Equipment designed for young, developing athletes in the sport of roller hockey or recreational skating is manufactured by Bauer, a company known for its ice hockey equipment. These products provide mobility and support, specifically engineered to fit the smaller foot size and lower body weight of younger users. The design incorporates features such as adjustable sizing, padded liners for comfort, and durable chassis for stability.
Properly fitted equipment enhances the skating experience for younger individuals by improving agility, control, and confidence. This specialized equipment offers protection against impacts and abrasions, contributing to safety during use. Historically, this type of equipment has evolved from basic roller skates to incorporate advancements in materials and engineering, resulting in improved performance and user experience.
The following sections will delve into the specific features, benefits, and considerations associated with selecting appropriate equipment of this type, including sizing guidelines, maintenance practices, and safety recommendations. Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring a positive and safe skating experience for young individuals.
Selection and Usage Guidance
The following provides essential guidance to ensure appropriate selection and proper usage of youth-specific inline skates, thereby optimizing performance and safety during use.
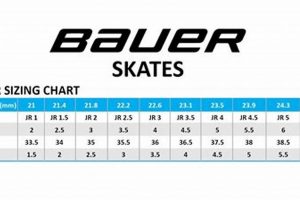
Tip 1: Accurate Sizing is Paramount. Prioritize obtaining precise foot measurements prior to purchase. Consult the manufacturer’s sizing chart and, if possible, conduct a physical fitting to ensure the skates are neither too restrictive nor excessively loose. Improper fit increases the risk of injury and diminishes control.
Tip 2: Protective Gear is Non-Negotiable. Equip the user with a certified helmet, elbow pads, knee pads, and wrist guards. These items are crucial for mitigating the severity of potential falls and impacts. Ensure all protective gear fits correctly and is securely fastened.
Tip 3: Gradual Progression of Skill Development. Encourage a staged approach to learning skating skills. Begin with basic balance and forward motion on a smooth, level surface. Gradually introduce more complex maneuvers, such as turning, stopping, and skating backwards, as proficiency increases.
Tip 4: Regular Inspection and Maintenance. Routinely examine the skates for signs of wear and tear, including loose wheels, damaged buckles, and compromised stitching. Promptly address any issues to maintain optimal functionality and safety. Clean wheels and bearings periodically to ensure smooth rolling performance.
Tip 5: Controlled Environments are Essential. Initially, restrict skating activities to designated areas, such as skate parks or smooth, paved surfaces, away from vehicular traffic. Supervise young skaters, especially those with limited experience, to ensure adherence to safety guidelines and responsible skating practices.
Tip 6: Proper Lacing and Fastening. Ensure laces are tightened securely and buckles are fastened appropriately. Properly secured skates provide necessary ankle support and prevent slippage during use. Reinforce the importance of secure fastening before each skating session.
Adherence to these guidelines promotes a safer and more enjoyable skating experience. Proper equipment selection and responsible usage are vital for fostering skill development and minimizing the risk of injury.
The subsequent section will address advanced skating techniques and competitive considerations for youth participants in roller sports.
1. Sizing Accuracy
Sizing accuracy constitutes a fundamental element in the appropriate selection of equipment for young skaters. Inadequate fitting directly impacts performance, comfort, and safety. Precise sizing ensures optimal control, minimizes the risk of injury, and facilitates skill development in the context of using equipment designed for youth.
- Ankle Stability and Control
Incorrect sizing compromises ankle stability. Skates that are too large offer insufficient support, increasing the likelihood of ankle sprains or instability during maneuvers. Skates that are too small restrict natural movement and can cause discomfort, hindering the development of proper skating technique. Precise sizing promotes secure ankle positioning within the skate, maximizing control and minimizing the risk of injury.
- Balance and Posture
Appropriate sizing directly affects a skater’s balance. Overly large skates shift the center of gravity, making it difficult to maintain balance, especially during forward motion or turning. Undersized skates can force unnatural foot positioning, leading to postural imbalances and potential strain on joints and muscles. Accurate sizing allows for a natural and balanced stance, enabling the skater to maintain equilibrium and control.
