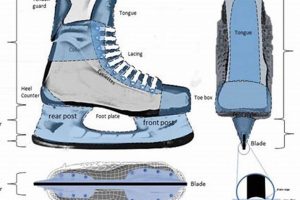
The process of fastening footwear designed for gliding on ice involves a specific technique to ensure a secure and supportive fit. This method utilizes elongated cords passed through eyelets, gradually tightening the boot around the foot and ankle. A properly executed procedure is essential for optimal performance and injury prevention on the ice.
Securing the specialized footwear correctly provides stability, control, and the necessary support for executing various maneuvers. Inadequate fastening can lead to discomfort, reduced agility, and an increased risk of ankle sprains or other related injuries. The historical evolution of the equipment reflects a continual pursuit of improved support and responsiveness, impacting both recreational and competitive ice skating.
Further discussion will delve into the specific techniques, optimal tightness levels for different skating styles, and the impact of varying lacing patterns on performance. The selection of appropriate cords and their maintenance will also be addressed.
Essential Considerations for Securing Ice Skates
Optimal fastening is crucial for performance and safety on the ice. The following tips provide guidance for achieving a secure and supportive fit.
Tip 1: Gradual Tightening: Avoid abrupt tightening. Progressively increase tension from the toe upwards, ensuring even distribution of pressure along the foot.
Tip 2: Ankle Support Emphasis: Prioritize support around the ankle joint. A firm, but not constricting, hold in this area minimizes the risk of instability and potential injury.
Tip 3: Knot Placement and Security: Position the knot at the upper portion of the boot, away from pressure points. Ensure the knot is firmly secured to prevent loosening during activity.
Tip 4: Cord Material Assessment: Select durable, non-stretch cords that maintain their integrity under repeated use. Inspect regularly for signs of wear and replace as needed.
Tip 5: Individualized Adjustment: Recognize that optimal tension varies based on foot anatomy, skating style, and personal preference. Experiment to identify the most comfortable and supportive configuration.
Tip 6: Heel Lock Verification: After securing, confirm that the heel remains firmly in place within the boot. Excessive heel movement indicates inadequate fastening and necessitates readjustment.
Tip 7: Regular Re-Evaluation: During prolonged skating sessions, periodically re-evaluate the tension. Minor adjustments may be necessary to maintain optimal support and comfort.
Proper securing promotes stability, control, and injury prevention, thus enhancing the overall skating experience. Adherence to these guidelines ensures a secure and supportive fit.
The subsequent sections will explore advanced techniques and considerations for maximizing the benefits of properly secured ice skates.
1. Tension distribution
Effective securing of footwear designed for use on ice hinges significantly on the even distribution of tension throughout the process. Unevenness in the application of force along the length of the boot can lead to localized pressure points, causing discomfort and potentially hindering performance. When the lower portion of the boot is too tight relative to the upper, circulation may be restricted, leading to numbness and reduced sensitivity, directly impacting the skater’s ability to feel the ice. Conversely, excessive tightness at the ankle can limit range of motion and increase the risk of tendon strain.
Optimal tension distribution is achieved through a methodical, zone-by-zone approach. Securing the area around the toes with moderate pressure, then gradually increasing tension towards the ankle, promotes a balanced and supportive fit. The specific tension applied to each zone should be adjusted according to the skater’s foot anatomy and skating style. For example, figure skaters often require greater ankle support than recreational skaters, necessitating a firmer hold in that region. Failure to achieve this balance can result in compromised control and increased fatigue, undermining the benefits of properly sharpened blades and well-maintained equipment.
The significance of tension distribution extends beyond mere comfort; it directly influences the skater’s ability to execute maneuvers with precision and confidence. Inadequate or uneven pressure can destabilize the foot within the boot, creating a lag between the skater’s intentions and the skate’s response. This lag can be particularly detrimental during complex sequences, where split-second adjustments are critical. The understanding and application of proper tension distribution techniques is, therefore, an integral component of safe and effective skating, regardless of skill level.
