Devices designed to be affixed to a canine’s paws, allowing traction on frozen water surfaces, are the central subject. These specialized implements aim to provide grip and stability, potentially enabling the animal to traverse icy terrains. For example, a small breed might use these adaptations for recreational activities on a frozen pond.
The purported advantages of such canine footwear include potential paw protection from sharp ice and enhanced mobility in winter environments. Their adoption can be seen as an extension of pet care practices, prioritizing the animal’s well-being and engagement in outdoor activities during colder seasons. The origin of purpose-built devices for this application is rooted in the desire to facilitate canine participation in winter sports and activities.
The subsequent sections will delve into the design considerations, materials, application methods, and safety aspects associated with these canine adaptations. Further investigation will explore the potential impact on canine gait and overall comfort during their use.
Canine Ice Traversal
The following guidelines aim to provide crucial information regarding the selection, fitting, and utilization of specialized canine footwear designed for icy conditions. Responsible and informed application is paramount.
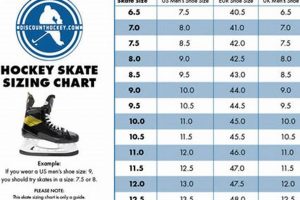
Tip 1: Selection Criteria: Prioritize fit. Ill-fitting devices can cause discomfort, impede movement, or result in injury. Measurements of the paw’s length and width are essential for accurate sizing, referencing the manufacturer’s specifications.
Tip 2: Gradual Acclimation: Introduce the devices incrementally. Initial sessions should occur indoors, allowing the animal to adjust to the altered sensation and weight distribution. Prolonged use should be avoided initially.
Tip 3: Surface Evaluation: Assess the ice surface before allowing canine traversal. Sharp, uneven, or excessively slick surfaces pose an elevated risk of injury, even with specialized footwear.
Tip 4: Secure Attachment: Ensure secure and proper fastening of the devices. Loose or improperly secured attachments can lead to detachment during use, compromising stability and potentially causing harm.
Tip 5: Gait Monitoring: Observe the canine’s gait for any signs of discomfort or altered movement patterns. Limping, reluctance to move, or excessive paw licking may indicate an improper fit or potential injury.
Tip 6: Material Assessment: Consider the material composition. Durable, water-resistant materials are essential for withstanding icy conditions. Regularly inspect for wear and tear, replacing devices as needed.
Tip 7: Environmental Awareness: Be mindful of the ambient temperature and duration of exposure. Prolonged exposure to extreme cold can lead to hypothermia, even with protective footwear.
Adhering to these guidelines facilitates a safer and more comfortable experience for the canine during icy conditions, potentially mitigating the risk of injury and enhancing mobility.
Further research into alternative traction solutions and canine paw care is recommended for comprehensive winter pet management.
1. Paw Measurement Accuracy
Paw measurement accuracy is a foundational element in the successful and safe application of specialized canine footwear intended for icy conditions. Precise measurements directly influence the fit and functionality, thereby affecting mobility, comfort, and injury prevention.
- Dimensional Precision
Dimensional precision refers to the accurate determination of the paw’s length, width, and potentially circumference, depending on the footwear design. Inaccurate measurements can result in footwear that is either too tight, restricting circulation and causing discomfort, or too loose, leading to slippage and instability. For example, if the paw width is underestimated, the footwear may constrict the paw, leading to chafing and potential sores. Conversely, an overestimated length might cause the footwear to slide off during use.
- Fit and Stability Correlation
The relationship between precise measurement and fit dictates the stability afforded by the footwear. A secure fit, achieved through accurate measurements, minimizes the risk of the device detaching during use, which could lead to sudden loss of traction and potential falls on icy surfaces. Furthermore, a well-fitted device ensures proper weight distribution across the paw, preventing concentrated pressure points that could cause discomfort or injury. Ill-fitting footwear, due to inaccurate measurements, compromises this stability.
- Gait Impact and Comfort
Inaccurate paw measurements can significantly impact a canine’s gait and overall comfort while using specialized footwear. A device that is too large or too small can alter the natural stride, leading to awkward movements and potential muscle strain. For example, if the footwear is too long, the canine may compensate by dragging its paw, increasing the risk of tripping and impacting efficiency. Similarly, overly tight footwear can cause pain and discomfort, discouraging use and potentially leading to behavioral resistance.
- Influence on Injury Prevention
Accurate paw measurement significantly contributes to the device’s ability to provide adequate protection from the elements and hazards on icy surfaces. Properly fitting footwear acts as a barrier against sharp ice, salt, and other abrasive materials that can cause cuts, abrasions, or chemical burns on the paws. Inaccurate measurements compromise this protective function, leaving the paws vulnerable to injury. Moreover, a secure fit minimizes the risk of the footwear twisting or shifting, which could expose the paw to hazardous conditions.
