The term refers to a specific characteristic of figure skates designed for artistic performance, namely how heavy they are. This is a crucial aspect because the mass of the skate influences an skater’s jump height, spin speed, and overall agility on the ice. For example, a skater transitioning from recreational skates to a more advanced model must consider the weight difference and how it will affect their existing technique.
The significance lies in the balance between performance and comfort. Lighter skates can facilitate more dynamic movements, allowing for higher jumps and faster spins. However, they may also provide less support, requiring stronger ankles and more refined technique. Historically, skate weight has decreased as materials and manufacturing processes have improved, enabling skaters to push the boundaries of what’s possible on the ice, but the “feel” preferred by skaters varies greatly.
Understanding this characteristic allows figure skaters to make informed decisions when selecting equipment, ultimately optimizing their performance and minimizing the risk of injury. The following sections will delve further into the materials, construction, and the fit considerations regarding these skates.
Optimizing Performance with Jackson Artiste Figure Skates
The following guidelines offer advice on choosing and maintaining figure skates, with an emphasis on managing the inherent weight characteristics for optimal performance.
Tip 1: Assess Skill Level. The skater’s proficiency dictates appropriate skate weight. Beginners may prioritize stability over lightness, whereas advanced skaters might benefit from a lighter construction for enhanced agility.
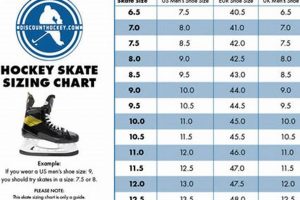
Tip 2: Prioritize Proper Fit. Correct fit is paramount. Ill-fitting skates can compromise performance, increase the risk of injury, and negate any weight advantage. A professional fitting is strongly recommended.
Tip 3: Consider Blade Selection. Blade selection significantly impacts overall weight and performance. Different blades offer varying degrees of rocker and pick configuration, affecting both weight and maneuverability.
Tip 4: Monitor Boot Stiffness. Boot stiffness is directly correlated with support and indirectly with weight. A boot that is too stiff can restrict movement, while one that is too flexible may lack adequate support.
Tip 5: Inspect for Wear and Tear. Regularly examine boots and blades for signs of damage. Excessive wear can compromise structural integrity, altering the intended weight distribution and performance characteristics.
Tip 6: Maintain Blade Sharpness. Sharp blades are crucial for edge control and overall performance. Dull blades require increased force, negating any advantage gained from a lighter skate.
Tip 7: Adjust Lacing Technique. Different lacing techniques can influence ankle support and flexibility. Experimenting with lacing patterns can optimize comfort and performance relative to the skate’s weight.
Selecting appropriate figure skates requires careful consideration of numerous factors, with weight being a key determinant of performance. By following these tips, skaters can make informed decisions and maximize their potential on the ice.
The article will conclude with a summary of best practices for figure skate maintenance and storage.
1. Balance
The equilibrium achieved while skating is inextricably linked to the equipment used, specifically the mass of the figure skate and its distribution. Skates that are too heavy can impede a skater’s ability to maintain balance, particularly during complex maneuvers like spins and jumps. Conversely, excessively light skates may provide insufficient stability, leading to a loss of control. The skater’s center of gravity, in conjunction with the weight of the skates, determines stability on the ice. Any significant change in skate weight will require a recalibration of the skater’s balance to maintain control and prevent falls.
The distribution of weight within the skate is also critical. A skate with a high center of gravity, due to a heavy boot or blade, can increase the likelihood of instability, particularly during landings. Manufacturers carefully design figure skates to optimize weight distribution and lower the center of gravity, thereby enhancing balance and control. For example, the Jackson Artiste series seeks to strike a balance between providing adequate support and minimizing unnecessary mass in the boot and blade, allowing skaters to maintain equilibrium during demanding routines.
Ultimately, the relationship between balance and skate weight is a delicate one, requiring careful consideration of individual skater characteristics and performance objectives. Understanding this interplay enables informed equipment choices, ultimately contributing to improved performance, reduced risk of injury, and enhanced enjoyment of the sport. The impact of weight on balance is not static; as skill level progresses, the skater’s ability to compensate for weight discrepancies improves, allowing for greater equipment customization.
