Skates equipped with significantly larger diameter wheels, typically exceeding 80mm, alter the performance characteristics of traditional inline or roller skates. This design provides enhanced roll and momentum due to the increased contact area and reduced rolling resistance. As an example, a skate featuring 110mm wheels will cover more ground per stride than a similar skate with 76mm wheels.
The implementation of oversized wheels offers several advantages, including improved speed, efficiency on varied surfaces, and enhanced shock absorption. Historically, smaller wheels were prevalent due to maneuverability considerations. However, advancements in materials and frame design have allowed for the incorporation of larger wheels without sacrificing stability. This has expanded the applications of skating, making it more accessible for distance skating, fitness training, and navigating uneven terrains.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific types of skating utilizing this equipment, the technology behind wheel and frame designs, and the implications for both recreational and competitive skating applications.
Guidance on Utilizing Oversized Skate Wheels
The following recommendations provide insight into maximizing the potential of skates equipped with wheels of an increased diameter. These suggestions are intended to optimize performance and enhance the skating experience.
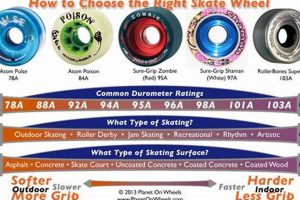
Tip 1: Wheel Hardness Selection: Wheel durometer, measured on the A scale, affects grip and rolling resistance. Lower durometers (e.g., 82A) provide increased grip, beneficial on slick surfaces. Higher durometers (e.g., 85A+) offer decreased rolling resistance, ideal for speed skating on smooth asphalt.
Tip 2: Frame Material Considerations: Frames constructed from extruded aluminum provide superior energy transfer and stiffness compared to composite frames. Aluminum frames enhance responsiveness and efficiency, particularly at higher speeds.
Tip 3: Bearing Maintenance Protocol: Regular cleaning and lubrication of bearings are essential for maintaining optimal roll. Debris accumulation significantly reduces bearing efficiency and increases friction.
Tip 4: Proper Ankle Support Implementation: Ensure the skate boot provides adequate ankle support to maintain stability at higher speeds. A secure fit minimizes the risk of ankle strain or injury.
Tip 5: Gradual Transition Strategy: Transitioning from smaller wheel skates requires adaptation. Begin with shorter skating sessions and gradually increase duration and intensity as comfort and control improve.
Tip 6: Terrain Awareness Enhancement: While larger wheels navigate uneven surfaces more effectively, vigilance is still required. Scan the skating path for potential hazards, such as cracks, debris, or obstacles.
Tip 7: Stride Length Optimization: Experiment with adjusting stride length to maximize efficiency. A longer stride may prove beneficial on flat, smooth surfaces, while a shorter, quicker stride is suitable for uphill climbs or technical maneuvers.
Adhering to these guidelines will promote a safer and more efficient skating experience, enabling the user to fully leverage the capabilities of the equipment.
The subsequent section will address the various disciplines within skating that are complemented by the use of oversized wheel configurations.
1. Speed Enhancement
The correlation between the size of the wheel and achieved velocity constitutes a primary advantage of utilizing skates equipped with large diameter wheels. The increased circumference inherently translates to greater distance covered per revolution, directly influencing the attainable speed and sustained momentum.
- Circumferential Advantage
A larger wheel possesses a greater circumference compared to a smaller one. Each rotation of the larger wheel propels the skater a further distance, assuming equivalent rotational velocity. This inherent geometrical advantage contributes significantly to the potential for increased speed. For instance, a 110mm wheel, in comparison to an 80mm wheel, will cover approximately 37.5% more distance per rotation.
- Reduced Rolling Resistance
The increased diameter facilitates a lower rolling resistance. A larger wheel more readily overcomes surface imperfections and minor obstacles, thereby minimizing energy dissipation. This reduction in resistance allows for the maintenance of higher speeds with less effort expenditure. This effect is particularly noticeable on surfaces that are not perfectly smooth.
- Improved Momentum Maintenance
Wheels of larger dimensions possess a greater moment of inertia. Consequently, once the wheel is in motion, it resists changes in its rotational velocity. This property contributes to the ability to maintain momentum for extended durations, reducing the frequency of required pushes and conserving energy. The effect is analogous to a larger flywheel in a mechanical system.