2. Ankle stabilization
Ankle stabilization represents a critical aspect of the interaction between the skater and the ice, directly influenced by the configuration of the footwear. The securing method employed plays a pivotal role in providing the necessary support to mitigate the risk of injury and enhance performance.
- Lateral Support and Motion Control
The primary function of appropriate fastening is to restrict excessive lateral movement of the ankle joint. This constraint is essential for maintaining balance and control during turns, jumps, and other dynamic maneuvers. Insufficient lateral support can lead to ankle sprains, while excessive restriction may hinder agility and responsiveness. Properly configured footwear, by distributing pressure effectively, promotes optimal motion control.
- Proprioceptive Feedback Enhancement
Secure fastening enhances proprioception, the body’s ability to sense its position in space. A snug fit around the ankle increases the skater’s awareness of their foot’s orientation and movement, enabling more precise adjustments and improved coordination. This enhanced feedback loop is particularly important for executing complex sequences and adapting to varying ice conditions.
- Impact Force Distribution
The lacing system contributes to distributing impact forces during landings and other high-stress activities. By providing a firm and consistent contact between the foot and the boot, the system helps to dissipate energy and reduce the risk of stress fractures or other injuries. The material properties and design of the cords and eyelets influence the effectiveness of this force distribution mechanism.
- Individualized Fit Customization
Optimal ankle stabilization is not a one-size-fits-all concept. The securing technique allows for individualized adjustments to accommodate varying foot anatomies, skating styles, and performance requirements. Skaters can manipulate the tension and pattern to achieve the desired level of support and responsiveness, ensuring a secure and comfortable fit that promotes both safety and performance.
The elements outlined above represent integral components of the relationship between footwear fastening and ankle stabilization. A comprehensive understanding of these aspects is crucial for skaters seeking to maximize their potential while minimizing the risk of injury. Attentive securing practices are essential for promoting both safety and performance on the ice.
3. Cord Material
The selection of cord material is intrinsically linked to the efficacy of securing footwear for ice-based activities. The material’s properties directly influence its ability to maintain tension, withstand wear and tear, and resist environmental factors. A cord composed of low-quality materials may stretch excessively under tension, leading to a loose fit and compromised ankle support. Conversely, a robust material ensures consistent tightness and promotes stability during complex movements. Real-world examples include the transition from natural fibers, which are prone to degradation, to synthetic alternatives like nylon or polyester, which offer superior durability and resistance to moisture. The practical significance of this understanding lies in the direct correlation between cord integrity and skater safety.
Further analysis reveals the nuanced requirements for cord material in different skating disciplines. Figure skating, for instance, demands materials with minimal stretch to facilitate precise control during intricate routines. Hockey, on the other hand, necessitates cords capable of withstanding high-impact forces and rapid adjustments. Manufacturers often incorporate specialized weaves or coatings to enhance the cord’s performance characteristics. These advancements contribute to a more secure and reliable fastening system. Regular inspection and timely replacement of worn or damaged cords are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing unforeseen equipment failures.
In conclusion, the connection between cord material and the overall effectiveness of securing ice skates is undeniable. The material’s properties dictate its ability to maintain tension, resist wear, and provide consistent support. Recognizing the importance of cord quality and implementing routine maintenance practices are essential for ensuring both safety and performance on the ice. Ignoring this critical component can lead to compromised stability and an increased risk of injury.
4. Knot security
The integrity of the knot securing footwear designed for ice-based activity directly influences the overall performance and safety of the user. A compromised knot can lead to loosening during activity, resulting in instability, reduced control, and potential injury. The subsequent points elaborate on key facets of this crucial connection.
