These specialized recreational devices incorporate a boot or shoe attached to a frame that houses a series of wheels arranged in a line, enabling the wearer to glide across smooth surfaces. Often favored for fitness, transportation, and recreational activities, they offer an engaging and efficient means of locomotion. A common example includes adjustable models designed for growing children or performance versions engineered for speed and agility.
The design fosters low-impact exercise, promoting cardiovascular health and muscular endurance. Historically, these devices evolved from earlier roller skates, with the inline configuration providing enhanced speed and maneuverability. This evolution significantly broadened the appeal of roller skating, attracting diverse user groups interested in exercise, competitive sports, or simply enjoying outdoor activities.
Subsequent sections will delve into various aspects such as choosing the appropriate models based on skill level, essential safety equipment, maintenance tips for prolonged use, and a comparison of leading brands and models in the current market.
Tips for Optimal Performance
Maximizing the utility of inline skates requires attention to several key areas. Proper selection, maintenance, and technique all contribute to a safer and more efficient skating experience.
Tip 1: Select the Appropriate Wheel Durometer. Wheel hardness impacts grip and speed. Lower durometer wheels (e.g., 78A-82A) offer more grip, ideal for beginners or rough surfaces. Higher durometer wheels (e.g., 84A-88A) prioritize speed on smooth surfaces. Choose based on skill level and intended environment.
Tip 2: Ensure Proper Boot Fit. A snug, but not constricting, fit is crucial. Overly tight boots cause discomfort and impede circulation. Boots that are too loose compromise control and increase the risk of ankle instability. Try on skates with the socks typically worn during skating.
Tip 3: Maintain Bearing Cleanliness. Debris within the bearings reduces speed and increases wear. Regularly clean bearings using a solvent-based cleaner and re-lubricate with a specialized bearing lubricant. This prolongs bearing life and improves performance.
Tip 4: Rotate Wheels Regularly. Due to asymmetrical wear patterns, rotating wheels extends their lifespan and maintains consistent performance. Rotate wheels according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, typically swapping wheels from front to back or diagonally.
Tip 5: Practice Proper Braking Technique. Mastering braking is essential for safety. The heel brake is the most common method; apply consistent pressure to the braking foot while maintaining balance. Practice braking in a controlled environment before venturing into busier areas.
Tip 6: Utilize Protective Gear Consistently. Helmets, wrist guards, elbow pads, and knee pads significantly reduce the risk of injury. Ensure gear fits properly and is in good condition before each skating session. Protective equipment is a non-negotiable safety measure.
Tip 7: Inspect Equipment Before Each Use. Before each skating session, inspect wheels for wear, check bearing smoothness, and ensure all straps and closures are secure. Addressing minor issues promptly prevents more significant problems during use.
These tips emphasize the importance of informed equipment selection, regular maintenance, and sound technique. Adherence to these guidelines promotes a safer and more enjoyable skating experience.
The subsequent sections will further explore specific models and brands, detailing their features and suitability for various skating styles and skill levels.
1. Wheel Durometer
Wheel durometer is a crucial characteristic influencing the performance and handling of inline skates. Measured on the Shore A scale, it quantifies the hardness of the wheel material, directly impacting grip, speed, and wear resistance. Understanding durometer is essential for selecting appropriate wheels tailored to specific skating conditions and skill levels.
- Grip and Surface Interaction
Softer wheels, typically ranging from 78A to 82A, provide superior grip, particularly on rough or uneven surfaces. The increased contact area between the wheel and the pavement enhances control and stability. This is advantageous for beginners or skaters prioritizing maneuverability over speed. In contrast, harder wheels sacrifice some grip for improved rolling efficiency.
- Speed and Rolling Efficiency
Wheels with a higher durometer, generally 84A and above, minimize rolling resistance, enabling greater speeds and sustained momentum. These harder wheels are better suited for smooth surfaces, such as indoor rinks or well-maintained paths, where grip is less of a concern. Experienced skaters often prefer harder wheels for competitive events or long-distance skating.
