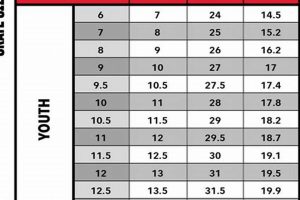
The specified equipment dimension indicates footwear designed for use on ice, with the numerical value representing a standardized foot length measurement. Individuals selecting this particular dimension typically find it corresponds to a specific foot length, generally aligning with a women’s size 10 in US sizing or a men’s size 7. This is a common measurement sought by both recreational and competitive skaters.
Properly fitted footwear is crucial for optimal performance and injury prevention on the ice. Ill-fitting equipment can lead to discomfort, blisters, reduced control, and increased risk of falls. Historically, ensuring accurate fit was a challenge, often requiring in-person fittings. The availability of standardized sizing and online resources has improved accessibility and convenience for consumers.
Subsequent discussions will elaborate on the specific types of equipment available within this dimensional category, including figure, hockey, and recreational models. Further analysis will also consider factors influencing fit beyond the numerical designation, such as foot width and skate boot construction.
Guidance for Selecting Appropriately Sized Ice Skates
The following recommendations are provided to assist in the selection of properly fitting equipment, specifically addressing concerns related to the “ice skates size 8” designation. Adherence to these guidelines can enhance performance and reduce the risk of injury.
Tip 1: Consult Manufacturer Size Charts: Prior to purchase, reference the specific size chart provided by the skate manufacturer. Sizing conventions can vary between brands, and relying solely on general shoe size may result in an improper fit.
Tip 2: Account for Sock Thickness: When measuring foot size, wear the type of socks typically used for skating. This will ensure an accurate measurement that accommodates the added thickness.
Tip 3: Prioritize Foot Length: While width is also a consideration, prioritize matching foot length to the appropriate size designation. Excess space at the toe can compromise control and stability.
Tip 4: Check for Heel Lock: The heel should be firmly locked into the back of the boot. Excessive heel lift can lead to blisters and reduced power transfer.
Tip 5: Assess Ankle Support: The equipment should provide adequate ankle support without restricting movement. Ensure the boot is stiff enough to prevent excessive pronation or supination.
Tip 6: Consider Professional Fitting: If possible, seek guidance from a qualified skate fitter. An experienced professional can assess foot shape and provide personalized recommendations.
Accurate equipment sizing is fundamental for both recreational enjoyment and competitive performance. By following these guidelines, individuals can enhance their skating experience and minimize the potential for discomfort or injury.
Subsequent sections will address the maintenance and care of the equipment, ensuring its longevity and continued performance.
1. Foot Length Standard
The “Foot Length Standard” forms the foundational basis for determining the appropriate “ice skates size 8”. This standard is not merely a numerical label but a precise measurement intended to correlate with the internal dimensions of the skate boot, ensuring a secure and functional fit. Understanding this standard is crucial for optimizing performance and preventing discomfort or injury.
- Mondopoint System
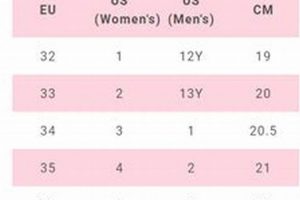
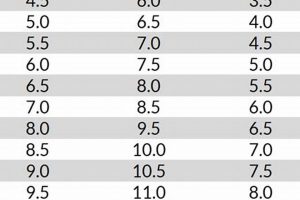
The Mondopoint system is a widely accepted international standard for shoe sizing that directly relates to foot length in millimeters. While not universally adopted by all skate manufacturers, understanding Mondopoint provides a clear reference point. For an equipment designated with an ‘8’, the Mondopoint length typically falls around 263-267mm. This standardized measurement allows for more accurate comparisons across brands, minimizing discrepancies arising from differing regional sizing conventions.
- US and European Sizing Variations
The US and European sizing systems, while commonly used, can present inconsistencies. A US size 8 in street shoes, for example, may not translate directly to an “ice skates size 8” due to differences in manufacturing and intended fit. Furthermore, the conversion between US and European sizes is not always linear. Therefore, relying solely on these systems without consulting a manufacturer’s size chart can lead to improper equipment selection. A European size is usually smaller than the US size for ice skates size 8.
