Equipment designed for young individuals participating in roller hockey or recreational skating, manufactured by Bauer, constitutes an important segment within the sporting goods market. These products are specifically engineered to accommodate the developing anatomy of children and adolescents, offering support and protection during use. Such specialized equipment facilitates the safe engagement in physical activities that require agility and maneuverability.
The value of appropriate sporting equipment cannot be overstated. It enhances performance, reduces the risk of injury, and fosters a positive experience for the user. The historical evolution of such gear demonstrates a continuous refinement of design and materials, driven by advancements in biomechanics and material science. This progress enables manufacturers to create products that better meet the needs of young athletes.
The following sections will delve into the specific features, size considerations, and maintenance protocols relevant to selecting and caring for such products. Focus will also be directed to the target age range and skill level, helping consumers make informed decisions when acquiring this type of equipment.
Guidance for Selecting Youth Inline Skates
The selection process for youth inline skates requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure the safety and performance of the young skater. Adherence to the following guidelines can assist in making an informed purchasing decision.
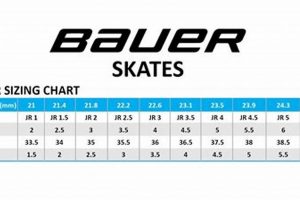
Tip 1: Size Accuracy: Precise fitting is paramount. Ensure the skates conform to the skater’s foot dimensions, leaving minimal space for movement within the boot. Utilize manufacturer-provided sizing charts to correlate foot length with appropriate skate size.
Tip 2: Ankle Support Evaluation: Examine the level of ankle support provided by the skate. Adequate support is crucial for stability and injury prevention, particularly for novice skaters. The ankle cuff should be rigid enough to resist excessive lateral movement.
Tip 3: Wheel Hardness Assessment: Wheel hardness, measured on the durometer scale, should be appropriate for the skating surface. Softer wheels offer greater grip on rough surfaces, while harder wheels provide increased speed on smoother surfaces. Consider the typical skating environment when selecting wheel hardness.
Tip 4: Frame Material Inspection: The skate frame, typically constructed from aluminum or composite materials, should be sufficiently durable to withstand the stresses of skating. Aluminum frames generally offer greater stiffness and responsiveness, while composite frames may provide enhanced comfort and vibration dampening.
Tip 5: Closure System Verification: The closure system, comprising laces, buckles, and/or straps, should provide a secure and adjustable fit. Ensure that the closure system is easy to operate and maintain. Proper closure prevents foot slippage within the boot.
Tip 6: Bearing Quality Consideration: Bearing quality, rated on the ABEC scale, influences the smoothness and speed of the wheels. Higher ABEC ratings generally indicate greater precision and lower friction. While higher-rated bearings may enhance performance, they are not always necessary for recreational skating.
Tip 7: Brake Inspection: Confirm the presence of a functional brake system, typically located on the heel of one skate. Ensure that the brake pad is in good condition and that the brake is properly adjusted for effective stopping power. Regularly inspect and replace the brake pad as needed.
Selecting the correct size, evaluating ankle support, assessing wheel hardness, inspecting frame material, verifying the closure system, considering bearing quality, and inspecting the brake are critical elements for a safe skating experience. Prioritize these factors to mitigate the risk of injury and maximize enjoyment.
Following the guidance presented in this section will contribute to an informed purchasing decision. The subsequent sections will explore maintenance and care recommendations, ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of the skates.
1. Proper Sizing
Proper sizing is a non-negotiable element in the context of youth inline skates. Ill-fitting skates present a spectrum of negative consequences, ranging from compromised performance to heightened injury risk. Precise sizing aligns the skater’s foot dimensions with the internal geometry of the skate boot, ensuring optimal control and comfort. Discrepancies in size undermine these factors and create a cascade of potential problems.
- Foot Measurement Accuracy
Accurate foot measurement is the initial step. Length and width should be determined using a calibrated measuring device, ideally while the child is standing, to account for foot expansion. This measurement then needs to be cross-referenced with the manufacturer’s sizing chart specific to inline skates. Generics sizes can lead to misfit.