2. Maneuverability
The ease with which a figure skater can execute intricate movements on the ice is directly influenced by the mass characteristics of the skate. Less weight typically translates to enhanced agility. Heavier skates demand greater muscular effort to initiate and control movements. The “Jackson Artiste” line, engineered for developing skaters, aims to strike a balance, minimizing excess mass while maintaining necessary support. This balance is exemplified in the execution of edge work; lighter skates allow for more nuanced adjustments, while a heavier option might provide greater stability during initial learning phases. A skater attempting a complicated turn, such as a bracket or rocker, will find the maneuverability facilitated by a lighter skate beneficial in maintaining flow and precision.
The weight of the skate affects a skater’s ability to perform jumps. A lighter skate requires less upward force to achieve the same height, reducing the overall energy expenditure. Consider the difference between performing a double Axel with a heavier, entry-level skate versus a lighter, more advanced model. The decreased effort required with the lighter skate translates to improved jump height and a lower risk of fatigue. Furthermore, lighter skates allow for faster spin rates. During a spin, a skater rotates their body around a central axis. Less mass reduces the moment of inertia, allowing for faster rotation with less applied torque. This effect is clearly visible when comparing spin speeds between skaters using different skate models; lighter skates often allow for a higher number of rotations per minute.
In summation, a skaters ability to smoothly execute jumps, turns, and spins is demonstrably linked to the weight. The “Jackson Artiste” models specifically address the need for accessible agility for learners. Ultimately, selecting a skate with optimal mass characteristics is a crucial element in maximizing potential and minimizing the physical demands of figure skating, enabling skaters to focus on technique refinement and artistic expression. While lighter skates are generally preferred for enhanced maneuverability, a balance must be struck with the necessary support and stability, especially for skaters who are still developing their core strength and control.
3. Material Composition
The weight of Jackson Artiste ice skates is directly dictated by the materials used in their construction. Each component, from the boot’s outer layers to the blade’s steel composition, contributes to the overall mass. For example, synthetic materials used in the boot often provide a lighter alternative to traditional leather, directly impacting the skate’s total heaviness. Similarly, the density of the steel used in the blade influences its weight and durability. The choice of materials, therefore, becomes a critical design factor in balancing performance requirements and skater comfort.
The type of foam padding inside the boot contributes significantly to the weight. Open-cell foams, while breathable, are typically heavier than closed-cell foams, which offer better insulation and are generally lighter. Similarly, different types of outsoles (e.g., plastic vs. leather) affect the overall mass. A lighter outsole reduces weight but might compromise durability, requiring a trade-off. The way the materials are layered and bonded impacts the total weight and the structural support. The use of lightweight adhesives and efficient manufacturing techniques can further reduce the mass of the final product without sacrificing integrity.
In summary, a skater choosing Jackson Artiste ice skates should be aware of how material choices influence the skate’s weight. Manufacturers continually innovate with new materials and designs to optimize this crucial aspect of skate performance. Understanding these material properties enables skaters to make informed decisions aligned with their skating goals, improving performance and diminishing the risk of injuries. This awareness of the “Material Composition” component enables them to perform to their best ability.
4. Boot Stiffness
Boot stiffness, a measure of a figure skate’s resistance to bending, is intrinsically linked to the total weight of the “ice skates jackson artiste”. Stiffer boots often require more material for reinforcement, leading to increased mass. Conversely, less rigid boots may utilize lighter materials, reducing overall weight but potentially compromising support. A practical example lies in the progression from beginner to advanced skate models; entry-level Jackson Artiste skates, designed for developing skills, typically exhibit less stiffness and weigh less than higher-level models engineered for complex jumps and landings. The relationship is causal: the desired level of support directly dictates the material volume and density needed, influencing the final weight. Understanding this interdependence allows skaters to select equipment suited to their skill level and performance demands.
