for advanced skaters executing complex routines or navigating tight spaces. Less stiff boots provide increased feel for the ice, enabling subtle adjustments and nuanced movements. The selection should align with the skater’s skill level and desired level of precision.
- Impact on Skating Discipline
Different skating disciplines necessitate varying degrees of boot stiffness. Figure skating often requires stiffer boots for executing jumps and landings, providing the necessary stability and support. Hockey players may prefer slightly less stiff boots for improved agility and responsiveness. Recreational skaters often opt for more flexible boots, prioritizing comfort and ease of use. This highlights the importance of considering the intended application when selecting boot stiffness.
The interplay between boot stiffness and skating performance underscores its significance in optimizing the overall experience. A careful evaluation of individual needs and skating style is essential for selecting the appropriate boot stiffness level, maximizing both performance and safety. Factors such as skill level, skating discipline, and physical condition should be considered when making this critical decision.
3. Ankle Support
Ankle support is a fundamental design parameter in ice skating equipment. It directly influences stability, control, and injury prevention, dictating the skater’s ability to perform movements safely and effectively. The level of ankle support significantly impacts the overall performance characteristics of the equipment.
- Lateral Stability and Control
Adequate lateral support is crucial for maintaining balance and executing precise turns. A boot with insufficient support allows excessive ankle movement, leading to instability and potential falls. Conversely, excessive stiffness can restrict natural movement. The design of the boot should strike a balance, providing firm support while allowing a degree of flexibility. Real-world examples include figure skaters requiring rigid support for jumps and landings, while hockey players benefit from moderate support for agility.
- Energy Transfer Efficiency
Ankle support contributes to efficient energy transfer from the skater’s leg to the blade. A stable ankle allows for a more direct application of force, enhancing propulsion and acceleration. Weak or unstable ankles dissipate energy, reducing power output. The stiffness of the boot, particularly in the ankle region, dictates the degree of energy loss. High-performance models often incorporate advanced materials and construction techniques to maximize energy transfer and minimize wasted effort.
- Injury Prevention Mechanisms
The primary function of ankle support is to protect the ankle joint from excessive stress and strain. By limiting the range of motion, the risk of sprains and other injuries is significantly reduced. This is particularly important for beginners or individuals with pre-existing ankle problems. The effectiveness of the support depends on the design and materials used. Proper lacing techniques and customized fitting further enhance injury prevention.
- Customization and Adjustability
Some models feature adjustable ankle support systems, allowing skaters to fine-tune the level of support to match their individual needs and preferences. This is particularly beneficial for skaters with varying skill levels or those recovering from injuries. Adjustments may include altering the stiffness of the ankle cuff or adding supplemental support pads. Customization ensures a comfortable and secure fit, maximizing both performance and safety.
The integration of effective ankle support mechanisms is a key differentiator among various ice skating equipment models. This critical feature contributes significantly to overall performance, safety, and user satisfaction. A careful consideration of ankle support characteristics is paramount for selecting equipment that meets the specific needs and performance goals of the individual skater.
4. Heat Moldability
Heat moldability, as it pertains to ice skating equipment, represents a manufacturing process that allows for customized fitting through the application of heat. The boot’s materials, typically a composite blend, are designed to become pliable when heated, conforming to the unique contours of the wearer’s foot. This adaptation reduces pressure points, enhances comfort, and improves overall performance. The effectiveness of heat moldability is influenced by factors such as the composition of the boot materials, the uniformity of heat distribution during the molding process, and the skill of the technician performing the procedure. Instances where heat moldability has demonstrably enhanced performance are common in professional skating. For example, a skater with pronation or supination issues may benefit from heat molding, which can create customized arch support. The practical significance lies in the potential to alleviate discomfort and reduce the risk of blisters or other foot-related ailments.
Further analysis reveals that heat moldability is not universally applicable to all models. The success of the molding process is contingent upon the specific materials used in the boot’s construction. Lower-end models may lack the necessary thermoplastic properties required for effective molding, while high-end models often feature advanced composites that offer superior moldability and retention. The molding process typically involves heating the boot in a specialized oven or using a heat gun to target specific areas. After heating, the skater wears the boot while it cools, allowing the materials to conform to their foot’s shape. This process might be repeated for further refinement.
In conclusion, heat moldability serves as a valuable feature for improving the fit and comfort of ice skating equipment. It addresses the inherent variability in foot shapes, allowing for a personalized fit that enhances performance and reduces discomfort. While not all models are heat-moldable, the technology offers a significant advantage when properly executed, leading to a more comfortable and efficient skating experience. Challenges may include uneven heat distribution or material degradation if the process is not performed correctly. The benefits of heat moldability underscore the ongoing efforts to optimize skating equipment for both recreational and competitive use.
