Devices combining protective gear with integrated rolling elements are designed to facilitate movement while mitigating impact during activities such as skating. These specialized pieces of equipment often incorporate padding and hard shells to shield vulnerable areas like knees, elbows, and wrists, while small wheels attached to the protector allow for controlled slides or glides during falls, potentially reducing the severity of injuries. For example, a skater might use these on their knees to provide a degree of mobility in case of a fall, allowing them to slide rather than abruptly stop.
The integration of rolling elements within protective equipment offers enhanced safety and maneuverability. Historically, protective gear focused primarily on static impact absorption. The addition of wheels introduces a dynamic element, transforming the energy of a fall into controlled movement. This can be advantageous in preventing sudden stops that might otherwise lead to fractures or sprains. The enhanced mobility also allows for more controlled recovery from unstable positions, contributing to increased confidence and potentially extending the lifespan of the protective gear itself.
Subsequent sections will delve into the specific types, materials, design considerations, and proper usage guidelines relevant to such hybrid protection systems. Furthermore, the following will address their suitability for various skating disciplines and the standards ensuring their safety and performance.
Essential Usage Guidance
The following guidelines are crucial for maximizing the safety and effectiveness of equipment integrating protective padding and rolling elements. Adherence to these points promotes user well-being and extends the lifespan of the gear.
Tip 1: Size and Fit Verification: Ensure the protector size corresponds to the user’s measurements. Overly loose protectors shift during use, compromising protective capabilities. Conversely, overly tight protectors restrict movement and circulation. Consult manufacturer sizing charts for accurate selection.
Tip 2: Secure Fastening Mechanisms: Verify all straps, buckles, or closure systems are properly engaged before each use. Loose or improperly fastened components negate the protector’s intended function. Regularly inspect these mechanisms for wear or damage, replacing components as needed.
Tip 3: Surface Condition Assessment: Prior to using equipment with rolling elements, assess the skating surface for debris, cracks, or unevenness. Such conditions may impede rolling functionality and increase the risk of falls or equipment damage.
Tip 4: Gradual Skill Progression: Users unfamiliar with rolling elements should initially practice on controlled, smooth surfaces. Progress to more challenging environments only after achieving proficiency and confidence in basic maneuvering.
Tip 5: Regular Maintenance and Inspection: Routinely inspect the protector’s padding, shell, and rolling elements for damage. Clean and lubricate rolling elements as specified by the manufacturer. Replace worn or damaged components immediately.
Tip 6: Understanding Limitations: Be aware that protectors incorporating rolling elements are designed to mitigate, but not eliminate, the risk of injury. Operating within one’s skill level and respecting environmental conditions remains paramount.
Tip 7: Appropriate Application: Employ the protectors for their intended skating discipline. Protectors designed for inline skating may not offer adequate protection for skateboarding or aggressive skating maneuvers.
Proper utilization, regular maintenance, and an understanding of the equipment’s capabilities are essential for optimizing the safety benefits offered by such integrated protective systems.
The subsequent conclusion will summarize the key advantages and emphasize the importance of informed decision-making when selecting and using similar protective gear.
1. Impact Energy Management
Impact energy management is a critical performance parameter in the design and function of protective equipment, especially for hybrid systems incorporating rolling elements. Within such “skate protectors with wheels”, the ability to effectively absorb and dissipate kinetic energy generated during a fall directly influences the degree of injury mitigation. Failure to manage this energy adequately can result in force transmission to the body, potentially leading to fractures, sprains, or contusions. The integration of materials with high energy absorption capabilities, such as specialized foams and deformable polymers, is therefore paramount.
Consider a scenario where a skater wearing knee protectors with wheels experiences a fall. Without adequate impact energy management, the force of the impact would be concentrated on the knee joint. Protectors designed with robust energy-absorbing materials, however, can distribute this force over a wider area and reduce its peak magnitude, thereby minimizing the risk of injury. Furthermore, the effectiveness of impact energy management is directly correlated with the protector’s ability to maintain its structural integrity. Repeated impacts can degrade the protective material, reducing its ability to absorb energy and compromising its effectiveness over time. Testing standards exist to evaluate this degradation, ensuring consistent protective performance throughout the product’s lifespan. Proper materials, design and production are crucial.