- Blister Formation and Discomfort
Ill-fitting equipment is a primary cause of blister formation and general discomfort. Excessive space within the skate leads to friction between the foot and the boot liner, causing blisters and chafing. Restricted space due to undersized skates can compress the foot, leading to pain and potential long-term foot problems. Precise sizing minimizes friction and compression, ensuring a comfortable skating experience and preventing skin irritation.
- Skill Development and Confidence
Improperly sized equipment inhibits skill development and can negatively impact a young skater’s confidence. Difficulty maintaining balance or experiencing discomfort can discourage participation and impede progress. Accurate sizing promotes comfort and stability, allowing the skater to focus on learning and refining skating skills without being hampered by ill-fitting equipment. This fosters confidence and encourages continued participation in the activity.
The interplay between sizing accuracy and the suitability of youth-specific skating equipment is paramount. Precise measurements and careful fitting are essential to ensure optimal performance, safety, and enjoyment for young skaters. Consistent monitoring of foot size as the skater grows is necessary to maintain optimal fit and prevent the negative consequences associated with inadequately sized equipment.
2. Ankle Support
Ankle support constitutes a critical element in equipment designed for youth, specifically engineered for developing musculoskeletal systems. The inherent instability of a young skater’s ankle necessitates structured support to mitigate the risk of injury. Insufficient ankle support can result in sprains, strains, and compromised balance, impeding skill development. Equipment featuring enhanced ankle support, often achieved through reinforced boot structures and strategically positioned padding, stabilizes the joint, promoting proper alignment and control during dynamic movements. For instance, a youth skater executing a crossover maneuver requires robust ankle support to maintain balance and prevent lateral ankle roll.
The design of youth inline skates frequently incorporates adjustable ankle cuffs. These cuffs allow for customized support levels, accommodating varying degrees of ankle strength and skill. A tighter cuff setting provides increased rigidity and stability, while a looser setting allows for greater range of motion. Furthermore, integrated lacing systems and power straps work in conjunction with the ankle cuff to secure the foot and prevent slippage within the boot. A real-world example involves a young skater transitioning from recreational skating to more aggressive styles, where the need for customized ankle support becomes paramount to accommodate the increased demands of complex maneuvers and higher impact landings.
Therefore, the presence and quality of ankle support in youth-specific inline skates are directly correlated with safety, performance, and the long-term health of the skater’s ankle joint. While challenges exist in balancing support with comfort and range of motion, manufacturers continually refine designs to optimize this crucial element. Understanding the importance of ankle support enables informed equipment selection, ensuring young skaters receive the necessary protection and stability to progress safely and confidently.
3. Wheel Hardness
Wheel hardness is a critical specification influencing the performance characteristics of equipment intended for young skaters. Measured on the durometer scale, typically indicated with an “A” rating, this property dictates the level of grip, speed, and durability, ultimately shaping the skater’s experience. Appropriate selection of wheel hardness is essential for optimizing control and safety.
- Grip and Surface Adhesion
Softer wheels, possessing lower durometer ratings (e.g., 74A-78A), exhibit greater surface adhesion, providing enhanced grip on various surfaces. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for beginners, offering increased stability and control during initial skill development. Softer wheels excel on rougher surfaces, such as outdoor pavements, as their flexibility allows them to conform to imperfections, minimizing vibrations and maximizing contact area. However, increased grip typically corresponds to reduced speed and faster wear.
- Speed and Rolling Resistance
Harder wheels, indicated by higher durometer ratings (e.g., 82A-85A), reduce rolling resistance, enabling higher speeds. These wheels are generally preferred by more experienced skaters who prioritize speed and efficiency. However, harder wheels offer less grip, increasing the potential for slippage, particularly on smooth or wet surfaces. Indoor surfaces, such as skating rinks, are often ideal for harder wheels due to their smooth and consistent nature.
