These are a specific model of ice hockey footwear produced by Bauer, a prominent manufacturer of hockey equipment. They represent an entry-level option within the company’s product line, designed primarily for recreational skaters or beginners entering the sport.
Acquiring appropriate hockey footwear is vital for performance and safety on the ice. This particular model provides a balance of support, comfort, and affordability, making it accessible to a broader range of consumers. Its design often incorporates features geared towards ease of use and durability, crucial for players developing their skills and experiencing the demands of the game.
The following sections will delve into the specific features, intended user base, and performance characteristics often associated with entry-level hockey footwear, providing a more comprehensive understanding of its role in the sport.
Tips for the Proper Use of Entry-Level Hockey Footwear
This section offers guidance on maximizing the lifespan and performance of entry-level ice hockey footwear. Adhering to these tips will enhance user experience and ensure equipment longevity.
Tip 1: Ensure Proper Fit. A snug fit, without excessive tightness, is essential. Ill-fitting footwear can lead to discomfort, blisters, and compromised performance. Consult sizing charts or seek professional fitting assistance.
Tip 2: Correct Lacing Technique. Lace the footwear firmly, paying particular attention to ankle support. Avoid over-tightening the laces, which can restrict circulation and cause discomfort. Maintain even pressure throughout the lacing sequence.
Tip 3: Regular Blade Maintenance. After each use, thoroughly dry the blades to prevent rust and corrosion. A soft cloth or towel is recommended. Consider using blade guards during storage and transportation to protect the edges.
Tip 4: Proper Storage Practices. Store the footwear in a well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. This prevents material degradation and odor buildup. Remove the insoles after use to facilitate drying.
Tip 5: Gradual Break-In Period. New footwear may require a break-in period to conform to the wearer’s foot. Use the footwear for shorter periods initially, gradually increasing the duration as comfort improves. This minimizes the risk of blisters and discomfort.
Tip 6: Avoid Excessive Heat. Do not expose the footwear to excessive heat sources, such as radiators or direct sunlight, to expedite drying. This can damage the materials and compromise the integrity of the boot.
Tip 7: Consistent Cleaning Regimen. Regularly wipe down the exterior of the footwear with a damp cloth to remove dirt and debris. This helps maintain the appearance and prevents the buildup of harmful substances.
Following these guidelines will contribute to improved performance, enhanced comfort, and extended lifespan of entry-level ice hockey footwear. Consistent application of these tips will ensure a more enjoyable and safe experience on the ice.
The subsequent discussion will explore common issues encountered with this type of footwear and potential solutions.
1. Affordability
Affordability constitutes a primary consideration for consumers entering the sport of ice hockey. The pricing of equipment often serves as a barrier to entry, particularly for families with limited resources or individuals new to the activity. In the context of entry-level hockey footwear, affordability dictates design choices, materials selection, and overall construction.
- Material Composition and Cost
The materials used in entry-level hockey footwear are typically selected to balance durability with cost-effectiveness. Synthetic materials, such as molded plastics and nylon fabrics, are commonly employed in place of higher-end materials like carbon fiber or premium leathers. This substitution allows manufacturers to reduce production costs and offer the product at a lower price point.
- Simplified Construction Techniques
The manufacturing process for affordable hockey footwear often involves simplified construction techniques compared to professional-grade models. This can include fewer layers of padding, basic stitching patterns, and less elaborate ankle support systems. Streamlining the production process reduces labor costs and accelerates manufacturing output.
- Target Market and Price Sensitivity
The target market for entry-level hockey footwear primarily consists of recreational skaters and beginner players. These consumers are generally more price-sensitive than experienced players who are willing to invest in higher-performance equipment. The pricing strategy for such footwear is carefully calibrated to appeal to this demographic and encourage participation in the sport.
- Impact on Performance and Durability
While affordability is a key factor, it inherently impacts the performance and durability of the equipment. Entry-level hockey footwear may offer less ankle support, reduced energy transfer, and a shorter lifespan compared to higher-end models. Consumers should be aware of these trade-offs when selecting their equipment.
In summary, affordability directly shapes the design, construction, and performance characteristics of entry-level ice hockey equipment. While it enables broader accessibility to the sport, it also presents certain limitations in terms of performance and longevity. Potential buyers must carefully weigh the benefits of affordability against the potential drawbacks when making their purchase decision.
2. Entry-level
The designation “entry-level,” when applied to ice hockey equipment such as Bauer M1 skates, defines a product tier specifically designed to accommodate new or inexperienced participants. This categorization carries significant implications regarding design, materials, performance characteristics, and target demographic.