- Knot Type and its Retention Characteristics
The specific knot employed dictates its inherent ability to resist slippage under tension. Certain knot configurations, such as the improved clinch knot or surgeon’s knot, offer superior holding power compared to simpler overhand knots. The choice of knot should align with the material properties of the cord and the anticipated forces exerted during skating. For example, a knot prone to unraveling under dynamic stress is unsuitable for competitive skating, where sudden movements and high-impact landings are commonplace. The longevity and security of the fastening are thereby compromised, potentially leading to premature failure and consequential safety hazards.
- Proper Knot Tying Technique
The execution of the knot is as critical as the knot’s inherent design. Incorrect tying can negate the advantages of even the most robust knot type. Over- or under-tightening, improper seating, and failure to adequately dress the knot (distributing tension evenly) can all diminish its holding power. A poorly tied knot may exhibit premature slippage or complete failure under load, directly impacting the skater’s stability and control. Therefore, thorough training in proper knot-tying techniques is essential for ensuring consistent and reliable performance.
- Material Compatibility and Friction
The interaction between the cord material and the knot configuration influences its security. Some materials, due to their surface properties, exhibit higher friction than others, enhancing the knot’s ability to resist slippage. Smooth, low-friction materials may require specialized knot types or additional security measures to prevent loosening. Furthermore, the material’s susceptibility to abrasion and degradation under repeated stress impacts the knot’s long-term integrity. Regular inspection for signs of wear and timely replacement of compromised cords are crucial for maintaining knot security and preventing failures.
- Knot Placement and Environmental Factors
The placement of the knot on the boot can also impact its security. Knots positioned in areas subject to friction or pressure from external objects (e.g., boot hooks, skate guards) are more prone to loosening or damage. Environmental factors, such as moisture and temperature fluctuations, can also affect the cord material and the knot’s integrity. Wet cords may become slippery, reducing friction and increasing the risk of slippage. Therefore, proper knot placement and protection from environmental hazards are essential for maintaining optimal security.
The interwoven elements of knot type, tying technique, material compatibility, and placement collaboratively determine the effectiveness of this crucial aspect. Diligence in these areas is fundamental for ensuring skater safety and optimizing performance, highlighting the significance of proper attention to detail in the broader context.
5. Heel lock
The concept of “heel lock” is inextricably linked to the method of securing ice skates. It represents a critical parameter in assessing the effectiveness of the securing process and its subsequent impact on skating performance and safety. Ensuring minimal heel displacement within the boot is paramount for maintaining control, stability, and preventing injuries.
- Minimizing Heel Lift for Enhanced Control
Heel lift, the vertical movement of the heel within the skate boot, directly diminishes a skater’s ability to transmit force efficiently to the blade. Excessive heel movement reduces responsiveness and precision, particularly during intricate maneuvers such as turns, jumps, and spins. Consider a figure skater executing a triple axel: any heel lift can disrupt the skaters balance and compromise the landing. Effective secures minimize this heel lift, allowing for more direct and immediate control over the skate.
- Impact on Ankle Stability and Injury Prevention
Inadequate heel lock increases the risk of ankle instability and potential injuries, such as sprains. When the heel is not firmly seated within the boot, the ankle is subjected to increased stress and strain, especially during high-impact activities. Hockey players, constantly engaged in rapid starts, stops, and changes of direction, are particularly susceptible to ankle injuries if their heel is not properly secured. By minimizing heel movement, the securing process provides enhanced ankle support and reduces the likelihood of such injuries.
- Correlation with Securing Patterns and Techniques
Different secures patterns can significantly influence heel lock. Certain patterns, such as those that emphasize tightening around the ankle and instep, are more effective at preventing heel lift than others. For instance, a secure that skips eyelets around the ankle may provide less heel lock compared to one that utilizes all eyelets to create a snug fit. Experimentation with various patterns is often necessary to achieve optimal heel lock, as individual foot anatomies and skating styles vary.