- Durability and Wear Rate
Wheel hardness directly influences wear rate. Softer wheels, due to their increased grip and surface conformity, tend to wear down more rapidly than harder wheels. Conversely, harder wheels, while providing greater longevity, may exhibit reduced performance over time if subjected to excessive wear from rough surfaces. The skater’s weight and skating style also impact wheel durability, with heavier skaters and more aggressive styles accelerating wear.
- Impact on Skating Technique
The choice of wheel hardness can significantly affect skating technique. Softer wheels require less effort to initiate turns and maneuvers due to their increased grip, facilitating easier skill acquisition for beginners. Harder wheels, however, demand more precise technique and control, rewarding skilled skaters with greater speed and responsiveness. Selecting the appropriate wheel hardness based on skill level and skating style is crucial for optimizing performance and preventing the development of improper techniques.
The interplay between wheel hardness, skater skill, and environmental conditions is paramount in equipment selection. Matching wheel characteristics to the intended usage environment and the skater’s proficiency ensures a safer, more efficient, and ultimately, more enjoyable skating experience for young individuals. Failure to consider these factors can lead to compromised performance, increased risk of injury, and potentially, discouragement from pursuing the activity.
4. Chassis Material
The chassis, the frame onto which the wheels are mounted, is a critical component of equipment designed for youth. Its material composition directly affects the skate’s weight, durability, power transfer, and overall handling characteristics. Within the context of products for younger users, the selection of chassis material balances performance considerations with the need for affordability and appropriate weight. For example, a heavier chassis can be more durable but may impede a young skater’s agility and increase fatigue. Common materials employed in the construction of chassis for youth-oriented equipment include reinforced polymers, aluminum alloys, and composite materials.
Reinforced polymers offer a balance of impact resistance and lightweight properties, making them suitable for entry-level models. Aluminum alloys provide increased stiffness and power transfer compared to polymers, enhancing responsiveness and control. However, aluminum chassis typically elevate the product’s price point. Composite materials, such as carbon fiber blends, are utilized in high-performance youth models, offering exceptional stiffness-to-weight ratios. This enables optimal power transfer and responsiveness for skilled young skaters engaging in competitive roller hockey or advanced recreational skating. The choice of material influences the skate’s ability to withstand stress from jumps, turns, and other dynamic movements, directly impacting the skater’s safety and performance.
In summary, the chassis material is a pivotal determinant of the performance and durability of youth equipment. Considerations regarding weight, stiffness, impact resistance, and cost guide material selection. Understanding the properties of various chassis materials is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with a young skater’s skill level, intended usage, and budgetary constraints. A properly selected chassis contributes significantly to a positive and safe skating experience.
5. Bearing Quality
Bearing quality is a key determinant of performance in youth inline skates. Bearings facilitate wheel rotation, and their quality directly influences speed, smoothness, and the overall skating experience. Inferior bearings create excessive friction, reducing speed and increasing the effort required to propel the skate. This is particularly detrimental to young skaters who may lack the strength and endurance to overcome the resistance. High-quality bearings, conversely, minimize friction, enabling effortless gliding and extended skating sessions. This contributes to skill development and fosters enjoyment of the activity. For example, a youth inline hockey player using skates with high-grade bearings will experience improved acceleration and agility on the rink.
The ABEC (Annular Bearing Engineers’ Committee) rating system provides a general indication of bearing precision, with higher numbers signifying tighter tolerances. However, ABEC ratings do not encompass all aspects of bearing quality. Material composition, lubricant type, and seal design also play crucial roles. Chrome steel bearings are a common choice for youth skates, offering a balance of durability and affordability. However, stainless steel bearings offer superior corrosion resistance, making them suitable for skating in wet or humid conditions. Self-lubricating bearings minimize maintenance requirements, while sealed bearings prevent the ingress of dirt and debris, extending bearing lifespan. For instance, a recreational skater using skates with sealed, self-lubricating bearings would experience consistent performance with minimal upkeep.