- Internal Boot Volume
The internal boot volume needs to comfortably accommodate the foot without excessive pressure or looseness. Pressure points can lead to discomfort, blistering, and numbness, while excessive space reduces responsiveness and increases the likelihood of ankle instability. A properly sized boot distributes pressure evenly across the foot.
- Sizing Discrepancies and Growth
Children’s feet grow rapidly. While it may be tempting to purchase skates a size or two larger to extend their usability, this practice is strongly discouraged. Oversized skates compromise control and increase the risk of falls and ankle sprains. Regularly check the fit and replace skates when necessary.
- Impact on Performance
The connection between foot and skate determines the efficiency of power transfer. Loose-fitting skates reduce this efficiency, making skating more tiring and less responsive. Snug, but not overly tight, skates maximize the skater’s ability to control movement and execute maneuvers with precision.
The implications of proper sizing for youth inline skates transcend mere comfort. It directly influences safety, performance, and the overall enjoyment of the sport. Adherence to accurate measurement protocols and a commitment to replacing skates as the child’s foot grows are essential for ensuring a positive and safe skating experience.
2. Ankle Support
Ankle support is a critical determinant in the safety and performance characteristics of inline skates designed for youth. Its influence spans stability, injury prevention, and the development of proper skating technique. Therefore, it requires meticulous consideration during the equipment selection process.
- Lateral Stability Provision
Inline skates inherently challenge lateral stability due to the in-line wheel configuration. Adequate ankle support, provided by a rigid or semi-rigid boot cuff, mitigates this instability. It reduces the propensity for ankle roll and minimizes the effort required to maintain balance. This is especially crucial for developing skaters who have not yet developed the necessary muscle strength and proprioception.
- Injury Mitigation
Ankle sprains are a common injury in inline skating. Strong ankle support can significantly reduce the risk of these injuries by limiting excessive ankle movement during falls or uneven terrain encounters. The cuff acts as a protective barrier, preventing the ankle joint from exceeding its range of motion, thus minimizing ligament strain.
- Technique Development Facilitation
Proper ankle support aids in the development of correct skating technique. By stabilizing the ankle joint, it allows young skaters to focus on other aspects of skating, such as stride mechanics and balance, rather than constantly compensating for ankle instability. This contributes to efficient skating and reduces fatigue.
- Boot Cuff Design Variance
The design and materials used in the boot cuff directly impact the level of ankle support provided. Higher cuffs generally offer greater stability but may restrict ankle mobility. Softer, more flexible cuffs allow for a greater range of motion but may compromise support. The optimal cuff design is a balance between stability and flexibility, tailored to the skater’s skill level and skating style.
Consequently, the interplay between ankle support and skill development is vital in bauer inline youth skates. A properly designed skate offers a balance, allowing young skaters to learn and improve their skating technique while reducing the potential for injury. The evaluation of ankle support should, therefore, be a primary focus when choosing such equipment.
3. Wheel Durometer
Wheel durometer, a measure of a wheel’s hardness, holds significant relevance in the context of inline skates designed for youth, influencing grip, speed, and durability, and ultimately shaping the skating experience.
- Grip and Surface Interaction
Wheel durometer dictates the level of grip afforded by the wheel on varying surfaces. Softer wheels, characterized by lower durometer ratings (e.g., 74A-78A), exhibit greater deformation upon contact, enhancing grip, particularly on rough or uneven surfaces. This is beneficial for young skaters learning basic maneuvers, where stability is paramount. Harder wheels (e.g., 82A-85A), on the other hand, offer less grip but lower rolling resistance, resulting in increased speed on smooth surfaces, suitable for more experienced skaters.