In summary, accurate paw measurements are not merely a preliminary step; they are integral to the proper functioning and safety of canine ice traversal devices. Precise dimensional assessment, fit optimization, gait preservation, and injury prevention are all directly linked to this foundational aspect, underscoring its importance in responsible winter pet care.
2. Material Durability
Material durability constitutes a critical factor in the effectiveness and longevity of specialized canine footwear designed for icy conditions. The capacity of the constituent materials to withstand the rigors of ice, snow, and abrasive surfaces directly impacts the functionality and safety of the device.
- Abrasion Resistance
The ability of the material to resist wear from friction is paramount. Icy surfaces, often mixed with sand or salt, are inherently abrasive. Materials lacking high abrasion resistance will degrade rapidly, compromising the structural integrity of the footwear and diminishing its protective capabilities. For example, a rubber sole with insufficient abrasion resistance might wear thin quickly, exposing the canine’s paw to the cold or sharp ice fragments.
- Cold Weather Flexibility
Materials must retain flexibility at sub-freezing temperatures to ensure proper function and canine comfort. Many materials become brittle and prone to cracking in extreme cold, which can render the footwear ineffective and potentially harmful. A plastic fastener that shatters due to cold temperatures, for instance, can cause the device to detach during use, leaving the paw unprotected.
- Water Resistance and Impermeability
Water resistance, or ideally, impermeability, prevents moisture penetration, which can lead to frostbite and discomfort. Wet materials lose insulation value and increase the risk of cold-related injuries. Fabrics or seams that allow water to seep in can freeze, creating rigid and uncomfortable conditions for the canine. A waterproof membrane or treated fabric is essential in maintaining a dry and comfortable internal environment.
- Tensile Strength and Tear Resistance
The material’s ability to withstand pulling forces and resist tearing is crucial for maintaining structural integrity during active use. Forces exerted during walking, running, and navigating uneven ice surfaces can stress the material, particularly at seams and attachment points. Low tensile strength increases the risk of tearing, which can compromise the functionality of the footwear and lead to premature failure. Reinforced stitching and durable fabrics are essential for withstanding these forces.
These facets underscore the necessity of carefully selecting materials with inherent durability characteristics. The longevity, safety, and efficacy of canine ice traversal devices depend directly on the ability of their constituent materials to withstand the demanding conditions encountered in icy environments. Failure to prioritize material durability can result in compromised performance, increased risk of injury, and reduced product lifespan.
3. Secure Attachment
The reliable affixation of specialized canine footwear to the paw is paramount for functionality and safety. Secure attachment mechanisms directly influence the efficacy of these devices on icy terrains. A failure in this connection can nullify the intended benefits, exposing the animal to potential hazards. For instance, a loosely fastened device may slip or detach entirely during ambulation, negating traction and increasing the risk of falls or injuries due to unprotected paws. The design and implementation of reliable attachment systems are, therefore, integral to the utility of canine ice traversing equipment.
Various securement methods are employed, including straps, buckles, hook-and-loop fasteners, and elasticized closures. The selection of an appropriate method depends on factors such as paw anatomy, activity level, and environmental conditions. A system utilizing multiple adjustable straps, for example, can distribute pressure evenly across the paw, minimizing the risk of constriction or chafing while ensuring a snug fit. Conversely, a single, inadequately sized strap may create pressure points, leading to discomfort or impede circulation. Regularly inspected fastening systems and appropriately adjusted securing mechanisms will maximize safety.
In summary, secure attachment is not merely a superficial aspect but a foundational requirement. The degree of affixation directly determines the device’s ability to perform its intended function. Properly designed and maintained fastening systems are essential for canine safety. This careful consideration promotes the responsible use of canine ice mobility devices.
4. Gait Monitoring
The observation and analysis of a canine’s gait, termed “gait monitoring,” becomes particularly salient when specialized footwear is employed, especially those intended for icy conditions. The use of such equipment inevitably alters the animal’s natural stride, and diligent monitoring serves as a critical indicator of comfort, stability, and potential injury. Any deviation from a normal gait pattern, such as limping, shortened stride length, or reluctance to bear weight on a specific limb, warrants immediate attention. This could signal an ill-fitting device, discomfort from rubbing or pressure points, or, more seriously, an underlying musculoskeletal issue exacerbated by the footwear. For instance, if a canine displays a hopping motion while wearing ice skates, it may indicate that the skates are improperly sized, causing instability and a compensatory movement pattern to maintain balance.