In conclusion, bearing quality significantly impacts the performance and usability of youth inline skates. Opting for skates equipped with high-quality bearings enhances speed, smoothness, and durability, leading to a more enjoyable and productive skating experience. Parents and coaches should consider bearing specifications when selecting youth skates, recognizing their contribution to skill development and overall safety. The selection should balance cost with performance requirements to ensure an appropriate and beneficial product. Neglecting bearing quality can lead to diminished performance, increased fatigue, and reduced enjoyment of the activity.
6. Brake System
The brake system constitutes a safety-critical feature in equipment designed for young skaters. Its effectiveness directly influences the ability to control speed and execute controlled stops, thereby mitigating the risk of collisions and injuries. The following elucidates key facets of the brake system in the context of youth-specific equipment.
- Heel Brake Design and Functionality
The heel brake, typically a rubber or composite pad mounted on the rear of one skate, is the most common braking mechanism in youth models. Activating the brake requires extending the braking leg forward and applying pressure to the pad, creating friction against the ground. The size and composition of the pad, along with the angle of the braking surface, determine the braking efficiency. Smaller pads require greater force to achieve effective deceleration, while larger pads offer increased stopping power. For example, a poorly designed heel brake may necessitate excessive force from a young skater, potentially compromising balance and control.
- Brake Pad Material and Wear
The material composition of the brake pad dictates its durability and braking performance. Softer compounds provide superior grip but exhibit accelerated wear, necessitating frequent replacement. Harder compounds offer greater longevity but may compromise braking effectiveness, particularly on smooth surfaces. Regular inspection of the brake pad is essential to ensure adequate thickness and proper functionality. Worn brake pads diminish stopping power and increase the risk of accidents. For instance, a youth skater practicing emergency stops with a worn brake pad may experience delayed braking response, increasing the potential for a collision.
- Adjustability and Replacement
The adjustability of the brake system influences its usability for skaters of varying skill levels and sizes. Some models feature adjustable brake height, allowing for customization based on individual preferences and leg length. The ease of brake pad replacement is another important consideration. A user-friendly replacement mechanism simplifies maintenance and encourages timely replacement of worn pads, maintaining optimal braking performance. A brake system requiring specialized tools or complex procedures may deter prompt maintenance, compromising safety.
- Progressive Braking Techniques
The effectiveness of the brake system is contingent upon the skater’s proficiency in progressive braking techniques. Abrupt application of the brake can lead to instability and loss of control. Gradual application of pressure, combined with proper body positioning, promotes smooth and controlled deceleration. Instruction in proper braking techniques is crucial for young skaters to maximize the effectiveness of the brake system and minimize the risk of accidents. For example, a youth skating instructor emphasizing gradual braking techniques will enhance students’ ability to control speed and execute controlled stops, improving overall safety.
Collectively, these facets highlight the critical role of the brake system in ensuring the safety and control of youth inline skates. The design, material composition, adjustability, and the skater’s braking technique collectively determine the effectiveness of the braking system. Attention to these factors promotes a safer and more controlled skating experience for young individuals. Regular maintenance and proper instruction in braking techniques are essential to maximize the benefits of the braking system and mitigate potential risks.
7. Protective Gear
Protective gear represents an indispensable component when utilizing youth inline skates. The inherent risks associated with skating, such as falls and collisions, necessitate the use of protective equipment to minimize the potential for injuries. Specifically, helmets, elbow pads, knee pads, and wrist guards serve as crucial safeguards for young skaters who are developing their coordination and balance. The application of these protective measures is not merely a recommendation, but rather a critical safety precaution for any youth engaging in inline skating activities. For instance, a fall without wrist guards can lead to fractures or sprains, conditions effectively prevented by appropriate protective gear. The integration of protective gear with skating equipment directly mitigates these risks, contributing to a safer skating experience.