- Stride Efficiency Optimization
With elevated velocity capabilities, each skating stride has the potential to cover greater ground. By extension, a skaters efficiency elevates, expending less energy to traverse greater distances. This results in a higher average speed and extended endurance. Optimal stride length is adjusted to leverage the larger wheel’s capacity.
These facets, in aggregate, underscore the contribution of the augmented wheel size to enhancing speed capabilities. By capitalizing on circumferential advantage, lowering rolling resistance, maintaining momentum, and improving stride efficiency, skates equipped with substantial wheel diameters provide a demonstrable advantage over their counterparts with smaller wheel dimensions. This advantage is observed across varied skating disciplines, from speed skating to recreational fitness applications.
2. Surface Adaptability
The capacity of skates to navigate varying terrain is a critical determinant of versatility and user experience. Equipment featuring wheels of substantial diameter demonstrates enhanced surface adaptability, expanding the range of environments suitable for skating activities.
- Obstacle Negotiation
Larger diameter wheels exhibit improved capability in traversing obstacles such as cracks, pebbles, and minor surface irregularities. The increased roll-over angle facilitates smoother transitions, minimizing abrupt disruptions to momentum and enhancing rider stability. This attribute allows skaters to maintain speed and control on less-than-ideal surfaces. An example would be navigating a paved bike path with occasional patches of rough asphalt or small debris.
- Vibration Dampening
The increased volume of material in larger wheels contributes to enhanced vibration dampening. This reduces the transmission of surface imperfections to the skater’s feet and ankles, resulting in a more comfortable and controlled riding experience. The dampening effect is particularly pronounced on surfaces with fine textures, such as coarse asphalt or slightly uneven concrete. This leads to a reduction in fatigue during extended skating sessions.
- Grip Optimization
While wheel size itself does not directly determine grip, the larger contact patch afforded by larger wheels can contribute to improved traction, particularly on surfaces with loose gravel or dirt. The greater surface area in contact with the ground provides a more secure interface, minimizing slippage. However, durometer and tire compound remain critical factors in grip performance. Larger wheels simply provide a potential advantage that can be further optimized through tire selection.
- Terrain Versatility
Skates equipped with larger diameter wheels exhibit increased suitability for a broader range of terrain types. From smooth indoor surfaces to moderately rough outdoor paths, the equipment adapts effectively, broadening the scope of potential skating environments. This versatility appeals to skaters who desire the flexibility to skate in diverse locations without requiring multiple sets of skates. This expands the utility of the equipment beyond specialized environments.
These factors collectively underscore the enhanced surface adaptability inherent in skates featuring larger diameter wheels. The ability to negotiate obstacles, dampen vibration, optimize grip, and navigate diverse terrain contributes to a more versatile and enjoyable skating experience. The integration of these attributes provides a significant advantage in environments characterized by variable surface conditions.
3. Rolling Efficiency
Rolling efficiency, defined as the minimization of energy loss due to friction during wheel rotation, is a crucial performance parameter directly influenced by wheel size in skating equipment. Larger diameter wheels inherently possess a greater capacity to maintain momentum and minimize energy dissipation compared to smaller wheels. This characteristic stems from reduced deformation during contact with the surface, leading to less hysteresis and energy loss as heat. The impact of enhanced rolling efficiency is significant, directly influencing skater speed, endurance, and overall energy expenditure. For example, a skater using equipment with optimally efficient wheels can cover a greater distance at a given speed compared to an individual using less efficient equipment, requiring less effort to achieve the same result. This differential is particularly pronounced during longer skating sessions or competitive events, where marginal gains in efficiency accumulate to produce tangible performance advantages.
The practical implications of prioritizing rolling efficiency in selecting skating equipment extend to various applications. In long-distance skating or marathon events, the reduced energy expenditure directly translates to improved endurance and reduced fatigue, potentially enabling skaters to maintain a competitive pace for extended periods. Similarly, for recreational skaters, enhanced rolling efficiency translates to a more effortless and enjoyable skating experience, reducing the physical strain associated with propulsion. Furthermore, in speed skating disciplines, the difference in rolling efficiency, even on a percentage basis, can be the decisive factor between winning and losing a race. The design and material composition of the wheels themselves also contribute to rolling efficiency, but the inherent advantage conferred by a larger diameter remains a fundamental principle.