Practical application of gait monitoring extends beyond simple observation. Owners should familiarize themselves with their canine’s normal gait prior to introducing specialized footwear. Video recording can provide a valuable baseline for comparison. During and after each use, close attention should be paid to the symmetry of movement, the length of each step, and the range of motion in each joint. Subtle changes, which may be overlooked during casual observation, can be detected with careful scrutiny. Furthermore, monitoring should incorporate palpation of the limbs post-exercise to identify any areas of tenderness or swelling, further indicating potential musculoskeletal strain. This rigorous approach provides early detection of problems.
In summary, gait monitoring is not merely an ancillary consideration but an essential component of responsible canine care when utilizing ice traversal devices. Early detection of gait abnormalities allows for timely intervention, preventing minor discomfort from escalating into significant injury. By prioritizing and implementing thorough gait monitoring practices, the safety and well-being of canines engaging in winter activities can be significantly enhanced, ensuring safe and rewarding outdoor experiences.
5. Ice Surface Assessment
Assessment of the ice surface forms a crucial precursor to the deployment of specialized canine footwear. The suitability of the ice surface directly dictates the effectiveness and safety of these devices. Variable ice conditions, encompassing factors such as thickness, texture, and the presence of debris or irregularities, can profoundly influence a canine’s ability to traverse the environment safely. Insufficient ice thickness poses an obvious hazard of collapse, whereas uneven surfaces or the presence of sharp objects introduces risks of injury, regardless of whether the animal is equipped with specialized footwear. Prior evaluation allows for a determination of whether conditions are appropriate for canine activity. A frozen pond that exhibits areas of thin ice, for example, would be deemed unsuitable despite appearing solid overall, necessitating relocation to a safer environment or cessation of the activity.
Proper assessment entails a multi-faceted approach. Visual inspection identifies obvious hazards such as cracks, holes, or accumulations of snow that may obscure underlying dangers. Physical probing, using a tool to assess ice thickness, provides a more quantitative evaluation of structural integrity. Monitoring weather conditions, both current and recent, is also essential, as temperature fluctuations can significantly alter ice stability. For instance, a period of warm weather following a freeze can weaken the ice structure, even if the surface appears solid. Furthermore, consideration should be given to the location of the ice formation. Ice near flowing water, such as rivers or streams, tends to be thinner and less stable than ice in standing bodies of water, representing a particularly hazardous area that should be avoided.
In conclusion, ice surface assessment is not merely a precautionary measure but an integral component of responsible canine care in winter environments. A thorough and systematic evaluation of ice conditions mitigates the risks associated with canine activity on frozen surfaces, ensuring both the animal’s safety and the effectiveness of any specialized footwear employed. By prioritizing careful assessment, canine owners can make informed decisions regarding the suitability of the environment, minimizing the potential for accidents and promoting positive outdoor experiences. The risks associated with inadequate surface evaluation far outweigh the time and effort required for proper assessment.
6. Gradual Acclimation
The process of gradual acclimation is paramount when introducing specialized canine footwear. Abrupt exposure to these devices can induce stress and reluctance, hindering the animal’s ability to adapt and potentially leading to negative associations with the equipment.
- Neuromuscular Adaptation
Specialized footwear alters a canine’s proprioception, requiring the animal to recalibrate its balance and coordination. Gradual acclimation allows for the development of new neuromuscular pathways, enabling the canine to move confidently and efficiently. Abrupt introduction may overwhelm the nervous system, leading to awkward movements and increased risk of falls. For example, short indoor sessions initially, followed by brief outdoor excursions, promote a smoother transition compared to immediate prolonged exposure on ice.
- Psychological Adjustment
Canines may initially perceive specialized footwear as a foreign and potentially threatening object. Gradual acclimation, paired with positive reinforcement, helps to alleviate anxiety and build a positive association with the devices. For instance, rewarding the canine for tolerating the footwear, even for brief periods, fosters cooperation and reduces resistance. Conversely, forced or rushed introductions can instill fear and aversion, making future use problematic.
- Skin and Paw Sensitivity
The paws are sensitive structures, and prolonged contact with unfamiliar materials can cause irritation or discomfort. Gradual acclimation allows the skin to adapt to the new pressure points and friction. Short, monitored periods of wear enable early detection of any adverse reactions, such as redness or chafing. Immediate prolonged use increases the risk of skin irritation and potential secondary infections.
- Device Familiarization
Gradual acclimation provides an opportunity for both the canine and the owner to familiarize themselves with the proper fitting and securement of the devices. This process ensures that the footwear is correctly positioned and adequately fastened, minimizing the risk of slippage or detachment during use. Hasty application, on the other hand, may result in improper fit and compromised performance.
These facets highlight the significance of a measured approach when introducing specialized canine footwear. By prioritizing gradual acclimation, owners can mitigate the risks associated with abrupt exposure, promoting a comfortable, safe, and positive experience for their animals. A responsible and patient approach is critical for successful integration of specialized equipment into a canine’s winter activities.