- Speed and Rolling Resistance
The interplay between wheel durometer and rolling resistance directly impacts a skater’s speed. Softer wheels, while providing superior grip, exhibit higher rolling resistance due to increased deformation. This translates to slower speeds and greater energy expenditure. Conversely, harder wheels minimize deformation, reducing rolling resistance and enabling higher speeds, albeit at the expense of grip. Youth skaters transitioning to more advanced techniques may benefit from harder wheels to capitalize on speed potential.
- Durability and Wear Rate
Wheel durometer influences the wheel’s resistance to wear and tear. Softer wheels, due to their pliable nature, tend to wear down more rapidly, particularly on abrasive surfaces like asphalt. Harder wheels, being more resistant to deformation, exhibit greater durability and a slower wear rate. However, harder wheels may be more susceptible to cracking or chipping upon impact with obstacles. The intended skating environment and frequency of use should inform the selection of an appropriate durometer rating.
- Vibration Absorption and Comfort
Softer wheels provide superior vibration absorption, enhancing comfort, particularly on rough surfaces. The increased deformation of the wheel cushions the skater from vibrations transmitted from the ground. Harder wheels, conversely, transmit more vibration, potentially leading to discomfort or fatigue, especially during extended skating sessions. For recreational skating or beginner skaters, a softer wheel durometer may enhance the overall experience.
Considerations of wheel durometer are crucial in selecting suitable Bauer inline youth skates. Matching wheel hardness to the skater’s skill level, skating environment, and desired performance characteristics optimizes safety, comfort, and enjoyment.
4. Frame Material
The frame material employed in the construction of Bauer inline youth skates directly influences the skate’s weight, durability, and power transfer efficiency. The choice of material, typically either aluminum or a composite polymer, determines the skate’s overall performance characteristics and suitability for different skill levels and skating styles. A more rigid frame material, such as aluminum, enhances power transfer from the skater’s foot to the wheels, resulting in increased speed and responsiveness. However, aluminum frames tend to be heavier and may transmit more vibrations, potentially impacting comfort. Composite frames, on the other hand, offer a lighter weight and improved vibration dampening but may compromise power transfer efficiency. For instance, a young, recreational skater may benefit from the comfort and lighter weight of a composite frame, while a competitive roller hockey player might prioritize the responsiveness and power transfer of an aluminum frame.
The frame’s structural integrity also dictates its ability to withstand the stresses of skating, particularly impacts and torsional forces. Aluminum frames generally exhibit greater resistance to deformation under stress, ensuring consistent performance over time. Composite frames, while durable, may be more susceptible to cracking or breaking under extreme conditions. Furthermore, the frame’s design, including its length and wheel configuration, affects the skate’s maneuverability and stability. Shorter frames provide greater agility, while longer frames enhance stability at higher speeds. Frame adjustability, a feature found in some higher-end models, allows skaters to fine-tune the skate’s handling characteristics to their individual preferences.
In summary, the frame material is a critical component of Bauer inline youth skates, impacting weight, durability, power transfer, and overall performance. Selecting the appropriate frame material requires careful consideration of the skater’s skill level, skating style, and the intended use of the skates. While aluminum frames offer superior performance for experienced skaters, composite frames may provide a more comfortable and forgiving option for beginners. Understanding the properties of different frame materials empowers consumers to make informed purchasing decisions that optimize their skating experience.
5. Closure System
The closure system within inline youth skates plays a vital role in securing the foot within the boot, directly influencing comfort, performance, and safety. Inadequate closure can lead to slippage, instability, and an increased risk of injury, while a well-designed system ensures proper foot containment and support. This is particularly critical for youth skates, as children’s feet are still developing, making them more susceptible to injury if not properly supported. A poorly designed closure system translates to a loss of power transfer, causing wasted effort and reducing maneuverability, while a secure closure maximizes control and responsiveness. For example, a skate with laces alone may allow for uneven pressure distribution and potential loosening during use, whereas a combination of laces, buckles, and straps offers a more customizable and secure fit.