- Wear Resistance and Durability
Durometer also affects the longevity of the wheel. Softer wheels tend to wear down more quickly, particularly on abrasive surfaces. Harder wheels offer greater resistance to wear, making them a more durable option for frequent use. The choice between softer and harder wheels involves a trade-off between grip and longevity.
- Skating Style and Discipline
Different skating styles necessitate different wheel durometers. Recreational skaters may prefer a balance between grip and speed, opting for a medium durometer wheel (around 82A-84A). Aggressive skaters who perform tricks and jumps often use harder wheels for increased durability and slide resistance. Speed skaters prioritize maximum rolling efficiency and thus utilize the hardest available wheels.
In summary, wheel durometer significantly impacts the performance of inline skates. The optimal choice depends on the skater’s skill level, preferred skating style, and the intended skating environment. Selecting the appropriate durometer enhances both safety and enjoyment while optimizing the skate’s overall performance characteristics.
2. Bearing Precision
Bearing precision is a critical determinant of rolling efficiency and speed in inline skates. Bearings facilitate smooth wheel rotation around the axle, and their precision directly affects friction, durability, and overall performance. Understanding bearing precision is essential for selecting appropriate components for varied skating applications.
- ABEC Rating System
The Annular Bearing Engineers’ Committee (ABEC) rating system is the most common standard for classifying bearing precision. ABEC ratings range from 1 to 9, with higher numbers indicating tighter tolerances and greater accuracy in bearing construction. Higher ABEC-rated bearings generally exhibit reduced friction and improved speed, particularly at higher velocities. However, the ABEC rating primarily measures manufacturing tolerances, not necessarily overall bearing quality or suitability for specific applications.
- Influence on Rolling Resistance
Bearings with higher precision minimize internal friction, resulting in lower rolling resistance. This translates to increased speed and reduced energy expenditure during skating. Skaters seeking optimal performance, such as speed skaters or marathon skaters, typically prioritize high-precision bearings to maximize their efficiency. Conversely, recreational skaters may find lower ABEC-rated bearings sufficient for their needs.
- Impact on Bearing Durability
While precision is important, other factors, such as material quality and bearing seal design, significantly influence bearing durability. High-precision bearings made from inferior materials may fail prematurely, negating the benefits of their tighter tolerances. Sealed bearings, which protect against dirt and moisture, tend to last longer than unsealed bearings, particularly in outdoor environments.
- Application-Specific Considerations
The ideal bearing precision depends on the intended skating application. Speed skating and racing benefit from high ABEC ratings (e.g., ABEC 7 or ABEC 9) to maximize speed. Recreational skating typically requires ABEC 3 or ABEC 5 bearings, which offer a balance between performance and affordability. Aggressive skating, involving jumps and impacts, often necessitates durable bearings with lower ABEC ratings to withstand the stresses of the activity.
In summary, bearing precision, as quantified by the ABEC rating system, significantly impacts the rolling efficiency and speed of inline skates. While higher precision generally equates to better performance, factors such as material quality, seal design, and the specific skating application also influence bearing selection. Informed choices regarding bearing precision contribute to a more efficient and enjoyable skating experience.
3. Frame Material
The frame material constitutes a fundamental element of inline skates, directly influencing weight, stability, power transfer, and overall skating performance. Its selection represents a critical decision in skate design and significantly impacts the user experience.
- Aluminum Frames
Aluminum frames provide a balance of stiffness and lightweight properties, offering efficient power transfer from the skater’s foot to the wheels. They are commonly found in intermediate to advanced level skates, providing responsiveness and control. Examples include extruded aluminum frames used in fitness skates and CNC-machined frames found in high-performance speed skates, demonstrating varied manufacturing processes and performance characteristics within the aluminum category.