- Accessibility and Affordability
Entry-level equipment prioritizes affordability to minimize the financial barrier for individuals starting the sport. Bauer M1 skates, therefore, employ less expensive materials and simplified construction methods compared to higher-end models. This focus on cost-effectiveness makes them accessible to a broader range of consumers.
- Emphasis on Comfort and Support
While advanced skates emphasize performance and customization, entry-level options like the Bauer M1 prioritize comfort and basic support. This is crucial for beginners who are still developing their skating technique and require a forgiving and comfortable fit to facilitate learning and prevent discomfort. The materials and padding used are selected to enhance comfort during initial use.
- Durability for Recreational Use
Entry-level skates are built to withstand the rigors of recreational use and beginner-level play. Bauer M1 skates incorporate durable materials and construction techniques to ensure longevity under typical usage conditions. While not designed for the intense demands of competitive hockey, they provide adequate durability for casual skating and initial skill development.
- Simplified Features and Design
Entry-level skates typically feature a simplified design and fewer advanced features compared to professional-grade equipment. This streamlining reduces manufacturing costs and simplifies the user experience. Bauer M1 skates will generally lack advanced features such as heat-moldable shells or customizable blade holders, focusing instead on essential functionality and ease of use.
In summary, the “entry-level” designation of Bauer M1 skates reflects a deliberate design philosophy centered on affordability, comfort, durability, and ease of use. These attributes make them a suitable option for individuals beginning their journey in ice hockey or seeking a cost-effective option for recreational skating. However, as skill and participation intensity increase, transitioning to higher-performance equipment becomes necessary to meet the evolving demands of the sport.
3. Recreational use
Bauer M1 skates are predominantly engineered for recreational use, implying a design philosophy prioritizing comfort, durability, and affordability over peak performance metrics demanded by competitive hockey. The consequence of this design choice is a product suited for casual skating, pond hockey, or infrequent participation in organized leagues. The materials selected and construction techniques employed reflect this intention, opting for resilient synthetics and simplified structures to withstand general wear and tear while minimizing production costs. This targeted application enables wider accessibility to the sport by reducing the initial financial investment.
The importance of recreational use as a defining characteristic of Bauer M1 skates is evident in their feature set. Ankle support, while present, is typically less rigid than that found in higher-end models, allowing for greater freedom of movement and comfort during extended skating sessions. Similarly, blade quality and holder design prioritize stability and ease of use rather than maximizing energy transfer and responsiveness. Examples of recreational use scenarios include family skating at public rinks, leisurely skating on frozen ponds or lakes, and participation in non-competitive hockey leagues. These contexts underscore the practical significance of understanding the intended purpose of the skates, preventing unrealistic expectations regarding performance capabilities.
In summary, the connection between recreational use and Bauer M1 skates is fundamental to their design and marketing. The skates represent a conscious compromise between performance and accessibility, catering to a segment of the market that values comfort, durability, and affordability over competitive advantages. While Bauer M1 skates may not be suitable for professional-level play, they effectively serve the needs of recreational skaters and beginner hockey players. Recognizing this intended application is crucial for both consumers selecting appropriate equipment and for understanding the broader landscape of ice hockey equipment manufacturing.
4. Durability
Durability represents a key performance characteristic of Bauer M1 skates, impacting longevity, user satisfaction, and overall value. Understanding the factors contributing to the robustness of this equipment is essential for prospective purchasers.
- Material Composition and Resistance to Wear
The materials used in the construction of Bauer M1 skates directly influence their resistance to wear and tear. Outer shell materials, such as molded plastics or reinforced nylon, must withstand impacts from pucks, skates, and other on-ice hazards. Similarly, the internal liner materials should resist abrasion from foot movement and moisture absorption. The quality of these materials determines the skate’s ability to endure regular use and maintain its structural integrity over time.
- Construction Techniques and Structural Integrity
The manufacturing process and construction techniques employed play a crucial role in the overall durability of the skates. Reinforced stitching, secure bonding of components, and robust ankle support systems contribute to the skate’s ability to withstand stress and maintain its shape. Poor construction can lead to premature failure of seams, detachment of components, and diminished structural integrity. Therefore, inspecting the construction quality is a critical aspect of assessing the skate’s potential lifespan.
- Blade Attachment and Integrity
The method of blade attachment and the quality of the blade itself are fundamental to the durability of ice skates. A securely fastened blade reduces the risk of detachment during use, while a high-quality steel blade resists corrosion and edge damage. The blade holder, typically made of durable plastic, should withstand impacts and maintain its structural integrity to ensure proper blade alignment and performance. Regular maintenance, such as sharpening and rust prevention, is essential for maximizing blade lifespan.