In conclusion, impact energy management is an inseparable design consideration for effective “skate protectors with wheels”. Its proper implementation hinges on material selection, structural design, and adherence to rigorous testing standards. Improved understanding and advancement in impact energy management directly correlates with improvements in skater safety and injury prevention and this should be always considered when selecting a piece of protective gear. A piece of protective gear without this feature should be out of the question.
2. Rolling Resistance Control
The integration of wheels into protective gear necessitates a precise understanding and control of rolling resistance. Rolling resistance, in this context, refers to the force opposing the motion of the wheels as they move across a surface. This force is influenced by factors such as wheel material, diameter, bearing quality, and the characteristics of the contact surface. Inadequate rolling resistance control can lead to instability and unpredictable movement, potentially increasing the risk of falls rather than mitigating them. For example, wheels with excessively low rolling resistance may cause a protector to slide uncontrollably on a smooth surface, negating the intended protective function. Conversely, wheels with high rolling resistance may hinder necessary movement during a fall, impeding the skater’s ability to regain balance or redirect momentum.
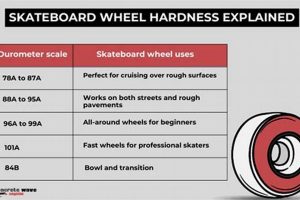
Proper rolling resistance is essential for controlled slides and glides, allowing the skater to dissipate energy gradually during a fall. This controlled movement can reduce the abrupt impact forces that contribute to injuries. The design of the wheel, including its durometer (hardness) and profile, plays a significant role in determining rolling resistance. Softer wheels offer greater grip and higher rolling resistance, suitable for surfaces requiring enhanced control. Harder wheels offer lower rolling resistance, enabling faster speeds and longer slides, but potentially reducing control on certain surfaces. Bearing quality also affects rolling resistance, with higher-quality bearings offering smoother rotation and reduced friction.
Consequently, effective rolling resistance control is a critical engineering consideration in the design of protective equipment with integrated wheels. It requires a careful balance between providing adequate maneuverability and ensuring predictable behavior during a fall. Striking this balance necessitates rigorous testing and material selection to optimize the interaction between the wheels and the intended skating surfaces. In conclusion, adequate rolling resistance control is an indispensable component in protective gears’ with integrated wheels design, and the quality impacts skater’s safety.
3. Ergonomic design
Ergonomic design is paramount in protective gear, particularly when combined with rolling elements. The integration of rolling elements amplifies the need for a design that conforms to the body’s natural movements and reduces the risk of discomfort or restriction, which could compromise performance or increase the potential for injury.
- Range of Motion and Articulation
Ergonomic design emphasizes unhindered movement. Protective gear with integrated wheels must allow for a full range of motion in the joints they are intended to protect. For example, knee protectors should permit adequate flexion and extension without binding or creating pressure points. Restrictive designs can alter a skater’s gait, potentially leading to muscle fatigue or instability.
- Secure and Adjustable Fit
A secure fit is crucial for protective efficacy. Ergonomic designs incorporate adjustable straps, closures, or liners to accommodate individual body shapes and sizes. This ensures the protector remains in its intended position during activity and impact. A loose-fitting protector can shift during a fall, leaving the joint vulnerable or interfering with the rolling element’s function.
- Weight Distribution and Balance
The weight of the protector and its components must be evenly distributed to avoid creating imbalances or strain. Ergonomic design considers the overall weight and its placement relative to the body’s center of gravity. Uneven weight distribution can lead to discomfort, fatigue, and potentially increase the risk of falls, particularly when the rolling elements are engaged.