5. Blade Radius
Blade radius, an often-overlooked characteristic of ice skating equipment, significantly influences a skater’s maneuverability, speed, and overall feel on the ice. Its relevance to equipment performance stems from its direct impact on edge control and turning capabilities. A clear understanding of its effects is crucial for equipment selection and optimization.
- Definition and Measurement
Blade radius refers to the curvature of the blade along its longitudinal axis, measured in feet. A smaller radius indicates a more pronounced curve, while a larger radius results in a straighter blade profile. This curvature directly affects the blade’s contact area with the ice, influencing grip and glide. Different radii cater to specific skating styles and skill levels. The measurement is typically provided by the manufacturer but can be verified using specialized gauges.
- Impact on Maneuverability
A smaller blade radius facilitates tighter turns and enhanced agility. This is advantageous for figure skaters executing intricate routines or hockey players requiring quick changes in direction. The increased curvature allows for greater edge engagement, enabling precise movements. However, it can also reduce stability at higher speeds. Conversely, a larger radius promotes stability and glide efficiency, ideal for long-distance skating or activities requiring sustained speed.
- Influence on Edge Control
Edge control, the ability to maintain a consistent and predictable grip on the ice, is directly linked to blade radius. A smaller radius provides a more aggressive edge, allowing for sharper turns and powerful stops. This requires greater skill and control to manage effectively. A larger radius offers a more forgiving edge, reducing the risk of unintentional slips or falls. Beginners often benefit from a larger radius, while advanced skaters typically prefer a smaller one.
- Adaptation to Skating Style
The optimal blade radius is contingent upon the individual’s skating style and preferred activities. Figure skaters commonly utilize smaller radii for enhanced agility and precision during jumps and spins. Hockey players often employ intermediate radii, balancing maneuverability with speed and stability. Recreational skaters may opt for larger radii for increased comfort and ease of use. Matching the blade radius to the intended application is essential for maximizing performance and enjoyment.
Understanding the interplay between blade radius and skating performance enables informed equipment selection and customization. While a smaller radius enhances agility and edge control, a larger radius promotes stability and glide efficiency. The optimal choice depends on individual skill level, skating style, and intended use, ultimately influencing the overall skating experience.
6. Liner Comfort
Liner comfort within ice skating equipment is a critical determinant of user experience and performance. It directly affects fit, support, and the reduction of friction, thereby influencing a skater’s ability to perform and the likelihood of discomfort or injury.
- Material Composition and Moisture Management
The materials used in the liner construction significantly impact comfort levels. Common materials include foams (e.g., EVA, memory foam), textiles (e.g., microfiber, nylon), and synthetic leathers. These materials must provide cushioning, insulation, and effective moisture management. Liners that fail to wick away perspiration can lead to discomfort, blisters, and reduced thermal regulation. The optimal material selection balances these factors to maintain a comfortable and dry environment within the boot.
- Anatomical Design and Padding Distribution
Anatomical design ensures the liner conforms to the natural shape of the foot, minimizing pressure points and maximizing contact area. Padding distribution is crucial, with strategic placement of thicker padding in high-impact areas such as the ankle, heel, and forefoot. Ill-designed padding can create localized pressure, leading to discomfort and potential injuries like lace bite. Proper anatomical contouring and strategic padding enhance comfort and support.
- Heat Moldability and Customization Options
Heat moldability allows the liner to be custom-fitted to the individual’s foot shape. This process involves heating the liner and then wearing it while it cools, allowing it to conform to the foot’s unique contours. Customization options, such as removable or adjustable padding, further enhance fit and comfort. These features address variations in foot shape and size, accommodating individuals who may experience discomfort with standard liners. Heat moldability and customization contribute to a more personalized and comfortable fit.
- Seamless Construction and Friction Reduction
Seamless construction minimizes friction between the liner and the foot, reducing the risk of blisters and chafing. Traditional liners with prominent seams can create pressure points and increase friction during repetitive movements. Seamless or strategically placed seams enhance comfort and prevent skin irritation. The inclusion of friction-reducing materials, such as low-friction textiles, further minimizes discomfort and promotes a smoother skating experience.
These aspects of liner comfort, when optimized, contribute significantly to the overall performance and enjoyment of skating. Prioritizing liner comfort during the selection process is paramount for ensuring a comfortable, supportive, and injury-free skating experience.