In summary, maximizing rolling efficiency is a core consideration when utilizing skates with larger wheels. While other factors, such as bearing quality and surface conditions, play a role, the inherent advantages of larger wheels in minimizing energy loss during rotation are undeniable. This understanding is practically significant for skaters seeking to optimize their performance, enhance their endurance, or simply derive greater enjoyment from the activity. The challenge lies in balancing the benefits of rolling efficiency with other considerations, such as maneuverability and stability, to achieve optimal performance for a given skating discipline and user preference.
4. Reduced vibration
Wheels of larger diameter exhibit a demonstrable capacity to attenuate vibration during skating activities. This phenomenon arises from the increased material volume and surface area of the wheel, which effectively dampens oscillations transmitted from the skating surface. The absorption and dissipation of vibrational energy result in a smoother and more controlled riding experience. Skates equipped with such wheels contribute to heightened comfort, reduced fatigue, and enhanced stability, particularly on uneven or textured surfaces. This reduction in vibration is not merely a matter of subjective comfort; it has quantifiable effects on performance and long-term musculoskeletal health.
The practical significance of vibration reduction becomes evident in diverse skating contexts. For long-distance skaters or individuals engaged in prolonged skating sessions, the minimization of repetitive jarring forces translates to decreased stress on joints and muscles. This mitigates the risk of discomfort, pain, and potential injury, such as tendonitis or stress fractures. In urban environments, where surfaces often exhibit irregularities, cracks, and varying textures, the capacity to dampen vibration enhances control and maneuverability, thereby improving safety and confidence. Furthermore, for skaters with pre-existing musculoskeletal conditions, the adoption of equipment featuring vibration-reducing wheels may enable continued participation in skating activities without exacerbating symptoms. A real-world example would be a skater with knee issues being able to skate for longer periods of time, at higher intensity, with less discomfort by using large wheel skates.
In conclusion, the attenuation of vibration is a crucial attribute of large wheel skates, contributing significantly to comfort, safety, and performance. This benefit is particularly relevant for individuals engaged in long-distance skating, navigating uneven terrains, or those with pre-existing musculoskeletal concerns. The ability of larger wheels to absorb and dissipate vibrational energy translates to a more enjoyable and sustainable skating experience, mitigating the risks associated with repetitive impact and promoting overall musculoskeletal well-being. While other factors, such as wheel material and frame design, also influence vibration damping, the increased diameter of the wheel remains a primary determinant in achieving this benefit.
5. Momentum maintenance
Momentum maintenance, the ability to sustain speed and motion with minimal external input, is a primary performance characteristic enhanced by skates equipped with large diameter wheels. The physics governing rotational inertia dictates that a larger wheel, possessing greater mass distributed further from its axis of rotation, will resist changes in its state of motion more effectively than a smaller wheel. This inherent property directly translates to improved glide, reduced effort expenditure, and enhanced overall efficiency for the skater.
- Rotational Inertia Influence
A wheel’s rotational inertia is proportional to its mass and the square of its radius. Larger wheels exhibit higher rotational inertia, requiring more energy to initiate rotation but also possessing a greater capacity to resist deceleration. This effect allows skaters to maintain speed more readily, particularly on smooth surfaces, as the wheels continue to rotate for longer periods with minimal additional effort. For instance, a skater descending a slight incline will maintain speed longer with larger wheels compared to smaller wheels, all other factors being equal.
- Surface Contact Dynamics
The contact patch between a larger wheel and the skating surface is elongated compared to that of a smaller wheel. This elongated contact area contributes to a smoother transition over minor surface irregularities, minimizing energy loss due to impacts and vibrations. The result is a more consistent rolling motion and improved momentum maintenance, even on less-than-ideal skating surfaces. This is particularly noticeable on asphalt or concrete surfaces where minor cracks and imperfections are unavoidable.