7. Temperature Considerations
Ambient temperature exerts a considerable influence on the efficacy and safety of specialized canine footwear designed for icy terrains. Extreme cold can affect the materials comprising the device, altering their flexibility, durability, and grip. Furthermore, low temperatures can impact the canine’s physiology, increasing the risk of cold-related injuries such as frostbite or hypothermia, even with protective measures in place. Consequently, temperature considerations represent a critical component in the responsible utilization of canine ice traversal devices. For instance, certain rubber compounds used in the soles of the footwear may become rigid and lose traction at sub-freezing temperatures, diminishing the device’s intended function. Similarly, prolonged exposure to extreme cold can negate the insulating properties of the footwear, leaving the canine susceptible to cold-induced paw damage.
The appropriate selection and utilization of these devices necessitate an understanding of material properties and their response to temperature variations. Footwear constructed from materials specifically engineered to maintain flexibility and insulation in cold conditions is essential. Regular monitoring of the ambient temperature and careful observation of the canine’s behavior provide valuable indicators of potential cold stress. Shivering, reluctance to walk, or lifting paws frequently may signal discomfort and the need for immediate intervention. Moreover, the duration of exposure to cold temperatures should be carefully controlled, even with appropriate footwear. Extended periods in sub-freezing conditions elevate the risk of systemic hypothermia, a potentially life-threatening condition. The application of paw balm, designed to create a protective barrier against moisture and cold, may further mitigate the risk of injury. The effect of cold temperature may also cause the ice to be more brittle, increasing the probability of sharp hazards that can cut the dog even while wearing protective gear.
In summary, temperature considerations constitute a non-negligible factor in the deployment of specialized canine footwear for icy conditions. Proper material selection, diligent monitoring, and judicious exposure limitations are essential for safeguarding canine welfare. The integration of these considerations into routine canine care promotes responsible winter activity and mitigates the risk of cold-related injury, improving the functionality and safety of canine ice traversing equipment. The challenges in predicting temperature fluctuations and microclimates underscore the need for continuous vigilance and adaptive strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries pertaining to the proper use, benefits, and safety considerations associated with canine ice traversal devices.
Question 1: What are the primary benefits of using these devices?
The purported advantages include paw protection from sharp ice, enhanced traction on slippery surfaces, and mitigation of potential cold-related injuries such as frostbite.
Question 2: How do these devices impact a canine’s natural gait?
Specialized footwear invariably alters a canine’s gait. Careful monitoring for signs of discomfort or altered movement patterns is crucial to ensuring proper fit and minimizing the risk of injury.
Question 3: What factors should be considered when selecting the appropriate size?
Accurate paw measurements, specifically length and width, are essential. Consult the manufacturer’s sizing guidelines to ensure a snug but not constricting fit.
Question 4: What materials are best suited for construction?
Durable, water-resistant materials with high abrasion resistance are preferred. These materials must maintain flexibility in sub-freezing temperatures to ensure optimal performance.
Question 5: How often should the devices be inspected for wear and tear?
Regular inspection is recommended, preferably before each use. Pay close attention to seams, fasteners, and the soles of the devices, replacing them as needed to maintain functionality.
Question 6: Are these devices suitable for all canine breeds and ages?
Suitability varies depending on the breed’s anatomy, the canine’s age, and its overall health. Consultation with a veterinarian is advisable, particularly for senior canines or those with pre-existing musculoskeletal conditions.
Proper utilization of canine ice traversal devices requires careful attention to detail, encompassing accurate sizing, material selection, and diligent monitoring of the animal’s comfort and movement.
The succeeding sections will explore alternative winter paw protection strategies and address specific concerns related to canine behavior in cold environments.
Dog Ice Skates
This exploration has illuminated various facets concerning canine ice traversal devices, emphasizing their potential benefits alongside critical safety considerations. The information presented underscores the importance of accurate fitting, appropriate material selection, secure attachment, consistent gait monitoring, thorough ice surface assessment, gradual acclimation, and awareness of temperature effects. These elements collectively dictate the effectiveness and safety profile of such devices, influencing the canine’s comfort, mobility, and overall well-being in icy environments. Rigorous adherence to these principles mitigates the risk of injury and promotes responsible winter pet care.
The ongoing pursuit of improved designs and materials, coupled with a commitment to informed utilization, is essential for maximizing the benefits and minimizing the potential drawbacks of canine ice skates. Future research should focus on refining device ergonomics, enhancing material durability, and developing standardized fitting protocols to ensure optimal performance and safety. The ultimate goal is to facilitate canine participation in winter activities while prioritizing their health and minimizing potential hazards.