7. Weight Distribution
Weight distribution, a critical factor in ice skating equipment design, profoundly influences stability, maneuverability, and energy efficiency. In the context of these skates, the position of the skater’s center of mass relative to the blade’s contact point directly affects the ease with which movements can be executed and the stability maintained during complex maneuvers. A poorly balanced skate can lead to inefficient energy transfer, increased fatigue, and a higher risk of falls. For example, if the weight is excessively forward, the skater may experience difficulty maintaining balance during backward skating or stopping. Conversely, excessive rearward weight distribution can hinder forward acceleration and turning efficiency.
The design parameters that influence weight distribution include the blade’s mounting position, the boot’s height and stiffness, and the materials used in construction. Manufacturers often employ advanced modeling techniques to optimize these parameters, aiming to achieve a neutral balance point that enhances the skater’s control and responsiveness. Real-world examples can be observed in the differences between figure skates and hockey skates; figure skates often have a more centered blade position to facilitate spins and jumps, while hockey skates may have a slightly more forward blade position to enhance forward acceleration and agility. Understanding these design choices allows skaters to select equipment that best suits their specific needs and skating style.
In conclusion, the weight distribution characteristics of these skates are essential for achieving optimal performance and safety. By carefully considering the interplay between design parameters and skating technique, manufacturers can create equipment that enhances the skater’s control, efficiency, and overall experience. While individual preferences may vary, a well-balanced skate is a prerequisite for maximizing potential on the ice. Addressing challenges related to weight distribution, such as accommodating different foot sizes and skating styles, remains a key area of ongoing innovation in skating equipment design.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses commonly encountered inquiries regarding the features, maintenance, and performance characteristics of this specific ice skating equipment. The information provided aims to clarify misconceptions and enhance user understanding.
Question 1: What differentiates the blade material from standard ice skates?
The blade is constructed from high-carbon stainless steel, providing enhanced edge retention and corrosion resistance compared to conventional carbon steel blades. This material composition ensures prolonged sharpness and durability, particularly under demanding usage conditions.
Question 2: How does boot stiffness affect skating performance?
Boot stiffness dictates the degree of energy transfer from the skater’s leg to the blade. Stiffer boots facilitate more direct energy transmission, enhancing power and control, while less stiff boots offer greater flexibility and responsiveness. The selection of appropriate boot stiffness depends on the skater’s skill level and intended use.
Question 3: What is the significance of the ankle support system?
The ankle support system provides lateral stability and reduces the risk of ankle injuries. It limits excessive ankle movement, ensuring proper alignment and control during skating maneuvers. The design and adjustability of the ankle support system directly impact the skater’s stability and comfort.
Question 4: What are the benefits of heat moldability in these skates?
Heat moldability allows for a customized fit, conforming the boot to the unique contours of the skater’s foot. This reduces pressure points and enhances comfort, particularly for individuals with non-standard foot shapes. The heat molding process optimizes the fit and reduces the likelihood of blisters or discomfort.
Question 5: How does blade radius influence maneuverability?
Blade radius, the curvature of the blade along its longitudinal axis, affects the skater’s ability to turn and execute precise movements. A smaller radius facilitates tighter turns and enhanced agility, while a larger radius promotes stability and glide efficiency. The selection of appropriate blade radius depends on the skater’s skating style and preferred activities.
Question 6: What maintenance procedures are recommended for optimal performance?
Regular maintenance includes drying the boot interior after each use, inspecting the blade for nicks and burrs, and sharpening the blade as needed. Proper maintenance ensures prolonged equipment lifespan and optimal performance characteristics. Furthermore, blade guards should be used when not in use to prevent damage.
The features, specifications, and maintenance requirements contribute to the overall performance and longevity. Proper care and informed selection are crucial for maximizing their benefits.
The subsequent section will provide comparative analysis with alternative models.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has systematically examined the multifaceted aspects of “tiger ice v2 skates,” encompassing material composition, design parameters, and performance implications. Critical features such as blade material, boot stiffness, ankle support, heat moldability, blade radius, liner comfort, and weight distribution have been meticulously explored to provide a comprehensive understanding of this specialized sporting equipment.
The cumulative insights emphasize the importance of informed decision-making when selecting ice skating equipment. A thorough evaluation of individual needs, skating style, and performance goals, coupled with a careful consideration of the “tiger ice v2 skates” characteristics, is paramount for maximizing potential and ensuring a safe and rewarding skating experience. Continued advancements in materials and design will likely further refine the performance characteristics and expand the application range of this equipment.