The practical significance of this understanding extends to injury prevention. Skaters attempting advanced maneuvers with boots that lack sufficient stiffness risk ankle instability and potential injuries. Conversely, using excessively stiff and heavy boots can restrict movement, hindering technique development and increasing fatigue. For instance, a skater transitioning to double jumps may require a stiffer boot for landing stability, but the added weight must be carefully considered to avoid impacting jump height and rotation speed. The choice requires a careful evaluation of the skater’s strength, technique, and the specific demands of their routines.
In summary, the connection between boot stiffness and skate weight is a critical consideration in figure skate selection. While increased stiffness generally implies greater weight, optimizing this balance is essential for both performance enhancement and injury mitigation. Recognizing the cause-and-effect relationship allows for more informed equipment choices, aligning skate characteristics with individual skating needs and performance goals. Future advancements in materials technology may offer lighter, stiffer alternatives, but the fundamental principle of balancing support and weight will remain paramount.
5. Blade Integration
The process of blade attachment to figure skate bootsreferred to as blade integrationdirectly impacts the overall weight and performance characteristics of “ice skates jackson artiste”. The selection of mounting hardware, the method of attachment (screws, rivets, or bonding agents), and the blade’s inherent design contribute to the final weight of the complete skate. Inefficient or overly robust integration methods, while potentially enhancing durability, can unnecessarily increase weight. A poorly integrated blade can also negatively impact balance and stability, regardless of the individual component weights. A real-world example is seen in the transition from entry-level to advanced skates: higher-level models often employ lighter, more streamlined blade integration techniques to reduce overall weight and improve responsiveness. This integration is a critical component of the complete system, because it connects the skater to the ice.
Furthermore, the precision of blade placement during integration significantly influences performance. Misaligned blades can cause improper weight distribution, leading to difficulties in edge control and jump landings. The choice between a traditionally mounted blade and a more modern, contoured sole integration impacts both weight and the skater’s connection to the ice. Manufacturers of “ice skates jackson artiste” strive to optimize blade integration by using lightweight, high-strength materials and precise mounting techniques. This optimization seeks to minimize weight while maintaining structural integrity and ensuring accurate blade positioning. The design and manufacturing are related to the overall functionality of these skates.
In summary, the manner in which a blade is integrated into “ice skates jackson artiste” plays a crucial role in determining the overall weight and performance. Careful consideration of materials, mounting methods, and blade placement is paramount to achieving optimal balance, stability, and maneuverability. Challenges remain in balancing the need for lightweight construction with the demands of durability and precise blade alignment. The integration process contributes to the broader objective of maximizing skater performance and minimizing the risk of injury, reinforcing the importance of a well-designed and executed integration strategy.
6. Skill Level
Skill level serves as a primary determinant in selecting appropriately weighted figure skates. The relationship is not arbitrary; it is governed by the physical demands placed on both the skater and the equipment during increasingly complex maneuvers. Choosing skates that are incongruent with a skater’s ability can impede progress, increase fatigue, and elevate the risk of injury.
- Beginner Skates and Weight Considerations
Entry-level skates prioritize stability and support over agility. Consequently, these skates often feature heavier construction. The added mass provides a more secure feel for novice skaters developing fundamental skills such as basic edges, forward strides, and simple turns. While lighter skates may seem appealing, they can lack the necessary support for developing proper technique, potentially leading to ankle instability and incorrect muscle development. A heavier skate, in this context, can act as a training aid, reinforcing correct posture and edge control.
- Intermediate Skates: Balancing Support and Agility
As skaters progress to intermediate skills, including single jumps and more complex spins, the weight of the skate becomes a more significant factor. Intermediate skates aim to strike a balance between support and agility. The skate’s weight should be light enough to facilitate the execution of jumps and spins, but still provide sufficient ankle support for stable landings. This balance often necessitates a transition to more advanced materials and construction techniques that reduce weight without compromising structural integrity. A skater performing a Salchow jump, for instance, requires a skate that is both supportive and responsive.