The effectiveness of protective gear is contingent on proper fit and appropriate usage. Ill-fitting equipment offers diminished protection and can even impede a skater’s movement. Therefore, it is essential to select equipment specifically designed for youth, ensuring a snug yet comfortable fit. Furthermore, the proper utilization of protective gear extends beyond simply wearing it; it requires consistent and correct application before each skating session. For example, a helmet that is loosely fastened provides minimal protection during a fall. Regularly inspecting protective gear for damage and replacing worn or compromised items is equally crucial in maintaining its effectiveness. A cracked helmet, even if seemingly minor, significantly reduces its ability to absorb impact, rendering it unreliable.
In conclusion, protective gear serves as a fundamental element in the safe usage of youth inline skates. It directly mitigates the risks associated with skating, minimizing the potential for injuries and promoting a more secure skating experience. The proper selection, fitting, and consistent usage of helmets, elbow pads, knee pads, and wrist guards are essential prerequisites for any youth engaging in inline skating. Emphasis on protective gear usage must be prioritized to ensure the well-being of young skaters and foster a culture of safety within the skating community.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding inline skates specifically designed for young individuals, providing clarity on critical aspects related to performance, safety, and equipment selection.
Question 1: What constitutes the primary distinction between equipment designed for youth versus equipment designed for adults?
Equipment engineered for youth incorporates design adaptations to accommodate the unique biomechanics and developmental needs of younger skaters. This includes size scaling, reduced weight, enhanced ankle support, and modified wheel durometer ratings to optimize control and maneuverability for smaller, less powerful skaters.
Question 2: How does one determine the appropriate size for youth equipment?
Accurate foot measurement is paramount. It is recommended to consult the manufacturer’s sizing chart and, ideally, conduct a physical fitting to ensure proper fit. Allowance for growth should be minimal; excessively large equipment compromises control and increases the risk of injury.
Question 3: What is the recommended frequency for replacing youth equipment?
Replacement frequency depends on usage intensity and growth rate. Equipment should be replaced when it becomes too small, exhibits significant wear and tear compromising functionality, or no longer provides adequate support and protection. Regular inspection is essential.
Question 4: What are the essential protective gear items required for youth inline skating?
A certified helmet, elbow pads, knee pads, and wrist guards are considered mandatory for ensuring safety. Protective gear must fit properly and be securely fastened before each skating session. The absence of any of these items significantly elevates the risk of injury.
Question 5: What is the optimal wheel hardness for youth equipment?
Softer wheels (74A-78A durometer) are generally recommended for beginners, providing enhanced grip and stability. More experienced skaters may benefit from harder wheels (80A-82A) offering increased speed and rolling efficiency. The selection should be tailored to the skater’s skill level and skating environment.
Question 6: How does one maintain youth equipment to ensure longevity and optimal performance?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning wheels and bearings, inspecting for loose hardware, and replacing worn brake pads. Proper storage in a dry environment is also crucial. Neglecting maintenance reduces equipment lifespan and can compromise safety.
In summation, selecting and maintaining suitable equipment is paramount for fostering a safe and enjoyable skating experience for young individuals. Proper fitting, appropriate protective gear, and consistent maintenance are essential considerations.
The subsequent section will explore advanced training techniques and competitive opportunities available to youth inline skaters.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has explored critical facets of equipment tailored to young individuals participating in inline skating. Key elements such as sizing accuracy, ankle support, wheel hardness, chassis material, bearing quality, and brake systems were examined, alongside the imperative role of protective gear. Each component contributes uniquely to the overall safety, performance, and user experience. Understanding these factors is paramount for making informed decisions during equipment selection.
The ongoing advancement of materials and engineering principles continues to refine youth inline skate design, improving performance capabilities and enhancing safety features. Continued research and diligence in selecting appropriate equipment will ensure that young skaters can safely and effectively develop their skills, fostering a lifelong engagement with the sport. Prioritizing safety and performance through informed equipment choices remains the responsibility of parents, coaches, and retailers.