- Composite Frames
Composite frames, often constructed from reinforced plastics or carbon fiber blends, offer vibration dampening and impact resistance. They are typically lighter than aluminum frames but may sacrifice some stiffness. Examples include entry-level recreational skates employing reinforced plastic frames and higher-end freestyle skates utilizing carbon fiber for enhanced responsiveness and weight reduction. The composition dictates the frame’s ability to absorb road vibrations, leading to a smoother ride.
- Frame Length and Wheelbase
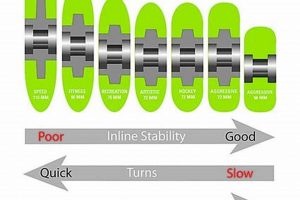
The length of the frame, or wheelbase, impacts maneuverability and stability. Shorter frames enhance agility and are favored for aggressive skating and freestyle maneuvers. Longer frames provide increased stability and are preferred for speed skating and long-distance cruising. Examples include short frames on aggressive skates enabling quick turns and long frames on speed skates maximizing straight-line speed and stability at high velocities. The wheelbase directly impacts the skate’s handling characteristics.
- Frame Mounting Systems
The method by which the frame attaches to the boot influences alignment and customization options. Standard mounting systems offer limited adjustability, while advanced systems allow for lateral and fore-aft adjustments to optimize foot positioning and power transfer. Examples include fixed mounting systems on entry-level skates and adjustable mounting systems on high-end skates enabling fine-tuning for individual biomechanics and preferences. Customization options improve comfort and performance by accommodating individual foot characteristics.
The selection of frame material and design features involves a trade-off between weight, stiffness, comfort, and durability. Informed consideration of these factors, aligned with the intended skating style and skill level, contributes to an enhanced skating experience and optimized performance characteristics.
4. Boot Comfort
Boot comfort is a foundational element of effective inline skating. The boot, serving as the primary interface between the skater and the equipment, directly influences control, stability, and endurance. Ill-fitting or uncomfortable boots can lead to compromised performance, increased risk of injury, and diminished enjoyment of the activity. Therefore, selecting inline skates with appropriate boot construction and fit characteristics is paramount.
Inadequate boot comfort can manifest in various ways, including blisters, chafing, pressure points, and numbness. These discomforts can disrupt skating technique, impede circulation, and ultimately limit the duration and intensity of skating sessions. For instance, a boot that is too narrow can constrict the foot, causing pain and reducing blood flow. Conversely, a boot that is too loose can result in excessive foot movement, leading to instability and friction. High-quality inline skates often feature heat-moldable liners, customizable footbeds, and adjustable closure systems designed to mitigate these issues. A practical example is the use of memory foam padding in high-end skate boots, conforming to the individual foot shape to minimize pressure and enhance comfort.
Furthermore, the boot’s construction impacts energy transfer and responsiveness. A stiff boot shell provides greater support and facilitates efficient power transmission, particularly during high-intensity skating. However, overly rigid boots can sacrifice comfort and flexibility. The integration of articulated ankle cuffs and breathable materials can strike a balance between support and comfort, allowing for a wider range of motion while maintaining stability. Prioritizing boot comfort, alongside performance considerations, ensures a more positive and productive inline skating experience. Addressing comfort challenges directly correlates with enhanced usability and long-term adherence to skating activities.
5. Closure System
The closure system on inline skates is critical for secure foot retention, impacting control, comfort, and safety. Varied designs accommodate different skating styles and user preferences, demanding consideration during skate selection.
- Buckle Systems
Buckle systems offer secure and adjustable closure, commonly found on recreational and fitness skates. Ratcheting buckles provide incremental adjustments, allowing precise tightening. Examples include micro-adjustable buckles on cuffs, enhancing ankle support, and instep buckles, securing the midfoot. Improperly fastened buckles compromise stability, increasing injury risk.
- Lace Systems
Lace systems enable customizable fit, allowing precise tension adjustments across the foot. Traditional laces provide uniform closure, while speed lacing systems facilitate quick tightening. Examples include waxed laces, preventing slippage, and recessed lace eyelets, minimizing abrasion. Incorrect lacing techniques can cause discomfort or impede circulation.