- Brannock Device Measurement
The Brannock device is a specialized tool used for measuring foot length and width. While primarily used in shoe stores, the principles behind its measurement are directly applicable to the selection of properly sized equipment. When using a Brannock device, it is imperative to measure the foot while standing, as the foot tends to elongate under weight. Accurately determining foot length with this device can significantly improve the likelihood of selecting the correct equipment dimensions.
- Allowance for Toe Space
The “Foot Length Standard” does not imply an exact match between foot length and internal boot length. A small allowance for toe space, typically around 0.5 to 1 centimeter, is generally recommended to allow for natural foot movement and prevent toe compression during skating. However, excessive toe space can compromise control and stability. The ideal amount of toe space is a balance between comfort and performance, which is influenced by skater preference.
The various facets of the “Foot Length Standard” underscore its importance in selecting correctly sized equipment. While factors beyond length, such as foot width and arch height, also contribute to overall fit, understanding and adhering to the fundamental “Foot Length Standard” provides a critical starting point. Consistent adherence to this standard across the industry would improve the customer experience and help to improve equipment fit over the long term.
2. Blade Alignment Impact
Blade alignment, intrinsically linked to the fit of “ice skates size 8”, directly influences stability, maneuverability, and the prevention of overuse injuries. Improper alignment can stem from several factors, including incorrect equipment dimensions, boot deformation, or manufacturing defects. When equipment does not accurately reflect the wearer’s foot size, the blade’s position relative to the skater’s center of gravity is compromised. This misalignment results in an uneven distribution of pressure, forcing the skater to compensate, ultimately affecting technique and increasing the risk of ankle strain, knee pain, or hip discomfort. For instance, when the blade is positioned too far inward (varus alignment) or outward (valgus alignment) relative to the skater’s natural stance, it leads to altered biomechanics, disrupting the efficiency of energy transfer during movements like turns and jumps.
Addressing alignment issues in the context of equipment dimension can involve several corrective measures. Custom orthotics can be utilized to support the arch and correct pronation or supination, thereby normalizing the foot’s position within the boot. Blade adjustments, performed by qualified technicians, can reposition the blade to better align with the skater’s anatomical structure. Furthermore, understanding the inherent relationship between blade alignment and skate size emphasizes the importance of professional fitting. An experienced fitter will assess the skater’s biomechanics, identify potential alignment issues, and recommend equipment that minimizes these problems from the outset. Professional fittings minimize the risk of chronic issues stemming from long periods of use.
The impact of blade alignment on skating performance and injury prevention cannot be overstated. Selecting equipment that precisely conforms to foot dimensions represents the first step toward ensuring proper alignment. Continued monitoring of equipment condition and periodic professional assessments are essential for maintaining optimal performance and mitigating the long-term consequences of misalignment. Proper blade alignment is crucial for efficient skating and avoiding injury, making the selection of the correct size 8 important.
3. Boot Stiffness Influence
Boot stiffness is a critical determinant of performance and safety. Its impact is closely tied to the dimensional category of equipment. The rigidity of the boot directly influences ankle support, energy transfer, and the overall responsiveness of the skater. Therefore, the appropriate level of stiffness must be carefully considered when selecting equipment.
- Ankle Support and Stability
Stiffer boots provide enhanced ankle support, limiting lateral movement and reducing the risk of ankle sprains. This is particularly crucial for beginners and skaters performing complex maneuvers, such as jumps and spins. Insufficient support can lead to instability and increased risk of injury. For instance, a skater attempting a double axel in insufficiently stiff equipment may be unable to maintain proper alignment, resulting in a fall. Therefore, it’s imperative to recognize its role for stability.
- Energy Transfer Efficiency
Boot stiffness directly affects the efficiency of energy transfer from the skater’s leg to the blade. A more rigid boot minimizes energy loss through deformation, allowing for more powerful and precise movements. Conversely, a softer boot absorbs more energy, reducing the skater’s ability to generate speed and execute complex maneuvers. Consider a hockey player needing to accelerate quickly; a stiffer boot allows for a more direct transfer of power, leading to faster acceleration.
- Responsiveness and Control
The stiffness of the boot influences the skater’s responsiveness and control. A stiffer boot provides a more direct connection between the skater’s movements and the blade, allowing for more precise turns and edges. A softer boot, while offering greater comfort, may compromise responsiveness, making it more difficult to execute intricate maneuvers. This also allow a more comfort and natural skating for beginner.