- Impact Resistance and Protection
Durability extends to the skate’s ability to protect the foot and ankle from impacts. Reinforced areas in the boot, particularly around the ankle and toe, provide crucial impact resistance. The quality of the padding and the design of the protective elements determine the skate’s ability to mitigate injury risk from collisions with other players, the boards, or the ice. Effective impact protection is a critical aspect of skate durability, contributing to both safety and longevity.
In conclusion, the durability of Bauer M1 skates is multifaceted, encompassing material quality, construction techniques, blade integrity, and impact resistance. These factors collectively determine the skate’s ability to withstand the rigors of recreational use and provide long-term value to the user. Understanding these elements allows for informed purchasing decisions and appropriate maintenance practices, ultimately maximizing the lifespan and performance of the equipment.
5. Ankle support
Ankle support in Bauer M1 skates, an entry-level ice hockey skate model, directly impacts the wearer’s stability and control on the ice. Insufficient ankle support can lead to instability, increasing the risk of injury and hindering skill development, particularly for novice skaters. The design of M1 skates often incorporates molded plastic or reinforced nylon in the ankle area to provide a degree of support, although typically less rigid than higher-end models. This design choice reflects the target demographic of recreational skaters and beginners who require a balance of comfort and basic support. A real-life example is a beginner skater attempting a crossover maneuver; inadequate ankle support may cause the ankle to roll inwards, resulting in a loss of balance and potential fall.
The level of ankle support offered by Bauer M1 skates affects the skater’s ability to efficiently transfer energy during strides and turns. A more rigid ankle structure allows for greater power transfer from the leg to the blade, enabling more forceful movements. However, excessive rigidity can restrict mobility and cause discomfort, especially during prolonged skating sessions. Therefore, the design of ankle support in M1 skates represents a compromise between these competing factors. Practical applications of this understanding include selecting appropriately sized skates and ensuring proper lacing techniques to maximize the available ankle support. Furthermore, recognizing the limitations of entry-level ankle support informs the skater’s expectations and encourages progressive skill development to compensate for equipment limitations.
In summary, ankle support is a critical component of Bauer M1 skates, influencing stability, control, and energy transfer on the ice. While M1 skates provide a foundational level of ankle support suitable for recreational use and beginner skill development, they may not meet the demands of more advanced skaters who require enhanced rigidity and responsiveness. The challenges associated with ankle support in entry-level skates highlight the importance of proper fitting, lacing techniques, and a realistic assessment of skill level. Understanding the relationship between ankle support and skating performance contributes to a safer and more enjoyable experience on the ice.
6. Blade material
Blade material in Bauer M1 skates directly influences performance characteristics such as glide, edge control, and durability, thereby affecting the overall skating experience.
- Steel Grade and Hardness
The grade of steel employed dictates its hardness and resistance to wear. Entry-level skates, including Bauer M1, often utilize a softer steel compared to professional-grade models. While softer steel is easier to sharpen, it requires more frequent maintenance and is more susceptible to nicks and dulling. The implication is a tradeoff between affordability and performance; skaters must balance cost considerations with the need for consistent edge quality.
- Surface Finish and Glide Efficiency
The smoothness of the blade surface impacts its glide efficiency across the ice. A highly polished surface minimizes friction, allowing for smoother and faster skating. Lower-grade steel and less refined manufacturing processes in Bauer M1 skates may result in a less-than-optimal surface finish, potentially reducing glide efficiency compared to premium models. This difference is most noticeable during sustained gliding or when attempting to maintain speed.
- Corrosion Resistance
The blade’s susceptibility to corrosion is a significant factor in its long-term durability. Moisture exposure can lead to rust formation, compromising the blade’s structural integrity and performance. Blade materials used in Bauer M1 skates may have limited corrosion resistance compared to higher-end stainless-steel blades. Regular maintenance, including drying and protective coatings, becomes crucial to mitigate corrosion and extend the blade’s lifespan.
- Edge Retention
The blade’s ability to maintain a sharp edge over time directly affects edge control and turning ability. Softer steel, commonly found in entry-level skates, tends to lose its edge more quickly than harder steel. This necessitates more frequent sharpening to maintain optimal performance. The reduced edge retention of Bauer M1 blades can impact a skater’s ability to execute precise turns and maintain control during quick maneuvers.
The blade material of Bauer M1 skates represents a compromise between affordability and performance, impacting glide, edge control, durability, and maintenance requirements. Understanding these trade-offs enables skaters to make informed decisions based on their skill level, skating frequency, and budget constraints. Regular blade maintenance remains crucial for maximizing the performance and lifespan of Bauer M1 skates.