- Advanced Skates: Prioritizing Agility and Responsiveness
At the advanced level, skaters performing double and triple jumps, intricate footwork sequences, and complex spins require skates that prioritize agility and responsiveness. These skates are typically constructed from lightweight materials and feature streamlined designs to minimize weight. The emphasis shifts from providing maximum support to facilitating rapid movements and precise edge control. Advanced skaters rely on their well-developed technique and core strength to compensate for the reduced support offered by lighter skates. A skater executing a triple Lutz, for example, needs a skate that is light enough to allow for rapid rotation and precise control during the takeoff and landing.
- Customization and Individual Preferences
While general guidelines exist for skate weight based on skill level, individual preferences and skating styles also play a significant role. Some skaters may prefer heavier skates for their perceived stability, while others may favor lighter skates for their enhanced agility. Factors such as body weight, muscle strength, and skating discipline (e.g., freestyle vs. ice dance) can influence these preferences. Ultimately, the ideal skate weight is a subjective determination that requires careful consideration of both skill level and individual needs. This level of customization is generally seen at more advanced skill levels.
In conclusion, the relationship between skill level and skate weight is a dynamic one, evolving as skaters progress through the stages of development. Selecting the appropriate skate weight is a crucial aspect of optimizing performance, preventing injuries, and maximizing enjoyment of the sport. While general guidelines provide a starting point, individual preferences and specific skating goals should also be taken into account to ensure the best possible equipment choice. The design and quality of “ice skates jackson artiste” should reflect an understanding of these relationships.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the “ice skates jackson artiste weight” and its impact on figure skating performance.
Question 1: Does a heavier skate necessarily equate to lower performance?
No, a heavier skate does not invariably result in diminished performance. For beginner skaters, added weight can enhance stability and support during skill development. However, at advanced levels, excessive weight may hinder agility and jump execution.
Question 2: How does skate weight affect jump height?
Skate weight directly influences jump height. Lighter skates require less force to lift, potentially increasing jump height. However, the benefits of lighter skates are contingent on the skater’s strength and technique.
Question 3: Does skate weight play a role in spin speed?
Yes, skate weight affects spin speed. Lighter skates reduce the moment of inertia, facilitating faster rotation. Conversely, heavier skates require greater effort to initiate and maintain spin speed.
Question 4: Can skate weight contribute to injuries?
Inappropriately weighted skates can increase the risk of injury. Skates that are too heavy can cause fatigue and strain, while those that are too light may provide inadequate support, leading to ankle instability.
Question 5: How does the Jackson Artiste model address weight concerns?
The Jackson Artiste line is designed to balance support and agility, minimizing excess mass while maintaining structural integrity. The specific weight varies depending on the model and size.
Question 6: Should skaters prioritize skate weight over fit and support?
No, skaters should not prioritize skate weight over fit and support. Proper fit and adequate support are paramount for performance and injury prevention. Weight should be considered in conjunction with these factors.
In summary, skate weight is a crucial factor influencing figure skating performance, but it should be evaluated in the context of skill level, individual preferences, and the need for proper fit and support.
The subsequent section will delve into strategies for optimizing skate maintenance to prolong their lifespan and maintain their intended performance characteristics.
Conclusion
This article has explored the multifaceted influence of “ice skates jackson artiste weight” on figure skating performance. Key aspects examined include the relationship between weight and balance, maneuverability, material composition, boot stiffness, blade integration, and skater skill level. A nuanced understanding of these interdependencies is crucial for informed equipment selection and optimized athletic outcomes. The interplay between these factors dictates the appropriateness of any particular skate model for a given skater and discipline.
Consideration of skate weight, in conjunction with proper fit and structural support, remains paramount for both performance enhancement and injury prevention. Continued advancements in materials science and manufacturing processes will undoubtedly lead to lighter, more responsive figure skates. However, the fundamental principles outlined herein will endure, guiding skaters and coaches in the pursuit of excellence. Further research into the biomechanics of skating, combined with data-driven equipment analysis, promises to refine the art and science of skate selection in the years to come.