- Skill Level and Discipline Considerations
The optimal level of boot stiffness varies depending on the skater’s skill level and the specific discipline. Beginners generally benefit from softer boots, which offer greater comfort and allow for more natural ankle movement. Advanced skaters, particularly those in figure skating or hockey, typically require stiffer boots to provide the necessary support and responsiveness for high-level performance. Competitive skaters may opt for custom-fitted boots with varying degrees of stiffness in different areas to optimize performance.
These components underscores the interplay between equipment dimensions and boot stiffness. Equipment selection should be based not only on foot length but also on the skater’s skill level, discipline, and individual needs. Consulting with a qualified skate fitter is recommended to ensure the appropriate level of stiffness is selected, maximizing both performance and safety. The proper match of foot size and boot stiffness will enhance skater control and prevent injuries.
4. Lacing System Effect
The lacing system on equipment of a specific dimension significantly influences fit, performance, and comfort. The effectiveness of the lacing system directly correlates with the accuracy of equipment dimension. A well-designed system, when applied to correctly sized equipment, provides nuanced adjustability, enabling the skater to customize the fit according to foot shape, skating style, and specific performance requirements. For example, a figure skater may tighten the laces in the lower portion of the boot to enhance ankle stability for jumps while loosening the upper laces for greater flexibility during spins. Conversely, a hockey player might prioritize uniform tightness throughout the boot to maximize power transfer during skating strides.
The lacing system effect is diminished if the equipment dimension is incorrect. If the skate is too large, even a meticulously tightened lacing system cannot compensate for the excess volume within the boot, leading to heel lift and reduced control. Inversely, equipment that is too small will cause excessive pressure on certain areas of the foot, regardless of how loosely the laces are tied. This compromises circulation and can lead to discomfort or even injury. Furthermore, different lacing patterns and materials can affect the overall system effectiveness. Speed lacing systems, for instance, allow for quick adjustments, while traditional laces offer a more precise and customizable fit. The choice of lace material, such as waxed or unwaxed laces, also impacts the lacing system’s ability to maintain tension throughout the skating session.
In conclusion, the lacing system effect is intrinsically linked to the accurate designation of equipment dimensions. When the equipment fits properly, the lacing system serves as a powerful tool for optimizing performance and comfort. However, if the dimensions are incorrect, the lacing system’s effectiveness is severely compromised, potentially leading to diminished performance and increased risk of injury. Understanding this relationship is crucial for selecting the correct equipment and maximizing its benefits.
5. Ankle Support Dynamics
Ankle support dynamics represent a crucial interplay between equipment design and biomechanical function, particularly when considering the dimensional designation. The equipment’s capacity to provide adequate support directly influences stability, control, and injury prevention.
- Boot Height and Stiffness
The height and stiffness of the skate boot are primary determinants of ankle support. A taller boot, extending further up the leg, inherently offers greater stability and resistance to lateral movement. Similarly, a stiffer boot material restricts ankle flexion and extension, limiting range of motion but enhancing support. For instance, figure equipment typically exhibits a higher and stiffer boot construction compared to speed equipment, reflecting the distinct demands of each discipline. A dimensionally incorrect skate will cause improper support.
- Lacing System Integration
The lacing system works in conjunction with the boot structure to modulate ankle support. A well-designed lacing system allows the skater to customize the level of support, tightening or loosening specific areas to accommodate individual foot morphology and skating style. For example, tightening the laces around the ankle joint can enhance stability during jumps, while loosening them can improve flexibility for spins. Inadequate lacing or a poorly designed system compromises the boot’s structural integrity, diminishing its ability to provide effective support.
- Internal Padding and Molding
The internal padding and molding contribute significantly to ankle support by providing cushioning and conforming to the skater’s foot. Properly fitted padding fills gaps between the foot and the boot, minimizing movement and enhancing stability. Heat-moldable boots allow for further customization, molding the internal padding to the unique contours of the skater’s foot, providing a more secure and supportive fit. The skate must be correctly sized.
- Skate Type and Discipline
Ankle support requirements vary significantly depending on the skating discipline. Figure skaters require high levels of ankle support to execute complex jumps and spins, while hockey players prioritize a balance of support and mobility for rapid movements and agile maneuvering. Speed equipment, conversely, often features a lower cut and more flexible boot construction, emphasizing freedom of movement over maximum support. Each discipline can change the type of support needed.