- Material Selection and Breathability
Ergonomic design takes into account the materials used in construction. Materials should be durable, lightweight, and breathable to minimize discomfort and maximize performance. Breathable materials prevent overheating and moisture buildup, reducing the likelihood of skin irritation or reduced grip. The interface between the protector and the skin is just as important as the outer protection. Material selection impacts comfort, hygiene, and long-term usability.
Ergonomic considerations play a pivotal role in optimizing the safety and performance of “skate protectors with wheels.” A design that prioritizes comfort, range of motion, secure fit, and balanced weight distribution is essential for ensuring the protector functions effectively without hindering the skater’s abilities or increasing the risk of injury. Therefore, Ergonomic design is critical when creating effective skating gear.
4. Durability under stress
The ability of protectors with integrated rolling elements to withstand repeated stresses directly correlates with their effectiveness and longevity. “Durability under stress” encompasses the capacity of the materials and construction to maintain structural integrity and protective capabilities under repeated impacts, abrasions, and environmental conditions. A lack of durability can result in premature failure, rendering the protector ineffective and potentially increasing the risk of injury. For instance, a knee protector whose shell cracks after a few falls offers minimal protection against subsequent impacts. Similarly, if the rolling elements seize or break due to stress, the protector’s intended sliding function is compromised, leading to a higher risk of abrupt stops and related injuries.
The materials used in protectors with wheels significantly impact their durability. High-density plastics, reinforced composites, and durable foams are commonly employed to withstand repeated impacts and abrasions. The quality of the wheels, bearings, and fastening systems also plays a crucial role. Cheap components are prone to failure under stress, jeopardizing the protector’s overall performance. Construction techniques, such as reinforced stitching, robust riveting, and secure bonding, are equally essential. These techniques prevent seams from tearing, components from detaching, and structural elements from failing under stress. Standardized testing protocols, such as those established by ASTM International and the Consumer Product Safety Commission, evaluate durability under simulated use conditions. These tests assess the protector’s resistance to impact, abrasion, and penetration, ensuring it meets minimum safety standards.
In conclusion, “durability under stress” is not merely a desirable attribute but a fundamental requirement for protectors with rolling elements. It ensures that the protector can withstand the rigors of skating, maintain its protective capabilities over time, and provide consistent safety for the user. Manufacturers and consumers must prioritize durability when selecting and using these protectors, understanding that a seemingly minor compromise in this area can have significant consequences for safety and well-being. The long-term benefits of purchasing durable, well-constructed protectors far outweigh the initial cost savings of opting for cheaper, less durable alternatives.
5. Adjustable Securement Systems
The integration of adjustable securement systems within protectors incorporating rolling elements is not merely a convenience, but a fundamental necessity for ensuring safety and efficacy. These systems, typically comprised of straps, buckles, hook-and-loop fasteners, or similar mechanisms, directly influence the protector’s ability to remain correctly positioned during use and impact. A properly adjusted and secured protector can effectively absorb and distribute impact forces, while a loose or improperly fitted protector can shift, exposing vulnerable areas to injury. Consider, for example, a knee protector with wheels that lacks a robust securement system. During a fall, the protector may slide down the leg, leaving the knee joint unprotected and negating the intended safety benefits. Conversely, a well-designed system allows the user to customize the fit, ensuring the protector remains firmly in place, regardless of the skater’s movements.
The effectiveness of adjustable securement systems is further enhanced by their ability to accommodate individual anatomical variations. Skaters come in various shapes and sizes, and a one-size-fits-all approach is inadequate for providing optimal protection. Adjustable systems allow users to fine-tune the fit, ensuring a snug and comfortable feel without restricting movement. The choice of materials and construction techniques also plays a crucial role. Durable straps, buckles, and fasteners are essential for withstanding repeated use and maintaining their integrity over time. Poorly constructed systems may fail under stress, rendering the protector ineffective. The placement of securement points is equally important. Strategically positioned straps can distribute pressure evenly across the protected area, minimizing discomfort and maximizing stability. Furthermore, adjustability facilitates the layering of clothing underneath the protector, allowing for comfortable use in varying weather conditions.