7. Liner comfort
Liner comfort in Bauer M1 skates, an entry-level model, significantly impacts the overall skating experience, especially for beginners. The liner’s design and materials directly affect foot support, cushioning, and moisture management, influencing comfort during prolonged use. A poorly designed liner can lead to discomfort, blisters, and reduced skating enjoyment, while a well-designed liner enhances comfort and allows for longer skating sessions. As an integral component of the skate, the liner is critical for ensuring a positive first experience for new skaters. For example, a liner made of stiff, non-breathable material can cause excessive sweating and friction, leading to blisters and discomfort. Conversely, a liner with adequate padding and moisture-wicking properties can help maintain a comfortable foot environment, reducing the risk of blisters and improving overall skating enjoyment.
The relationship between liner comfort and performance in Bauer M1 skates extends beyond mere comfort considerations. A comfortable liner provides a more secure and stable fit, enhancing the skater’s ability to control the skates and execute basic maneuvers. The liner’s padding helps to minimize foot movement within the boot, improving energy transfer and responsiveness. The presence of adequate arch support in the liner also contributes to foot stability and reduces fatigue. Practical applications include selecting skates with liners that conform well to the foot’s shape and utilizing proper lacing techniques to achieve a snug but not overly tight fit. Furthermore, wearing moisture-wicking socks can help to maintain a dry and comfortable foot environment.
In summary, liner comfort is a critical factor in the Bauer M1 skating experience, affecting both comfort and performance. While M1 skates prioritize affordability, the quality and design of the liner should not be overlooked. A comfortable liner enhances the overall skating experience, promoting greater enjoyment and encouraging continued participation in the sport. Challenges associated with liner comfort in entry-level skates highlight the importance of proper fitting, sock selection, and appropriate lacing techniques. Understanding this relationship contributes to a more informed purchasing decision and a more comfortable skating experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries and misconceptions surrounding the Bauer M1 skate model, providing objective information for prospective buyers and users.
Question 1: Are Bauer M1 skates suitable for competitive hockey?
Bauer M1 skates are primarily designed for recreational skating and beginner-level play. Their construction and materials are not optimized for the rigors of competitive hockey. Individuals seeking skates for competitive use should consider higher-end models designed for performance and durability.
Question 2: What is the expected lifespan of Bauer M1 skates?
The lifespan of Bauer M1 skates varies depending on usage frequency, intensity, and maintenance practices. With proper care and moderate recreational use, these skates may last for several seasons. However, heavy use or inadequate maintenance can significantly shorten their lifespan.
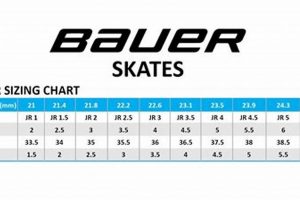
Question 3: How should Bauer M1 skates be properly fitted?
Proper fitting is crucial for comfort and performance. The skates should fit snugly around the foot with minimal heel slippage. Professional fitting assistance is recommended to ensure accurate sizing. Consult Bauer’s sizing charts for guidance, but in-person fitting remains the most reliable method.
Question 4: What type of blade maintenance is required for Bauer M1 skates?
Regular blade maintenance is essential for optimal performance. This includes drying the blades after each use to prevent rust, sharpening the blades as needed to maintain a sharp edge, and using blade guards during storage and transport to protect the edges from damage.
Question 5: Can the blades on Bauer M1 skates be replaced?
The blades on Bauer M1 skates are typically riveted to the chassis and are not easily replaceable. Replacing the blades may require specialized tools and expertise. It is generally more cost-effective to replace the entire skate than to attempt blade replacement.
Question 6: What are the primary differences between Bauer M1 skates and higher-end models?
Key differences include materials, construction, support, and performance features. Higher-end models typically incorporate more durable materials, advanced construction techniques, enhanced ankle support, and performance-oriented features such as heat-moldable shells and customizable blade holders. Bauer M1 skates prioritize affordability over these advanced features.
In summary, Bauer M1 skates are designed for recreational skating and beginner-level play. Proper fitting, maintenance, and realistic expectations are crucial for maximizing their performance and lifespan.
The following section will explore alternative skate models and their suitability for different skill levels and usage scenarios.
Bauer M1 Skates
This exploration has delineated the Bauer M1 skates as an entry-level product, emphasizing characteristics such as affordability, durability suitable for recreational use, and foundational ankle support. The analysis of blade material and liner comfort further clarifies the intended user base: individuals new to ice skating or engaging in infrequent, non-competitive activity. These skates, while providing a necessary starting point, inherently present limitations when compared to higher-end models designed for specialized performance requirements.
Prospective purchasers must align equipment selection with their skill level, frequency of use, and competitive aspirations. While the Bauer M1 skates offer an accessible entry point to the sport, continued progression and heightened performance demands necessitate a transition to equipment that reflects those advancements. Prudent evaluation of individual needs remains paramount in ensuring a safe and rewarding experience on the ice.