Different closure systems offer varying levels of adjustability and security. Laces provide a fine-tuned fit across the entire foot but can be time-consuming to adjust and may loosen during extended use. Buckles offer a quick and easy method for securing the upper part of the boot, providing a secure fit with minimal effort. Power straps, often positioned across the instep, enhance heel lock and prevent forward movement of the foot within the boot, contributing to improved stability and power transfer. The optimal closure system often combines these elements to achieve a balance of adjustability, security, and ease of use. For instance, skates featuring a combination of laces for fine-tuning the fit around the forefoot, a buckle for securing the ankle, and a power strap for heel lock often provide the most comprehensive and effective closure.
Understanding the connection between the closure system and overall skate performance is paramount. It allows consumers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and skating style. Choosing a skate with a closure system that offers a secure, adjustable, and comfortable fit minimizes the risk of injury and maximizes the enjoyment of skating. Moreover, regular maintenance of the closure system, including checking laces for wear and tear, ensuring buckles are functioning properly, and replacing straps as needed, is essential for maintaining its effectiveness and prolonging the life of the skates. Ultimately, the closure system is an integral component of inline youth skates, deserving careful consideration to ensure a safe and positive skating experience.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Bauer Inline Youth Skates
This section addresses common inquiries pertaining to Bauer inline youth skates. The information provided aims to clarify key aspects related to selection, usage, and maintenance, fostering informed decision-making.
Question 1: What criteria should guide the selection of an appropriate size?
The selection process should prioritize accurate foot measurement, utilizing a calibrated device to determine both length and width. The resultant measurements must then be compared against the manufacturer’s specific sizing chart for the skate model in question. Allowance for growth should be minimal, as oversized skates compromise control and safety.
Question 2: How does wheel durometer affect performance?
Wheel durometer, measured on the “A” scale, influences grip, speed, and durability. Softer wheels (lower durometer) provide enhanced grip but reduced speed and durability. Harder wheels (higher durometer) offer increased speed and durability at the expense of grip. The selection should align with the skater’s skill level and the intended skating surface.
Question 3: What level of ankle support is recommended?
The optimal level of ankle support balances stability and mobility. Beginner skaters benefit from stiffer cuffs that provide greater stability and reduce the risk of ankle injuries. More experienced skaters may prefer more flexible cuffs that allow for a greater range of motion. Regardless of skill level, the ankle should be adequately supported to prevent excessive pronation or supination.
Question 4: How often should the wheels be rotated or replaced?
Wheel rotation is recommended regularly to ensure even wear. The frequency of rotation depends on skating frequency and surface conditions. Uneven wear patterns indicate the need for rotation. Wheel replacement is necessary when the wheels are significantly worn down or exhibit damage that compromises performance and safety.
Question 5: What are the key maintenance procedures for bauer inline youth skates?
Routine maintenance includes cleaning the skates after each use, inspecting the wheels and bearings for damage, lubricating the bearings periodically, and ensuring the closure system is functioning properly. Promptly addressing any issues prevents further damage and prolongs the life of the skates.
Question 6: Are there specific safety gear requirements?
The use of appropriate safety gear is strongly recommended. This includes a properly fitted helmet, wrist guards, elbow pads, and knee pads. Protective gear significantly reduces the risk of injuries in the event of a fall.
In summary, informed selection, diligent maintenance, and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial for maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks associated with using such products. This contributes to a safer and more enjoyable skating experience.
The subsequent section will address advanced considerations for the selection and use of these skates, building upon the foundational knowledge presented here.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis of “bauer inline youth skates” has underscored the critical interplay between equipment design, safety considerations, and skater development. The optimal selection necessitates a detailed understanding of sizing protocols, support structures, wheel durometer characteristics, and closure system mechanisms. These elements, when properly addressed, contribute significantly to a young skater’s ability to learn and progress safely.
Continued advancements in materials science and biomechanical engineering will likely drive future refinements in skate design. Stakeholders are encouraged to prioritize safety and informed decision-making to maximize the benefits and minimize potential risks associated with participation in inline skating. Diligence in equipment selection and maintenance remains paramount for fostering a positive and secure sporting experience.