- Power Straps
Power straps, typically utilizing hook-and-loop fasteners, enhance heel lock and ankle support. Placed across the instep or ankle, they augment the primary closure system. Examples include angled power straps, improving forward lean, and padded straps, increasing comfort. Insufficiently tightened power straps reduce stability during dynamic movements.
- Combination Systems
Many inline skates integrate multiple closure types to optimize fit and performance. Combining buckles, laces, and power straps provides targeted support and adjustability. Examples include skates with lace-up inner boots, buckle closures on the cuff, and power straps across the midfoot, maximizing comfort and control. Hybrid systems address diverse user needs.
The effectiveness of the closure system directly influences skating efficiency and safety. Secure, well-adjusted closures enhance power transfer, minimize foot movement within the boot, and reduce the likelihood of ankle injuries. Selection should consider intended skating style, foot shape, and desired level of support.
6. Brake System
The brake system represents a fundamental safety component of inline skates, directly impacting the user’s ability to control speed and avoid collisions. Its integration into inline skate design addresses the inherent challenge of managing momentum on wheeled footwear. A functioning brake system enables skaters to decelerate and stop predictably, reducing the risk of accidents. The effectiveness of the brake directly correlates with the skater’s skill level and the environmental conditions. For instance, a worn brake pad on a fitness skate increases stopping distance, especially on wet surfaces, posing a significant hazard. Conversely, a properly maintained brake system empowers skaters to navigate complex environments safely.
The most common brake system configuration involves a heel brake, a rubber pad affixed to a mounting bracket on the rear of one skate, typically the right. To engage the brake, the skater extends the braking leg forward, tilting the skate upward to apply pressure to the brake pad. This system provides a relatively intuitive method of deceleration, suitable for beginners and recreational skaters. Alternative braking methods, such as T-stops or parallel slides, require advanced skills and are often preferred by experienced skaters for performance or aesthetic reasons. Certain skate models, particularly those designed for aggressive skating, may omit a traditional brake system, relying solely on skill-based techniques for speed control.
Ultimately, the brake system serves as a critical safety mechanism for inline skates. Its proper functioning is indispensable for mitigating risks associated with speed and momentum. Regular inspection and maintenance of the brake components are essential for ensuring reliable performance. As skating proficiency increases, alternative braking methods may supplement or supplant the traditional heel brake; however, understanding and mastering the fundamental braking principles remains paramount for safe and responsible participation in the activity.
7. Wheel Size
Wheel size significantly impacts the performance characteristics of inline skates. Measured in millimeters (mm), wheel diameter directly influences speed, maneuverability, and energy expenditure. Larger wheels generally provide greater speed and smoother rolling over varied surfaces, while smaller wheels offer enhanced agility and quicker acceleration. The appropriate wheel size depends on the intended skating style, skill level, and the environment in which the skates are used. For example, speed skates often feature wheels with diameters of 100mm or larger to maximize velocity, while aggressive skates typically utilize smaller wheels, around 55mm to 72mm, to facilitate tricks and grinds. Incorrect wheel size selection can compromise performance and increase the risk of injury.
The relationship between wheel size and skating experience is readily observed across different disciplines. Fitness skaters often choose wheels in the 80mm to 90mm range, striking a balance between speed and maneuverability for recreational use. Marathon skaters, prioritizing sustained speed over long distances, frequently opt for wheels exceeding 110mm in diameter. The increase in wheel size corresponds to a noticeable reduction in the number of strides required to maintain a given speed, improving energy efficiency. Wheel size also influences the skate frame design; larger wheels necessitate longer frames, which can affect stability and turning radius. Frame material strength must also be considered when using larger wheel sizes to avoid frame flexing. The interplay between wheel size and other components underscores the importance of understanding their combined effect.