These components demonstrate the multifaceted nature of ankle support dynamics in relation to equipment. Proper equipment selection, considering both size and individual needs, is paramount for optimizing performance and minimizing the risk of injury. Professional fitting ensures precise calibration of these factors, maximizing the benefits of proper ankle support dynamics.
6. Heel Lock Security
Heel lock security, a crucial aspect of properly fitted equipment, directly influences stability, power transfer, and injury prevention. The interaction between the heel and the interior of the skate boot must be secure to ensure optimal performance within the specified dimensional parameters. Any slippage or movement of the heel compromises control and increases the likelihood of blisters or other foot ailments.
- Dimensional Accuracy and Heel Fit
The equipment must precisely correspond to foot length to establish a secure heel lock. Excessive length leads to heel lift, negating the intended design. A properly sized skate will cradle the heel, minimizing movement during skating. For instance, if the heel can be lifted more than a quarter of an inch within the boot, the equipment is likely too large, compromising stability and increasing the risk of blisters. A correctly sized dimension will minimize this issue.
- Lacing System and Ankle Support
The lacing system plays a pivotal role in achieving and maintaining heel lock security. Tightening the laces around the ankle and instep draws the heel firmly into the heel cup, enhancing stability and control. Certain lacing techniques, such as heel-lock lacing, specifically target this area, providing additional security. Failure to adequately tighten the laces or utilizing an ineffective lacing pattern compromises heel lock security, diminishing performance. A dimensionally correct skate is needed.
- Boot Material and Molding
The material composition and molding characteristics of the skate boot contribute to heel lock security. Stiffer materials, such as carbon fiber composites, offer greater support and resistance to deformation, minimizing heel movement. Heat-moldable boots allow for customized fitting, conforming to the unique contours of the foot and heel, further enhancing security. A well-molded boot in the correct dimensions will cup the heel to lock it in.
- Insole and Arch Support
The insole and arch support influence heel lock security by maintaining proper foot alignment within the boot. Custom or aftermarket insoles can correct pronation or supination, stabilizing the foot and preventing excessive heel movement. Inadequate arch support can lead to foot fatigue and reduced heel lock security, particularly during extended skating sessions. In this way the correct dimension is properly supported.
These facets highlight the complex interplay between dimensional accuracy, equipment design, and biomechanical function. Achieving optimal heel lock security requires careful consideration of all these factors, emphasizing the importance of professional fitting and informed equipment selection. A correctly sized skate is the foundation of heel lock security.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding equipment with a specific dimensional designation. These responses aim to provide clarity and inform decision-making.
Question 1: Is “ice skates size 8” equivalent to a standard shoe size 8?
No, a one-to-one correlation does not exist. Equipment sizing often differs from standard shoe sizing. Refer to the manufacturer’s size chart for accurate conversion.
Question 2: What factors, beyond foot length, influence equipment fit?
Foot width, arch height, and ankle circumference significantly impact equipment fit. A professional fitting accounts for these variables.
Question 3: Can equipment designated with “ice skates size 8” be heat-molded for a customized fit?
Some models are designed for heat-molding. Consult the product specifications or a qualified technician for details.
Question 4: How should equipment be maintained to prolong its lifespan?
Blades should be dried immediately after each use. Boots should be stored in a well-ventilated area. Periodic sharpening is also essential.
Question 5: What are the potential consequences of using improperly fitted equipment?
Ill-fitting equipment can lead to blisters, reduced control, ankle instability, and an increased risk of injury.
Question 6: Where can professional equipment fitting services be obtained?
Specialty sporting goods stores, pro shops at skating rinks, and certified skate technicians offer professional fitting services.
Accurate equipment fitting is critical for performance and safety. These answers provide a foundation for informed decision-making. Consulting a professional is recommended.
The next section will cover the differences between figure skates and hockey skates.
Conclusion
This exploration of “ice skates size 8” has highlighted the crucial interplay between dimensional accuracy, biomechanical function, and equipment design. The provided information underscores the necessity of precise equipment selection, taking into account factors beyond mere foot length. Proper fit directly influences stability, control, and the prevention of injuries. It encompasses heel lock security, ankle support dynamics, and the effective utilization of lacing systems.
The diligent application of this knowledge is paramount. Future advancements in manufacturing and fitting technologies promise to further refine the skating experience. Adherence to these principles, coupled with informed decision-making, represents the cornerstone of responsible participation in ice sports. It allows all individuals the opportunity to pursue their skating endeavors with confidence and safety.