- Importance of Proper Boot Fit and Selection
While securing techniques can improve heel lock, they cannot compensate for an improperly fitted boot. A boot that is too large or ill-shaped will inherently provide inadequate heel support, regardless of how tightly it is secured. The initial selection of a boot that closely conforms to the skater’s foot is essential for achieving optimal heel lock. This underscores the significance of professional fitting services and careful consideration of boot size and shape before purchase.
In conclusion, heel lock is a multifaceted concept that is integral to achieving secure and comfortable skating experience. The interrelation between specific securing techniques, appropriate boot selection, and individual foot anatomy is important to achieve minimal heel displacement, contributing to enhanced control, stability, and injury prevention on the ice.
6. Eyelet Integrity
Eyelet integrity represents a crucial, yet often overlooked, element in the securing of ice skates. These small, reinforced apertures facilitate the passage of cords, distributing tension across the boot and providing a secure, customized fit. Compromised eyelets, whether due to corrosion, deformation, or detachment, disrupt this carefully engineered system, leading to uneven pressure distribution and a diminished ability to achieve adequate ankle support. For example, a detached eyelet on the lower portion of the boot can prevent the skater from properly tightening the forefoot area, leading to instability and potential discomfort. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in recognizing that even minor damage to an eyelet can have a disproportionately negative impact on overall skating performance and safety.
Further examination reveals that the material composition and construction of eyelets directly influence their durability and resistance to wear. Metallic eyelets, while generally robust, are susceptible to corrosion in humid environments or through prolonged exposure to moisture. Plastic eyelets, while corrosion-resistant, may be prone to cracking or deformation under stress. The choice of eyelet material should therefore align with the anticipated environmental conditions and the level of stress imposed during skating. Regular inspection of eyelets for signs of damage, such as cracks, deformation, or corrosion, is essential for proactive maintenance. Replacing compromised eyelets promptly prevents further degradation and maintains the integrity of the securing system.
In summary, the relationship between eyelet integrity and the secure lacing of ice skates is one of direct cause and effect. Damaged or compromised eyelets undermine the ability to achieve a snug, supportive fit, increasing the risk of instability and injury. Prioritizing regular inspection and timely replacement of damaged eyelets are essential steps in maintaining the overall integrity of the securing system and ensuring a safe and enjoyable skating experience. The seemingly small detail of eyelet condition is, in fact, a critical factor in the comprehensive equation of skater safety and performance.
7. Lacing pattern
The specific configuration of cords traversing the eyelets of ice skates, termed the lacing pattern, significantly influences the boot’s fit, support characteristics, and overall performance. Different patterns distribute tension in distinct ways, impacting ankle stability, heel lock, and the skater’s ability to execute precise movements. The selected pattern is not merely aesthetic; it directly contributes to the functionality and effectiveness of the securing process.
- Traditional Parallel Lacing
This pattern involves threading cords directly across the boot, creating parallel lines between eyelets. It generally provides a uniform distribution of tension and is suitable for skaters seeking a comfortable, all-around fit. However, it may lack the specialized support required for advanced maneuvers. Examples include recreational skates, where comfort is often prioritized over high-performance support. The implications are a balance between comfort and controlled support.
- Criss-Cross Lacing
The criss-cross pattern involves alternating the cord’s direction between each eyelet pair, creating an ‘X’ shape. This configuration tends to provide a more secure fit, particularly around the ankle, by increasing friction between the cords and the boot. Hockey skates frequently employ this pattern to enhance ankle stability and responsiveness during quick turns and stops. This increased security and stability are primary implications of its usage.
- Zone-Specific Lacing
This advanced pattern utilizes different lacing techniques in distinct zones of the boot to optimize support and comfort. For example, the lower portion may employ a looser pattern for flexibility, while the ankle area utilizes a tighter criss-cross pattern for enhanced stability. Figure skating boots often incorporate this technique to cater to the unique demands of jumps and spins. The implications are better stability and tailored comfort.