- Aerodynamic Considerations
While not the primary factor, the larger surface area presented by larger wheels can influence aerodynamic drag, particularly at higher speeds. However, the aerodynamic penalty is generally outweighed by the gains in rotational inertia and reduced rolling resistance. Sophisticated wheel designs often incorporate aerodynamic profiles to mitigate drag, further optimizing momentum maintenance. In competitive speed skating, even minor aerodynamic advantages can contribute to improved performance.
- Stride Efficiency Amplification
The enhanced momentum maintenance afforded by larger wheels allows skaters to optimize their stride frequency and power output. The reduced need for frequent pushing translates to improved efficiency, enabling skaters to conserve energy and maintain higher average speeds over longer distances. This is especially relevant for endurance skating or marathon events, where minimizing energy expenditure is paramount. A skater with efficient technique using large wheel skates will demonstrate a more fluid and less tiring stride compared to one using smaller wheels.
The interplay between rotational inertia, surface contact dynamics, aerodynamic considerations, and stride efficiency collectively contributes to the superior momentum maintenance exhibited by skates equipped with larger diameter wheels. This attribute enhances overall skating performance, improves efficiency, and enables skaters to achieve higher speeds and greater distances with reduced effort. While factors such as bearing quality, wheel hardness, and skater technique also influence momentum, the fundamental advantage conferred by wheel size remains a critical determinant of skating performance.
6. Frame compatibility
Frame compatibility is a crucial element in the effective utilization of large wheel skates. The skate frame, serving as the chassis for the wheels, must be designed to accommodate the increased diameter and width of larger wheels. Failure to ensure appropriate frame compatibility results in compromised performance, stability, and potentially, equipment failure. For example, attempting to install 110mm wheels on a frame designed for 80mm wheels will likely result in wheel rub against the boot or frame, hindering rotation and creating a safety hazard.
The design of the frame directly influences the maneuverability and stability of large wheel skates. A longer frame wheelbase, typically required to accommodate larger wheels, provides increased stability at higher speeds but can reduce agility in tight turns. Frame material also plays a significant role; aluminum frames offer superior stiffness and energy transfer compared to composite frames, maximizing the benefits of larger wheels for speed and efficiency. Specialized frames engineered for specific skating disciplines, such as speed skating or urban skating, incorporate design features tailored to optimize performance with large wheels. A speed skating frame, for instance, prioritizes aerodynamics and stiffness for maximum speed transfer, while an urban frame may emphasize durability and maneuverability for navigating obstacles.
In summary, frame compatibility is not merely a matter of fitting larger wheels onto a skate; it is a critical integration point that determines the overall performance and safety of the equipment. Selecting a frame specifically designed for the intended wheel size and skating discipline ensures optimal performance and maximizes the advantages of larger wheel skates. Neglecting this aspect can lead to compromised handling, reduced efficiency, and potential risks. The choice of frame material, wheelbase, and design features are all essential factors in achieving a compatible and high-performing setup.
7. Bearing quality
Bearing quality is a critical determinant of performance in skates featuring large diameter wheels. The function of bearings is to facilitate smooth and efficient rotation of the wheels around their axles. In the context of large wheel skates, where momentum and sustained speed are paramount, the quality of the bearings directly impacts rolling efficiency, energy expenditure, and overall skating experience.
- ABEC Rating and Precision
The Annular Bearing Engineers’ Committee (ABEC) rating system (ABEC 1, 3, 5, 7, 9) quantifies the manufacturing tolerances of bearings. Higher ABEC ratings indicate tighter tolerances and greater precision. Higher precision bearings, though often more expensive, contribute to reduced friction and smoother rotation, especially crucial for maintaining the momentum afforded by larger wheels. For example, a speed skater utilizing 110mm wheels would benefit significantly from ABEC 7 or 9 bearings compared to ABEC 1 bearings.
- Material Composition and Durability
The materials used in bearing construction significantly affect durability and resistance to wear and corrosion. High-quality bearings often employ hardened steel races and ceramic balls, which offer superior durability and reduced friction compared to bearings made from lower-grade materials. The increased loads and sustained speeds associated with large wheel skates place greater stress on bearings, making material quality a critical factor. Improper material can lead to increased friction and early degradation of performance.