In summary, wheel size represents a key determinant of inline skate performance, affecting speed, maneuverability, and energy efficiency. Selection requires careful consideration of the intended application and the interplay between wheel size and other skate components. A properly chosen wheel size enhances the skating experience and contributes to improved safety and performance outcomes. Challenges may arise in balancing competing demands for speed and agility, requiring informed trade-offs based on individual preferences and skating goals. The implications of wheel size extend to broader considerations of skate design and the optimization of equipment for specific skating disciplines.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries and misconceptions concerning inline skates, providing factual responses to enhance understanding.
Question 1: What factors determine appropriate wheel durometer selection?
Wheel durometer selection depends on skating surface, skill level, and desired balance between grip and speed. Softer wheels (78A-82A) provide better grip on rough surfaces, while harder wheels (84A+) offer increased speed on smooth surfaces. Skilled skaters might prefer harder wheels for efficiency, whereas beginners may value the enhanced control of softer wheels.
Question 2: How often should inline skate bearings be cleaned and lubricated?
Bearing maintenance frequency depends on usage and environmental conditions. Under normal conditions, cleaning and lubrication every 2-4 weeks is recommended. Exposure to dirt, water, or sand necessitates more frequent maintenance to prevent performance degradation and bearing damage. Consistent maintenance prolongs bearing lifespan and preserves rolling efficiency.
Question 3: What are the potential consequences of improper boot fit?
Improper boot fit can result in blisters, chafing, numbness, and compromised stability. Boots that are too tight restrict circulation, while boots that are too loose reduce control and increase the risk of ankle injury. Prioritizing correct boot size and fit is critical for comfort and injury prevention. A snug, but not constricting, fit is optimal.
Question 4: How does frame material influence inline skate performance?
Frame material affects weight, stiffness, and power transfer. Aluminum frames offer a balance of stiffness and lightweight properties, providing efficient power transfer. Composite frames, constructed from reinforced plastics, provide vibration dampening and impact resistance. Choosing the appropriate frame material depends on skating style and desired performance characteristics.
Question 5: Is it possible to convert inline skates to ice skates or vice versa?
While specialized kits exist for converting inline skates to ice skates and vice versa, the feasibility and performance depend on the quality and compatibility of the conversion kit. Converting skates may compromise performance compared to dedicated inline or ice skates. Assessing the specific kit and intended use case before attempting a conversion is advisable.
Question 6: What is the significance of the ABEC rating in inline skate bearings?
The Annular Bearing Engineers’ Committee (ABEC) rating quantifies bearing precision. Higher ABEC ratings (e.g., ABEC 7 or ABEC 9) indicate tighter tolerances and potentially reduced friction, leading to smoother rolling. However, ABEC rating alone does not determine bearing quality or suitability. Material quality, seal design, and intended use are also crucial considerations.
The responses provided address common inquiries, highlighting the importance of informed equipment selection, proper maintenance, and safety considerations. Understanding these aspects contributes to a more positive and productive skating experience.
The subsequent section will present a detailed comparison of leading brands and models in the current market.
Concluding Remarks
This exploration of these devices has illuminated critical factors influencing performance, safety, and user satisfaction. From wheel durometer and bearing precision to frame material and boot comfort, each element plays a significant role in the overall skating experience. A comprehensive understanding of these aspects empowers individuals to make informed decisions, optimizing their equipment for specific needs and skill levels.
As technology advances and materials evolve, further refinements in inline skate design are anticipated. Continued research and development will likely yield improvements in energy efficiency, maneuverability, and overall performance. The pursuit of optimized designs remains central to enhancing the accessibility and enjoyment of this activity for both recreational and competitive users. A commitment to informed equipment selection and proper maintenance ensures continued safe and rewarding participation in the sport.




![Top-Rated: Best Skate Wheels Guide [Year] How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks Top-Rated: Best Skate Wheels Guide [Year] | How to Skateboard: A Beginner's Guide to Your First Board & Tricks](https://cruzskateshop.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-200-300x200.jpg)