- Power Pull Lacing
Power pull systems incorporate specialized hooks or pulleys to amplify the tension applied to the cords, providing a more secure and customizable fit. These systems allow skaters to fine-tune the tightness in specific areas of the boot, such as the ankle or instep, to achieve optimal support. Speed skating boots frequently utilize power pull systems to maximize energy transfer and control. The implications include the ability for customized tightness and support.
The multifaceted relationship between lacing pattern and ice skate performance underscores the importance of careful consideration when selecting a securing technique. The choice depends on factors such as skating style, skill level, and individual foot anatomy. Recognizing the impact of different patterns allows skaters to optimize their equipment for enhanced control, comfort, and safety. Selecting the proper pattern can be pivotal to the quality of the skater’s experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following addresses common inquiries regarding the securing of ice skates, providing clarity on best practices and addressing prevalent misconceptions.
Question 1: What constitutes the appropriate tightness when securing ice skates?
The optimal tension is subjective and contingent upon skating style, skill level, and individual preferences. The footwear should feel snug and supportive, particularly around the ankle, without restricting circulation or causing discomfort. Experimentation is recommended to determine the ideal level of tightness. Gradual tightening, starting from the toes and progressing upwards, promotes even pressure distribution.
Question 2: How frequently should securing cords be replaced?
Cord replacement frequency depends on usage intensity and material quality. Regular inspection for signs of wear, such as fraying or stretching, is crucial. Cords exhibiting such damage should be replaced immediately to prevent potential failure during skating. High-performance skaters may require more frequent replacements compared to recreational users.
Question 3: Is there a recommended method for preventing securing cords from loosening during skating?
Employing a secure knot, such as the improved clinch knot or surgeon’s knot, is essential. Ensuring that the knot is properly tightened and seated before commencing skating minimizes the risk of slippage. Periodically re-evaluating the knot’s integrity during extended sessions is also advisable.
Question 4: What is the significance of heel lock in ice skate securing?
Heel lock refers to the degree of heel movement within the boot. Minimal heel movement is crucial for maintaining stability and control. Excessive heel lift can lead to reduced responsiveness and an increased risk of ankle injuries. Selecting a boot that conforms closely to the foot’s shape and utilizing appropriate securing techniques can optimize heel lock.
Question 5: Do securing patterns influence skating performance?
Yes, different securing patterns distribute tension uniquely, impacting ankle support and foot stability. Criss-cross patterns generally offer enhanced ankle support, while parallel patterns may provide a more comfortable fit. Zone-specific secures, which combine different techniques in distinct areas of the boot, allow for customized support and flexibility.
Question 6: Can improper securing contribute to foot or ankle pain?
Yes, inadequate securing can lead to various foot and ankle problems. Over-tightening can restrict circulation, causing numbness and discomfort. Insufficient support can increase the risk of sprains and strains. Properly secured skates distribute pressure evenly and provide adequate support, minimizing the likelihood of such issues.
In summary, proper securing is integral to a safe and enjoyable skating experience. Adhering to recommended techniques, regularly inspecting equipment, and addressing any signs of wear or damage are essential practices.
The subsequent section will delve into advanced maintenance procedures for ice skating equipment.
Securing Ice Skates
This examination of securing ice skates has underscored the complexity inherent in achieving optimal performance and safety on the ice. From the critical selection of cord materials and knot configurations to the nuanced understanding of tension distribution and heel lock, each element contributes significantly to the skater’s stability and control. The analysis of various securing patterns further highlights the importance of tailoring the method to individual needs and skating styles.
Ultimately, the proper execution of securing ice skates transcends mere procedural action; it represents a commitment to preparedness and risk mitigation. Skaters should prioritize meticulous attention to detail, ensuring that each aspect of the securing process is executed with precision and diligence. By embracing this proactive approach, individuals can enhance their capabilities and minimize the potential for injury, fostering a more secure and rewarding experience on the ice. The continuous pursuit of refined securing techniques remains paramount for optimizing both performance and safety within the sport.