In conclusion, adjustable securement systems are an integral component of protectors incorporating rolling elements, directly impacting their safety and performance. These systems are essential for ensuring a secure and customized fit, accommodating individual anatomical variations, and maintaining the protector’s position during use and impact. Prioritizing the design, materials, and construction of adjustable securement systems is therefore crucial for manufacturers and consumers alike, as a well-designed system can significantly enhance the protector’s effectiveness and contribute to a safer skating experience. The securement system is as important as the wheels and padding, and all three must work together in harmony.
Frequently Asked Questions about Skate Protectors with Wheels
This section addresses common inquiries regarding protectors integrating rolling elements. It aims to provide clarity on their features, usage, and limitations, facilitating informed decision-making.
Question 1: What distinguishes skate protectors with wheels from conventional skate protection?
Traditional skate protection primarily focuses on absorbing impact forces. Protectors integrating rolling elements incorporate wheels to allow for controlled sliding during falls, potentially reducing abrupt stops and associated injuries. The hybrid design aims to convert impact energy into kinetic energy via controlled movement.
Question 2: Are skate protectors with wheels suitable for all skating disciplines?
Suitability varies depending on the specific skating discipline. While beneficial for general skating or recreational activities, these protectors may not offer adequate protection for aggressive skating or high-impact maneuvers. The wheel design may impede certain movements required in specialized skating styles.
Question 3: How does the addition of wheels affect the protector’s impact absorption capabilities?
The integration of wheels can potentially alter the impact absorption characteristics of the protector. However, reputable manufacturers design these protectors to maintain a satisfactory level of impact absorption while providing the added benefit of controlled sliding. Impact energy management depends heavily on materials used and overall design.
Question 4: What maintenance is required for skate protectors with wheels?
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This includes cleaning the wheels and bearings, inspecting for wear and tear, and replacing worn components as needed. Following the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines is essential.
Question 5: Do skate protectors with wheels conform to established safety standards?
Protectors intended for sale are expected to adhere to relevant safety standards. Verifying certification from recognized organizations (e.g., ASTM International) is advisable to ensure the protector meets minimum performance requirements. Buyers should examine the packaging and product information for certification details.
Question 6: What factors should be considered when selecting skate protectors with wheels?
Key considerations include fit, impact absorption capabilities, rolling resistance, durability, and intended use. Assessing reviews, consulting sizing charts, and carefully evaluating product specifications are crucial steps in the selection process. Consider reading expert reviews and recommendations as well.
In summary, protectors integrating rolling elements offer a unique approach to skate safety by combining impact protection with controlled sliding. Understanding their limitations and selecting models that adhere to established safety standards is crucial for maximizing their benefits.
The subsequent article section will discuss real-world applications and case studies related to protective gear integrating rolling elements.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored the multifaceted nature of skate protectors with wheels, underscoring critical aspects such as impact energy management, rolling resistance control, ergonomic design, durability under stress, and the significance of adjustable securement systems. These elements collectively determine the protective efficacy and usability of such equipment. The integration of rolling elements into protective gear represents a departure from traditional static impact absorption methods, introducing a dynamic component that aims to mitigate injury through controlled movement. However, the effectiveness of this approach hinges on careful engineering and adherence to established safety standards.
Ultimately, the selection and utilization of skate protectors with wheels demand a discerning approach. Skaters must prioritize models that offer a balance between impact protection and controlled mobility, while adhering to appropriate safety guidelines and understanding the limitations of the equipment. The ongoing development and refinement of these protective technologies hold the potential to enhance skater safety, but responsible decision-making remains paramount. Continuous research, rigorous testing, and informed consumer choices are essential for ensuring that skate protectors with wheels contribute to a safer and more enjoyable skating experience.





![Easy Roller! How to Clean Roller Skate Wheels [Guide] How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks Easy Roller! How to Clean Roller Skate Wheels [Guide] | How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks](https://cruzskateshop.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-43-300x200.jpg)