- Sealing and Lubrication
Effective sealing prevents contaminants, such as dirt and moisture, from entering the bearing and compromising performance. High-quality bearings feature robust sealing mechanisms that protect internal components and maintain lubrication. Proper lubrication minimizes friction and heat buildup, contributing to smoother rotation and extended bearing lifespan. The demands placed on large wheel skates, especially in outdoor environments, necessitate effective sealing and lubrication to maintain optimal performance. The correct amount and type of lubricant is also crucial.
- Impact on Rolling Efficiency
Superior bearing quality directly translates to improved rolling efficiency. Reduced friction within the bearings minimizes energy loss, allowing skaters to maintain speed with less effort. This is especially crucial for long-distance skating or competitive events, where marginal gains in efficiency can accumulate to produce significant performance advantages. The increased rolling efficiency of high-quality bearings complements the inherent momentum advantage offered by larger diameter wheels, maximizing overall skating performance.
In summary, bearing quality is inextricably linked to the performance of large wheel skates. The precision, material composition, sealing, and lubrication of bearings collectively determine rolling efficiency, durability, and overall skating experience. Investing in high-quality bearings is a prudent decision for skaters seeking to maximize the benefits of large wheel skates, particularly for those engaged in speed skating, long-distance skating, or recreational skating on varied surfaces.
Frequently Asked Questions
The subsequent questions and answers address prevalent inquiries regarding skates equipped with wheels of increased diameter. The information presented is intended to provide clarity and insight into the characteristics and applications of this equipment.
Question 1: What constitutes a “large” wheel in the context of skating?
The designation “large” typically refers to wheels exceeding 80mm in diameter. However, the specific size considered “large” may vary depending on the skating discipline and individual preferences.
Question 2: Do larger wheels inherently provide increased speed?
Yes. Larger wheels, due to their increased circumference, cover more distance per rotation, contributing to enhanced speed potential. Factors such as bearing quality and skater technique also influence attainable velocity.
Question 3: Are large wheel skates suitable for beginners?
While larger wheels offer benefits such as improved roll and shock absorption, they may present a greater challenge for novice skaters due to increased speed and reduced maneuverability. Gradual progression from smaller wheels is generally recommended.
Question 4: How does wheel durometer affect the performance of large wheel skates?
Wheel durometer, measured on the A scale, influences grip and rolling resistance. Softer wheels (lower durometer) provide increased grip, while harder wheels (higher durometer) offer decreased rolling resistance. Selection should align with skating surface and desired performance characteristics.
Question 5: What frame characteristics are essential for large wheel skates?
Frame compatibility is crucial. The frame must be designed to accommodate the diameter and width of the wheels. Aluminum frames are generally preferred for their stiffness and energy transfer capabilities.
Question 6: Is maintenance more critical for large wheel skates compared to traditional skates?
Maintenance, particularly regarding bearing cleaning and lubrication, is essential for all skates. However, the increased speeds and stresses associated with large wheel skates necessitate diligent maintenance practices to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
The preceding questions represent a selection of common inquiries. Further investigation into specific applications and equipment characteristics is encouraged to facilitate informed decision-making.
The subsequent section will explore the diverse range of applications for large wheel skates across various skating disciplines.
Conclusion
This exploration of large wheel skates has elucidated the key attributes that differentiate them from traditional skating equipment. The analysis has demonstrated the impact of wheel size on speed, surface adaptability, rolling efficiency, vibration reduction, momentum maintenance, frame compatibility, and bearing quality. These factors collectively determine the performance and suitability of large wheel skates for various applications.
The selection and utilization of large wheel skates require careful consideration of individual skating goals, skill level, and environmental conditions. Continued advancements in materials and design are expected to further refine the capabilities of this equipment, expanding its applications within both recreational and competitive skating. Further research into the long-term effects on biomechanics and performance is warranted to fully understand the potential and limitations of this technology.


![Get Rolling! Best Roller Skates With Wheels [Guide] How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks Get Rolling! Best Roller Skates With Wheels [Guide] | How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks](https://cruzskateshop.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-414-300x200.jpg)